Difference between revisions of "Schwannoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split-out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
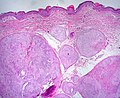
'''Schwannoma''' is a relatively common [[peripheral nerve sheath tumour]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*A common [[neuropathology]] [[CNS tumours|tumour]] that occasionally shows-up elsewhere. | |||
*Tumour of tissue surrounding a nerve. | |||
**Axons adjacent to the tumour are normal... but may be compressed. | |||
*May be a part of [[neurofibromatosis type 2]]. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid17893219>{{cite journal |author=Wippold FJ, Lubner M, Perrin RJ, Lämmle M, Perry A |title=Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: Antoni A and Antoni B tissue patterns |journal=AJNR Am J Neuroradiol |volume=28 |issue=9 |pages=1633–8 |year=2007 |month=October |pmid=17893219 |doi=10.3174/ajnr.A0682 |url=http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/reprint/28/9/1633}}</ref> | |||
*Antoni A: | |||
**Cellular. | |||
**'Fibrillary, polar, elongated'. | |||
*Antoni B: | |||
**Pauci-cellular. | |||
**Loose microcystic tissue. | |||
*Verocay bodies - paucinuclear area surrounded by nuclei - '''diagnostic feature'''. | |||
*Hyaline thickened [[blood vessel]]s. | |||
*Thick capsule. | |||
*In the GI tract: classically have a ''peripheral lymphoid cuff''.<ref name=pmid15728600>{{cite journal |author=Levy AD, Quiles AM, Miettinen M, Sobin LH |title=Gastrointestinal schwannomas: CT features with clinicopathologic correlation |journal=AJR Am J Roentgenol |volume=184 |issue=3 |pages=797–802 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15728600 |doi= |url=http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/full/184/3/797}}</ref> | |||
*+/-Hemosiderin deposition within tumour. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Tumour does ''not'' smear well.<ref>MUN. 24 November 2010.</ref> | |||
*Antoni A: may look somewhat like scattered matchsticks. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Meningioma]]. | |||
*[[Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma]] - if surrounded by a rim of lymphoid tissue, i.e. [[Lymph node pathology|intranodal]]. | |||
*[[Leiomyoma]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
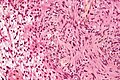
Image:Schwannoma_-_Antoni_A_and_B_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Schwannoma - Antoni A & B - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Schwannoma_-_Antoni_A_and_B_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Scwhannoma - Antoni A & B - very high mag. (WC) | |||
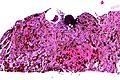
Image:Psammomatous_melanotic_schwannoma_-_high_mag.jpg | Psammomatous melanotic schwannoma - high mag. (WC) | |||
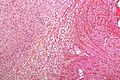
Image:Nerve_root_schwannoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Nerve root schwannoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.pathguy.com/~lulo/lulo0003.htm Antoni A (pathguy.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/content/full/28/9/1633/F8 Antoni A & Antoni B side-by-side (ajnr.org)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case639.html Cystic schwannoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
===Schwannoma subtypes=== | |||
There are four:<ref name=pmid12792904>{{cite journal |author=Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM |title=The pathobiologic spectrum of Schwannomas |journal=Histol. Histopathol. |volume=18 |issue=3 |pages=925–34 |year=2003 |month=July |pmid=12792904 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
#Conventional schwannoma. | |||
#Cellular schwannoma. | |||
#Plexiform schwannoma. | |||
#Melanotic schwannoma. | |||
====Conventional schwannoma==== | |||
*Most common. | |||
====Cellular schwannoma==== | |||
*May mimic [[MPNST]]. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case518.html Cellular schwannoma (upmc.edu)]. | |||
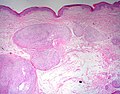
====Plexiform schwannoma==== | |||
*May mimic [[MPNST]] if cellular - esp. in childhood. | |||
Images: | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Plexiform_Schwannoma_2.jpg | Plexiform schwannoma - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Plexiform_Schwannoma_1.jpg | Plexiform schwannoma - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
====Melanotic schwannoma==== | |||
*May be confused with [[melanoma]]. | |||
*Psammomatous form (''psammomatous melanotic schwannoma'') associated with a heritable disorder ([[Carney complex]]). | |||
Note: | |||
*[[Carney complex]]:<ref name=pmid12792904/> | |||
**Cutaneous lentigines. | |||
**Myxomas (skin (subcutaneous), subcutanous, [[Atrial myxoma|heart]]). | |||
**Endocrine neoplasms. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case387.html Psammomatous melanotic schwannoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid12692193>{{cite journal |author=Hirose T, Tani T, Shimada T, Ishizawa K, Shimada S, Sano T |title=Immunohistochemical demonstration of EMA/Glut1-positive perineurial cells and CD34-positive fibroblastic cells in peripheral nerve sheath tumors |journal=Mod. Pathol. |volume=16 |issue=4 |pages=293–8 |year=2003 |month=April |pmid=12692193 |doi=10.1097/01.MP.0000062654.83617.B7 |url=http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880761a.html }}</ref> | |||
*S-100 +ve. | |||
*Glut1 +ve. | |||
*CD34 +ve. | |||
*Cytokeratins ~70% +ve.{{fact}} | |||
*SOX10 +ve.<ref name=pmid18636017>{{cite journal |author=Nonaka D, Chiriboga L, Rubin BP |title=Sox10: a pan-schwannian and melanocytic marker |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=32 |issue=9 |pages=1291–8 |year=2008 |month=September |pmid=18636017 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181658c14 |url=}}</ref> | |||
**-ve in [[synovial sarcoma]], [[rhabdomyosarcoma]], [[chondrosarcoma]]. | |||
*EMA -ve. (???) | |||
**Usually +ve (~75% of the time) in meningiomas.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Rushing | first1 = EJ. | last2 = Bouffard | first2 = JP. | last3 = McCall | first3 = S. | last4 = Olsen | first4 = C. | last5 = Mena | first5 = H. | last6 = Sandberg | first6 = GD. | last7 = Thompson | first7 = LD. | title = Primary extracranial meningiomas: an analysis of 146 cases. | journal = Head Neck Pathol | volume = 3 | issue = 2 | pages = 116-30 | month = Jun | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1007/s12105-009-0118-1 | PMID = 19644540 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Peripheral nerve sheath tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Peripheral nerve sheath tumours]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 28 September 2013
Schwannoma is a relatively common peripheral nerve sheath tumour.
