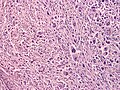
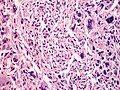
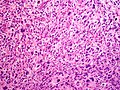
Atypical fibroxanthoma
| Atypical fibroxanthoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
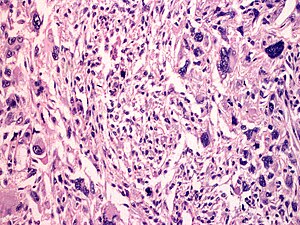 Atypical fibroxanthoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | dermal lesion with marked nuclear atypia, mitoses, mulitnucleated cells, cell have foamy cytoplasm |
| LM DDx | malignant melanoma, pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, sarcomatoid squamous carcinoma |
| IHC | S-100 -ve, CK34betaE12 -ve, p63 -ve, desmin -ve |
| Site | skin - see skin tumours, usu. head & neck |
|
| |
| Clinical history | rapid growth, elderly |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good |
| Clin. DDx | malignant skin tumours |
| Treatment | complete excision |
Atypical fibroxanthoma, abbreviated AFX, is poorly differentiated skin tumour with likeness to undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma.
General
- Typically head & neck region.[1]
- Thought to be related to pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma;[2][3] some say it is the same thing.[4]
- Usually benign.
- May metastasize - case report-type of occurrence.[5]
Clinical:
- Rapid growth.
- Elderly.
- Good prognosis.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[7]
- Dermal lesion - key point.
- Marked nuclear atypia.
- Mitoses.
- Mulitnucleated cells.
- Foamy cytoplasm - key feature.
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma.
- Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma (MFH) - deeper than the dermis.
- Leiomyosarcoma.
- Sarcomatoid squamous carcinoma.
Notes:
- No Grenz zone. (???)
Images
www:
A markedly atypical lesion of far less worrisome significance is the pleomorphic hyalinizing angioectatic tumor of soft parts (subcutis).


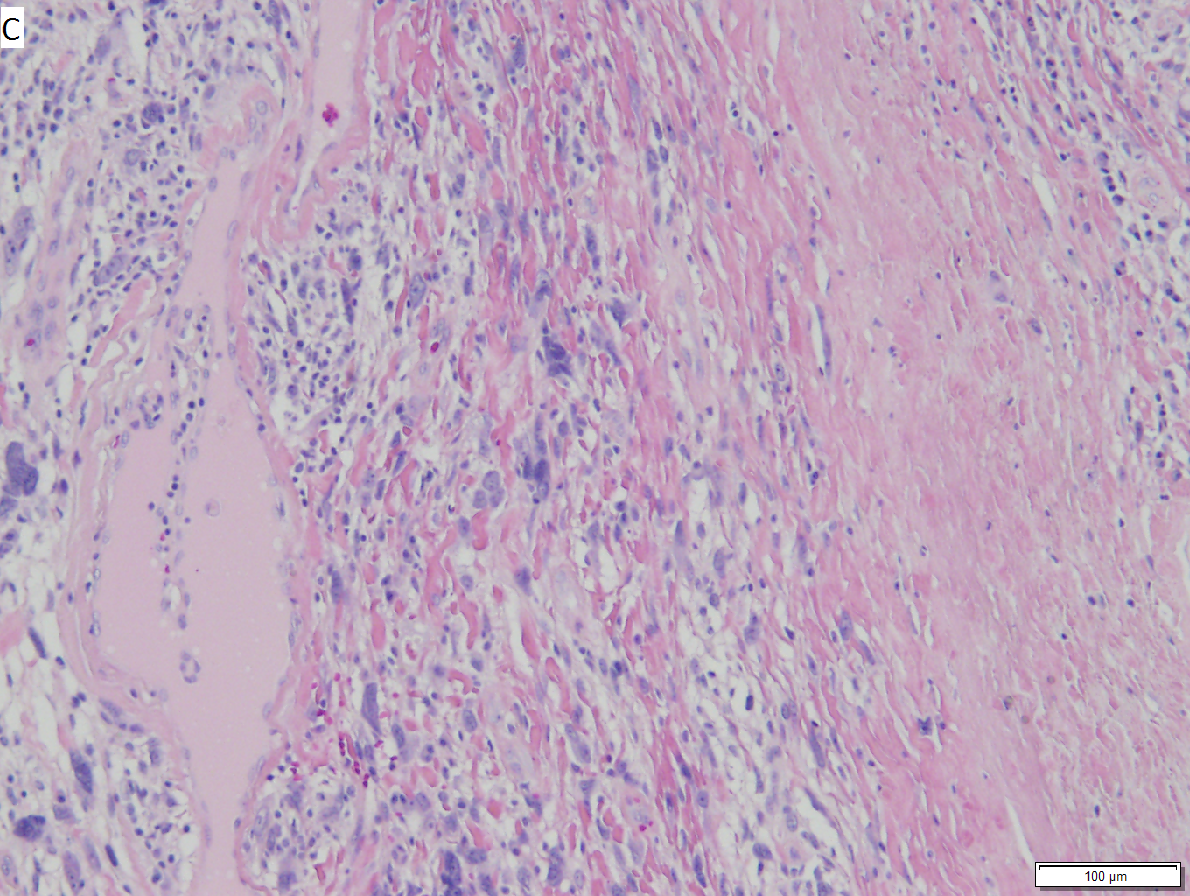



Pleomorphic hyalinizing angioectatic tumor of soft parts (subcutis). A. The key distinction is at low power, wherein cluters of thin-walled, indented (ectatic) blood vessels are seen. B. The ectatic vessels have a thin endothelial lining and a thick subjacent rim of amorphous eosinophilia. Note the multinucleated cells in the stroma. C. Hyaline material extends beyond vessels to entrap stromal cells. D. Cellularity in part raises the possibility of a sarcoma. E. High power further raises the suspicion of malignancy, given the aberrant nuclei with prominent nucleoli. F. Reassurance occurs because 1) there are virtually no mitoses, 2) there is no necrosis, and 3) there are readily identifiable nuclear inclusions as seen in these tumor cells.
IHC
Features:[7]
- S100 -ve (done to r/o melanoma).
- CK34betaE12 -ve.
- p63 -ve (done to exclude SCC).
