Glycogen storage diseases
(Redirected from Pompe disease)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Glycogen storage diseases a group of diseases characterized by the accumulation of glycogen.
Clinical picture
- Exercise intolerance
- Usually due to specific muscle enzyme defects
DDx:
- Mitochondriopathies
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT2) deficiency
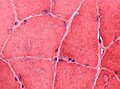
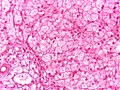
General microscopic
Features:[1]
- +/-Vacuolated muscle fibres.
- acid phosphatase+ve in vaculoes.
- PAS+ve.
Images:
Electron microscopy
- Electron dense deposits.
Specific diseases
Pompe disease
- AKA glycogen storage disease type II, AKA acid maltase deficiency, AKA alpha-1,4-glucosidase deficiency.[2]
General
- Deficiency of alpha-1,4-glucosidase; it degrades glycogen to glucose in lysosomes.
- Autosomal recessive inheritance.
- Identified in 1932 by dutch pathologist Johannes C. Pompe.[3]
- A enzyme replacement therapy exists. [4]
Clinical
- infantile onset (usually at age 4-8months):
- Floppy baby.
- Macroglossia.
- Hepatomegaly.
- Big heart - often early death from cardiac failure.
- late onset (usually at age 1-2years):
- Progressive muscle weakness (myopathy).
- Usually only mild cardiac involvement.
Note: clinical course correlates with remaining enzyme activity.[5]
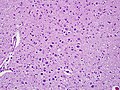
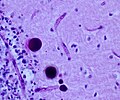
Diagnosis
- Mutations in acid alpha-glucosidase.
- Elevated serum CK (<10x).
- Cytoplasmic (lysosomal) vacuoles (Acid phosphatase +ve).
- Muscle fibers with vacuoles enlarged.
- Type 1 fibers more often affected.
- PAS+ve deposits.
- Autophagic (Lysosomal) vacuoles in electron microscopy.
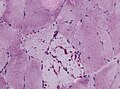
Cori disease
General
- Hepatomegaly.
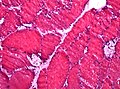
Microscopic
Features:
- Hypertrophic hepatocytes with pale cytoplasm.
- Classically: PAS +ve, PAS-D -ve.
- Portal fibrosis.
Image:
Stains
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/606800. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.
- ↑ Pompe J-C. Over idiopatische hypertropie van het hart. Ned Tijdscr Geneeskd 1932; 76:304.
- ↑ Amalfitano, A.; Bengur, AR.; Morse, RP.; Majure, JM.; Case, LE.; Veerling, DL.; Mackey, J.; Kishnani, P. et al. "Recombinant human acid alpha-glucosidase enzyme therapy for infantile glycogen storage disease type II: results of a phase I/II clinical trial.". Genet Med 3 (2): 132-8. doi:10.109700125817-200103000-00007. PMID 11286229.
- ↑ Hermans, MM.; van Leenen, D.; Kroos, MA.; Beesley, CE.; Van Der Ploeg, AT.; Sakuraba, H.; Wevers, R.; Kleijer, W. et al. (Jan 2004). "Twenty-two novel mutations in the lysosomal alpha-glucosidase gene (GAA) underscore the genotype-phenotype correlation in glycogen storage disease type II.". Hum Mutat 23 (1): 47-56. doi:10.1002/humu.10286. PMID 14695532.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/232400. Accessed on: 25 January 2011.