Squamous papilloma
| Squamous papilloma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
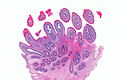
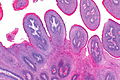
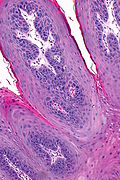
 Squamous papilloma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | squamous cell papilloma |
|
| |
| LM | branching papillae (papilla = nipple-like projection with a fibrovascular core), basal cell hyperplasia, koilocytes |
| LM DDx | squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (esp. verrucous, papillary and exophytic subtypes), verruca vulgaris, oral condyloma |
| Site | head and neck |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | excision |
Squamous papilloma, also squamous cell papilloma, is a benign squamous lesion, typically of the head and neck.
Laryngeal papilloma redirects here.
The caruncle lesion is dealt with in papilloma of the caruncle. The lesion in the esophagus is dealt with in squamous papilloma of the esophagus.
General
- Benign.
- Typically related to HPV 6 and HPV 11.
Gross
Features:[1]
- Exophytic mass.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Branching papillae.
- Papilla = nipple-like projection with a fibrovascular core.
- Basal cell hyperplasia.
- Koilocytes.
Note:
- The threshold for dysplasia is somewhat higher in the head and neck than in the uterine cervix.
DDx:
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck - verrucous, papillary and exophytic subtypes.
- Verruca vulgaris - have granular layer, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis.[2]
- Oral condyloma - broader projections with a blunted appearance.[2]
Images
www:
- Laryngeal papilloma - low mag. (webpathology.com).
- Laryngeal papilloma - high mag. (webpathology.com).
- Low-grade squamous dysplasia (els-cdn.com).[3]
Sign out
LARYNGEAL LESION ("LARYNGEAL PAPILLOMA"), RIGHT, BIOPSY:
- SQUAMOUS PAPILLOMA.
Not definite
TONGUE PAPULE, RIGHT, BIOPSY: - SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM WITH PARAKERATOSIS AND VERY SCANT STROMA WITH FEATURES SUGGESTIVE OF A SQUAMOUS PAPILLOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Dysplastic
LARYNGEAL LESION ("LARYNGEAL PAPILLOMA"), LEFT, BIOPSY:
- SQUAMOUS PAPILLOMA WITH LOW-GRADE DYSPLASIA.
- NEGATIVE FOR HIGH-GRADE DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
- CLOSE FOLLOW-UP IS RECOMMENDED.
Micro
The sections show fibrovascular cores covered by stratified squamous epithelium with basal cell hyperplasia and edema. Scattered lymphocytes are present in the epithelium. No mitotic activity is appreciated. There is no significant nuclear atypia. Dyskeratotic cells are seen focally. Parakeratosis is present. Koilocytes are not apparent.
Low-grade dysplasia
The sections show fibrovascular cores covered by stratified squamous epithelium. Scattered lymphocytes are present in the epithelium. Rare mitotic activity is appreciated in the lower third of the epithelium. Mild nuclear atypia (hyperchromasia and mild nuclear enlargement in the lower third of the epithelium) is present. Dyskeratotic cells are seen focally. Parakeratosis is present. Koilocytes are seen focally.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Head and Neck Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 33. ISBN 978-0443069604.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Head and Neck Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 426. ISBN 978-0443069604.
- ↑ Hedström, J.; Grenman, R.; Ramsay, H.; Finne, P.; Lundin, J.; Haglund, C.; Alfthan, H.; Stenman, UH. (Oct 1999). "Concentration of free hCGbeta subunit in serum as a prognostic marker for squamous-cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx.". Int J Cancer 84 (5): 525-8. PMID 10502732.