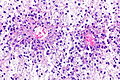
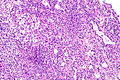
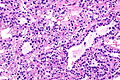
TFEB-rearranged renal cell carcinoma
(Redirected from TFEB-rearranged RCC)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| TFEB-rearranged renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
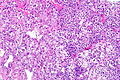
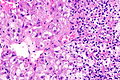
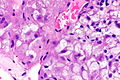
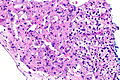
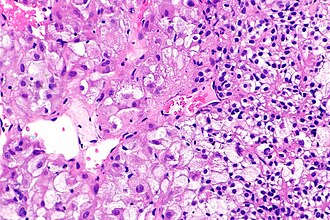 Renal cell carcinoma with morphology and IHC profile suggestive of TFEB RCC. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | solid architecture with occasional rosette-like structures; two cell populations (1) large epithelioid cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm, (2) small lymphocyte-like cells |
| LM DDx | renal cell carcinoma, unclassified, angiomyolipoma (epithelioid), other renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm |
| IHC | TFEB +ve (nuclear staining), HMB-45 +ve, TFE3 -ve |
| Molecular | TFEB rearrangement, t(6;11)(p21;q12) and others |
| Grossing notes | total nephrectomy for tumour grossing, partial nephrectomy grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Clinical history | typically children or young adults |
| Prevalence | very rare ~ 2 dozen reported cases |
| Prognosis | aggressive (?) |
| Clin. DDx | other kidney tumours |
| Treatment | nephrectomy |
TFEB-rearranged renal cell carcinoma, also TFEB RCC, is a rare renal cell carcinoma recognized by the WHO classification.[1][2]
It was previously known as renal tumour with t(6;11) translocation, also t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma. It was first described in children.
It was added to WHO classification of renal neoplasia in the 2012 Vancouver modification.[3]
This entity should not be confused with ELOC-mutated renal cell carcinoma (previously known as TCEB1-mutated renal cell carcinoma).
General
- Very rare - approximately 2 dozen reported cases as of 2014.[2][4]
- Lymph node metastases are common.
- Traditionally thought of as a pediatric tumour... but cases in adults are reported.[2][5]
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Solid with occasional rosette-like structures.
- Two cell populations:
- Large epithelioid cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Small lymphocyte-like cells.
DDx:
- Renal cell carcinoma, unclassified.
- Angiomyolipoma (epithelioid).
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Other renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Biphasic hyalinizing psammomatous renal cell carcinoma.
Images
www
IHC and morphology compatible
IHC
- TFEB +ve (nuclear staining).
- TFE3 -ve.
- Melan A +ve (13 +ve of 13 cases[9]).
- HMB-45 +ve (12 +ve of 13 cases[9]).
- PAX8 +ve/-ve (14 +ve of 23[9]).
- CAM5.2 +ve (8 +ve of 13[9]).
- RCC +ve (10 +ve of 14[9]).
- CD10 +ve (10 +ve of 14[9]).
- Cathepsin K +ve.[citation needed]
- PD-L1 +ve.[10]
Note:
- Melan A and HMB-45 are considered a good screen for this entity and recommended for renal tumour with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Molecular
Others translocations involving TFEB have been described:[10]
- ACTB-TFEB.
- NEAT1-TFEB.
See also
- Kidney tumours.
- Renal tumour with Xp11.2 translocation.
- Chromosomal translocations.
- Pediatric pathology.
References
- ↑ Alaghehbandan R, Siadat F, Trpkov K (February 2022). "What's new in the WHO 2022 classification of kidney tumours?". Pathologica 115 (1): 8–22. doi:10.32074/1591-951X-818. PMC 10342217. PMID 36645398. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10342217/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hora, M.; Urge, T.; Trávníček, I.; Ferda, J.; Chudáček, Z.; Vaněček, T.; Michal, M.; Petersson, F. et al. (2014). "MiT translocation renal cell carcinomas: two subgroups of tumours with translocations involving 6p21 [t (6; 11)] and Xp11.2 [t (X;1 or X or 17)].". Springerplus 3: 245. doi:10.1186/2193-1801-3-245. PMID 24877033.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN.; Egevad, L.; Epstein, JI.; Grignon, D.; Hes, O.; Moch, H. et al. (Oct 2013). "The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver Classification of Renal Neoplasia.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (10): 1469-89. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318299f2d1. PMID 24025519.
- ↑ Argani, P.; Yonescu, R.; Morsberger, L.; Morris, K.; Netto, GJ.; Smith, N.; Gonzalez, N.; Illei, PB. et al. (Oct 2012). "Molecular confirmation of t(6;11)(p21;q12) renal cell carcinoma in archival paraffin-embedded material using a break-apart TFEB FISH assay expands its clinicopathologic spectrum.". Am J Surg Pathol 36 (10): 1516-26. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182613d8f. PMID 22892601.
- ↑ Ishihara, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Takamori, H.; Kuroda, N. (Sep 2011). "Renal carcinoma with (6;11)(p21;q12) translocation: Report of an adult case.". Pathol Int 61 (9): 539-45. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02711.x. PMID 21884304.
- ↑ Hora, M.; Hes, O.; Urge, T.; Eret, V.; Klecka, J.; Michal, M. (2009). "A distinctive translocation carcinoma of the kidney ["rosette-like forming," t(6;11), HMB45-positive renal tumor].". Int Urol Nephrol 41 (3): 553-7. doi:10.1007/s11255-008-9495-8. PMID 18998233.
- ↑ URL: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Tumors/RenalCellt0611ID5011.html. Accessed on: December 29, 2014.
- ↑ Davis, IJ.; Hsi, BL.; Arroyo, JD.; Vargas, SO.; Yeh, YA.; Motyckova, G.; Valencia, P.; Perez-Atayde, AR. et al. (May 2003). "Cloning of an Alpha-TFEB fusion in renal tumors harboring the t(6;11)(p21;q13) chromosome translocation.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100 (10): 6051-6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0931430100. PMID 12719541.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Smith, NE.; Illei, PB.; Allaf, M.; Gonzalez, N.; Morris, K.; Hicks, J.; Demarzo, A.; Reuter, VE. et al. (May 2014). "t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma (RCC): expanded immunohistochemical profile emphasizing novel RCC markers and report of 10 new genetically confirmed cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (5): 604-14. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000203. PMID 24618616.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Caliò A, Harada S, Brunelli M, Pedron S, Segala D, Portillo SC, Magi-Galluzzi C, Netto GJ, Mackinnon AC, Martignoni G (April 2021). "TFEB rearranged renal cell carcinoma. A clinicopathologic and molecular study of 13 cases. Tumors harboring MALAT1-TFEB, ACTB-TFEB, and the novel NEAT1-TFEB translocations constantly express PDL1". Mod Pathol 34 (4): 842–850. doi:10.1038/s41379-020-00713-6. PMID 33208882.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 607924
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 281. ISBN 978-0781765275.