General
- A common neuropathology tumour that occasionally shows-up elsewhere.
- Tumour of tissue surrounding a nerve.
- Axons adjacent to the tumour are normal... but may be compressed.
- May be a part of neurofibromatosis type 2.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Antoni A:
- Cellular.
- 'Fibrillary, polar, elongated'.
- Antoni B:
- Pauci-cellular.
- Loose microcystic tissue.
- Verocay bodies - paucinuclear area surrounded by nuclei - diagnostic feature.
- Hyaline thickened blood vessels.
- Thick capsule.
- In the GI tract: classically have a peripheral lymphoid cuff.[2]
- +/-Hemosiderin deposition within tumour.
Notes:
- Tumour does not smear well.[3]
- Antoni A: may look somewhat like scattered matchsticks.
DDx:
- Meningioma.
- Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma - if surrounded by a rim of lymphoid tissue, i.e. intranodal.
- Leiomyoma.
Images
www:
- Antoni A (pathguy.com).
- Antoni A & Antoni B side-by-side (ajnr.org).
- Cystic schwannoma - several images (upmc.edu).
Schwannoma subtypes
There are four:[4]
- Conventional schwannoma.
- Cellular schwannoma.
- Plexiform schwannoma.
- Melanotic schwannoma.
Conventional schwannoma
- Most common.
Cellular schwannoma
- May mimic MPNST.
Images:
Plexiform schwannoma
- May mimic MPNST if cellular - esp. in childhood.
Images:
Melanotic schwannoma
- May be confused with melanoma.
- Psammomatous form (psammomatous melanotic schwannoma) associated with a heritable disorder (Carney complex).
Note:
- Carney complex:[4]
- Cutaneous lentigines.
- Myxomas (skin (subcutaneous), subcutanous, heart).
- Endocrine neoplasms.
Images:
IHC
Features:[5]
- S-100 +ve.
- Glut1 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- Cytokeratins ~70% +ve.[citation needed]
- SOX10 +ve.[6]
- -ve in synovial sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, chondrosarcoma.
- EMA -ve. (???)
- Usually +ve (~75% of the time) in meningiomas.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Wippold FJ, Lubner M, Perrin RJ, Lämmle M, Perry A (October 2007). "Neuropathology for the neuroradiologist: Antoni A and Antoni B tissue patterns". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28 (9): 1633–8. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0682. PMID 17893219. http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/reprint/28/9/1633.
- ↑ Levy AD, Quiles AM, Miettinen M, Sobin LH (March 2005). "Gastrointestinal schwannomas: CT features with clinicopathologic correlation". AJR Am J Roentgenol 184 (3): 797–802. PMID 15728600. http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/full/184/3/797.
- ↑ MUN. 24 November 2010.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer B, Woodruff JM (July 2003). "The pathobiologic spectrum of Schwannomas". Histol. Histopathol. 18 (3): 925–34. PMID 12792904.
- ↑ Hirose T, Tani T, Shimada T, Ishizawa K, Shimada S, Sano T (April 2003). "Immunohistochemical demonstration of EMA/Glut1-positive perineurial cells and CD34-positive fibroblastic cells in peripheral nerve sheath tumors". Mod. Pathol. 16 (4): 293–8. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000062654.83617.B7. PMID 12692193. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n4/full/3880761a.html.
- ↑ Nonaka D, Chiriboga L, Rubin BP (September 2008). "Sox10: a pan-schwannian and melanocytic marker". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 32 (9): 1291–8. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181658c14. PMID 18636017.
- ↑ Rushing, EJ.; Bouffard, JP.; McCall, S.; Olsen, C.; Mena, H.; Sandberg, GD.; Thompson, LD. (Jun 2009). "Primary extracranial meningiomas: an analysis of 146 cases.". Head Neck Pathol 3 (2): 116-30. doi:10.1007/s12105-009-0118-1. PMID 19644540.