Difference between revisions of "Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour]], [[invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas]] | | LMDDx = [[pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour]], [[invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = PAS +ve, PASD +ve | ||
| IHC = trypsin +ve (key stain), lipase +ve, chromogranin +ve (scattered, focal) | | IHC = trypsin +ve (key stain), lipase +ve, chromogranin +ve (scattered, focal) | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
Revision as of 05:14, 21 October 2014
| Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
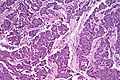
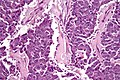
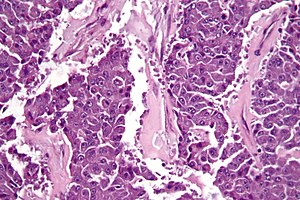 Acinar cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cells reminiscent of pancreatic acinus cells (granular, basophilic cytoplasm - usu. abundant; round/oval nucleus with prominent nucleolus); variable architecture (nests, sheets, trabecular, glandular) |
| LM DDx | pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour, invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas |
| Stains | PAS +ve, PASD +ve |
| IHC | trypsin +ve (key stain), lipase +ve, chromogranin +ve (scattered, focal) |
| Site | pancreas |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | subcutaneous fat necrosis, polyarthritis |
| Symptoms | joint pain |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Blood work | eosinophilia |
| Radiology | mass lesion - typically head of pancreas |
| Prognosis | poor - median survival ~18 mo. |
| Clin. DDx | other pancreatic tumours |
Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas is a rare malignant epithelial tumour of the pancreas.
It is also known as pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma[1] and acinar cell carcinoma.
It should not to be confused with acinic cell carcinoma, a tumour of the salivary gland.
General
- Rare.
- Solid epithelial exocrine tumour.[2]
- Poor prognosis; mean survival of 18 months in one series.[3]
Clinical:[3]
- Increased serum lipase.
- Associated with arthralgias (joint pain).
- Classic presentation - Schmid triad:[4]
- Subcutaneous fat necrosis.
- Polyarthritis.
- Eosinophilia.
Gross
- Usually head of pancreas.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Cells reminiscent of pancreatic acinus cells:
- Granular, basophilic cytoplasm - usu. abundant.
- Round/oval nucleus.
- Nucleolus prominent.
- Architecture:
- Nests, sheets, trabecular, glandular.
DDx:
Images
www:
- Acinar cell carcinoma - several images (upmc.edu).
- Acinar cell carcinoma - several images (harvard.edu).
- Acinar cell carcinoma - 1 (nature.com).
- Acinar cell carcinoma - 2 (nature.com).[5]
Stains
Features:[3]
- PAS +ve (granular).
- PASD +ve.
IHC
- Trypsin +ve -- key stain.
- Lipase +ve.
- Chromogranin +ve (scattered, focal).
- CD56 -ve. (?)
See also
References
- ↑ Thomas, PC.; Nash, GF.; Aldridge, MC. (2003). "Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma presenting as acute pancreatitis.". HPB (Oxford) 5 (2): 111-3. doi:10.1080/13651820310001153. PMID 18332967.
- ↑ URL: http://brighamrad.harvard.edu/Cases/bwh/hcache/380/full.html. Accessed on: 15 January 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Klimstra, DS.; Heffess, CS.; Oertel, JE.; Rosai, J. (Sep 1992). "Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas. A clinicopathologic study of 28 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 16 (9): 815-37. PMID 1384374.
- ↑ Jang, SH.; Choi, SY.; Min, JH.; Kim, TW.; Lee, JA.; Byun, SJ.; Lee, JW. (Feb 2010). "[A case of acinar cell carcinoma of pancreas, manifested by subcutaneous nodule as initial clinical symptom].". Korean J Gastroenterol 55 (2): 139-43. PMID 20168061.
- ↑ Klimstra, DS. (Feb 2007). "Nonductal neoplasms of the pancreas.". Mod Pathol 20 Suppl 1: S94-112. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800686. PMID 17486055.