Difference between revisions of "Spine"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→See also: +link to Schmorl's node) |
|||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
==Schmorl's node== | ==Schmorl's node== | ||
{{Main|Schmorl's node}} | {{Main|Schmorl's node}} | ||
==Vertebral fracture== | |||
:This deals with ''benign'' vertebral fractures. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Benign. | |||
*Usually elderly with osteoporosis.<ref name=pmid24147259>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sisodia | first1 = GB. | title = Methods of predicting vertebral body fractures of the lumbar spine. | journal = World J Orthop | volume = 4 | issue = 4 | pages = 241-247 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.241 | PMID = 24147259 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Non-viable bone. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Pathologic fracture]]. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 31 January 2014
Pieces of spine are seen in neuropathology.
Common specimens
- Synovial cyst.
- Lumbar wound infection.
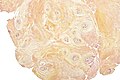
Synovial cyst
General
- May cause back pain.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Simple epithelium.
Notes:
- If epithelium missing -- then ganglion cyst.
Sign out
WRIST LESION ("GANGLION"), EXCISION:
- BENIGN SYNOVIAL CYST.
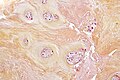
Degenerative disc disease
- Vertebral disc redirects here.
General
- Herniated disc cause back pain.
- May result in cauda equina syndrome.
- Composed of fibrous cartilage.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Benign fibrous tissue.
- Nests of chondrocytes (as in immature cartilage).
Images
www:
Sign out
CERVICAL DISC, DISCECTOMY: - DISC WITH DEGENERATIVE CHANGES. - NO EVIDENCE OF MALIGNANCY.
LUMBAR DISC, DECOMPRESSION: - DEGENERATIVE DISC DISEASE.
Schmorl's node
Main article: Schmorl's node
Vertebral fracture
- This deals with benign vertebral fractures.
General
- Benign.
- Usually elderly with osteoporosis.[4]
Microscopic
Features:
- Non-viable bone.
DDx:
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.spineuniverse.com/conditions/synovial-cysts-spine. Accessed on: 5 November 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Cartilage/Cartil.htm. Accessed on: 2 January 2010.
- ↑ Modic, MT.; Ross, JS. (Oct 2007). "Lumbar degenerative disk disease.". Radiology 245 (1): 43-61. doi:10.1148/radiol.2451051706. PMID 17885180.
- ↑ Sisodia, GB. (2013). "Methods of predicting vertebral body fractures of the lumbar spine.". World J Orthop 4 (4): 241-247. doi:10.5312/wjo.v4.i4.241. PMID 24147259.