Difference between revisions of "Pseudopyloric mucous glands"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
* | *Seen in [[Crohn's disease]] in the [[terminal ileum]].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Geboes | first1 = K. | last2 = Ectors | first2 = N. | last3 = D'Haens | first3 = G. | last4 = Rutgeerts | first4 = P. | title = Is ileoscopy with biopsy worthwhile in patients presenting with symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease? | journal = Am J Gastroenterol | volume = 93 | issue = 2 | pages = 201-6 | month = Feb | year = 1998 | doi = 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00201.x | PMID = 9468242 }}</ref> | ||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Revision as of 16:13, 1 March 2014
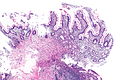
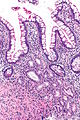
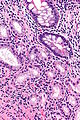
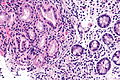
Pseudopyloric mucous glands, also pyloric gland metaplasia,[1] is a change seen intestine. It is associated with Crohn's disease.
Pseudopyloric mucous glands is abbreviated PMG. Pyloric gland metaplasia is abbreviated PGM.
General
- Seen in Crohn's disease in the terminal ileum.[2]
Microscopic
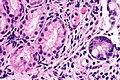
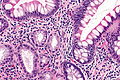
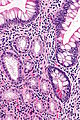
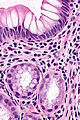
Features:
- Round glands with abundant pale cytoplasm - stubby champagne flute.
- Usually in the deep aspect of the mucosa.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.medunigraz.at/22698. Accessed on: 6 August 2013.
- ↑ Geboes, K.; Ectors, N.; D'Haens, G.; Rutgeerts, P. (Feb 1998). "Is ileoscopy with biopsy worthwhile in patients presenting with symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease?". Am J Gastroenterol 93 (2): 201-6. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00201.x. PMID 9468242.