Difference between revisions of "Leydig cell tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
(tweak) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
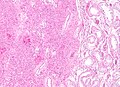
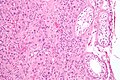
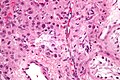
| Caption = Leydig cell tumour. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Leydig cell tumour. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = cytoplasmic vacuolization, cytoplasm - clear to eosinophilic, +/-''Reinke crystals'' (cylindrical crystalloid - eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies), +/-[[nucleoli]] common, round nuclei | | Micro = cytoplasmic vacuolization, cytoplasm -- clear to eosinophilic, +/-''Reinke crystals'' (cylindrical crystalloid -- eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies), +/-[[nucleoli]] common, round nuclei | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[spermatocytic seminoma]] (testis only), [[pregnancy luteoma]] (females only), [[Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour]] | | LMDDx = [[spermatocytic seminoma]] (testis only), [[pregnancy luteoma]] (females only), [[Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour]] | ||
Revision as of 04:13, 18 November 2013
| Leydig cell tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Leydig cell tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cytoplasmic vacuolization, cytoplasm -- clear to eosinophilic, +/-Reinke crystals (cylindrical crystalloid -- eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies), +/-nucleoli common, round nuclei |
| LM DDx | spermatocytic seminoma (testis only), pregnancy luteoma (females only), Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour |
| IHC | inhibin-alpha +ve, calretinin +ve, melan A +ve |
| Gross | solid, red/tan |
| Site | testis |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Blood work | +/-elevated testosterone |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other testicular tumours |
Leydig cell tumour, also known as interstitial cell tumour, is an uncommon benign sex cord-stromal tumour, typically seen in the testis.
Interstitial cell tumour should not be confused with Renomedullary interstitial cell tumour.
General
- Arises from the interstitial cell.
- May be associated with increased testosterone.
Gross
- Solid, lobulated.
- Red/tan.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Vacuolization (cytoplasm) - key feature.
- Cytoplasm - clear to eosinophilic - important.
- Reinke crystals - classic finding, usually not present.
- Cylindrical crystalloid eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies.
- Nucleoli common.
- Round nuclei.
DDx:
- Spermatocytic seminoma - may have eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Pregnancy luteoma - occurs during pregnancy, as the name implies.
Images
www:
IHC
- Inhibin-alpha +ve.
- Calretinin +ve.[2][3]
- Melan A +ve.[4]
- AKA MART-1.
- Expressed in melanoma, adrenal tissue, steroid-secreting tumours.
See also
References
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 581. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ URL: http://www.antibodybeyond.com/reviews/cell-markers/leydig-cell-marker.htm. Accessed on: 18 May 2010.
- ↑ Bar-Shira Maymon B, Yavetz H, Yogev L, et al. (2005). "Detection of calretinin expression in abnormal immature Sertoli cells in non-obstructive azoospermia". Acta Histochem. 107 (2): 105–12. doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2005.02.002. PMID 15950053.
- ↑ Yao DX, Soslow RA, Hedvat CV, Leitao M, Baergen RN (September 2003). "Melan-A (A103) and inhibin expression in ovarian neoplasms". Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 11 (3): 244–9. PMID 12966351.