- Scant staining not considered +ve.
- Desmin -ve (done to r/o leiomyosarcoma).
- CD99 +ve.[9]
- Usually +ve in melanoma... but negative in squamous carcinoma.
Others:
- Vimentin +ve.
- SMA +ve.[citation needed]
New et al. suggests:[10]
- Vimentin, SMA, CD68, cytokeratins, p63, desmin, CD99, CD10, S100, CD117, LN-2, procollagen I.
A panel:
Sign out
Incompletely excised
SKIN LESION, MID BACK, SHAVE BIOPSY: - ATYPICAL SPINDLE CELL NEOPLASM, SEE MICRO AND COMMENT. COMMENT: The diagnosis of atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) is favoured. The main differential diagnosis is pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma. The extent of the lesion cannot be determined, as it is present at the deep margin. This lesion should be re-excised, as it could represent an aggressive malignancy.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1056204-overview. Accessed on 2 September 2011.
- ↑ Withers, AH.; Brougham, ND.; Barber, RM.; Tan, ST. (Jun 2011). "Atypical fibroxanthoma and malignant fibrous histiocytoma.". J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2011.05.004. PMID 21664889.
- ↑ Tchernev, G.; Tronnier, M.; Ananiev, J.; Taneva, T.; Patterson, JW.; Gulubova, M.; Trafeli, JP.; Gegova, A. et al. (Aug 2013). "Atypical fibroxanthoma-a diagnosis of exclusion!". Wien Med Wochenschr 163 (15-16): 380-386. doi:10.1007/s10354-012-0173-1. PMID 23319144.
- ↑ Ghazarian, Danny; 16 September 2011.
- ↑ New, D.; Bahrami, S.; Malone, J.; Callen, JP. (Dec 2010). "Atypical fibroxanthoma with regional lymph node metastasis: report of a case and review of the literature.". Arch Dermatol 146 (12): 1399-404. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.206. PMID 20713774.
- ↑ Beer, TW.; Drury, P.; Heenan, PJ. (Aug 2010). "Atypical fibroxanthoma: a histological and immunohistochemical review of 171 cases.". Am J Dermatopathol 32 (6): 533-40. doi:10.1097/DAD.0b013e3181c80b97. PMID 20526171.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 521. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Vandergriff, TW.; Reed, JA.; Orengo, IF. (2008). "An unusual presentation of atypical fibroxanthoma.". Dermatol Online J 14 (1): 6. PMID 18319023.
- ↑ Monteagudo, C.; Calduch, L.; Navarro, S.; Joan-Figueroa, A.; Llombart-Bosch, A. (Jan 2002). "CD99 immunoreactivity in atypical fibroxanthoma: a common feature of diagnostic value.". Am J Clin Pathol 117 (1): 126-31. doi:10.1309/2EXB-70CW-3U6P-VQ6H. PMID 11789717.
- ↑ New, D.; Bahrami, S.; Malone, J.; Callen, JP. (Dec 2010). "Atypical fibroxanthoma with regional lymph node metastasis: report of a case and review of the literature.". Arch Dermatol 146 (12): 1399-404. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2010.206. PMID 20713774.