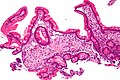
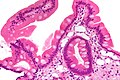
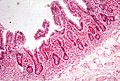
Whipple's disease
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Whipple's disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
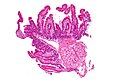
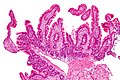
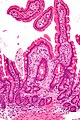
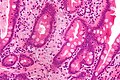
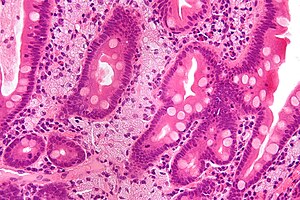 Whipple's disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | rod-shaped microorganisms - typically in macrophages; lamina propria macrophages usually abundant |
| LM DDx | mycobacterium avium complex |
| Stains | PAS +ve (microorganisms), AFB -ve |
| Site | duodenum |
|
| |
| Clinical history | usu. middle aged men |
| Signs | diarrhea |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | antibiotics |
Whipple's disease is a rare infectious disease that is classically found in the duodenum.
General
Etiology:
Epidemiology:
- Very rare.
- Classically middle aged men.
Clinical
- Malabsorption (diarrhea), arthritis + others.
- Symptoms are non-specific.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics - for months and months.
Gross
- Pale yellow or white spots.[3]
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Rod-shaped microorganisms - typically found in macrophages.
- Macrophages usually abundant - key feature that should raise Dx in DDx.
- Organisms periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) positive.
DDx:
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) - not hole-y.
- Crushed Brunner's glands - PAS-Alcian blue stain +ve (like Whipple's disease).
Images
Stains
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Liang Z, La Scola B, Raoult D (January 2002). "Monoclonal antibodies to immunodominant epitope of Tropheryma whipplei". Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 9 (1): 156?9. PMC 119894. PMID 11777846. http://cvi.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11777846.
- ↑ Alkan, S.; Beals, TF.; Schnitzer, B. (Dec 2001). "Primary diagnosis of whipple disease manifesting as lymphadenopathy: use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of Tropheryma whippelii.". Am J Clin Pathol 116 (6): 898-904. doi:10.1309/7678-E2DW-HFJ5-QYUJ. PMID 11764080.
- ↑ Salkic, NN.; Alibegovic, E.; Jovanovic, P. (May 2013). "Endoscopic appearance of duodenal mucosa in Whipple's disease.". Gastrointest Endosc 77 (5): 822-3; discussion 823. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2013.01.016. PMID 23490230.
- ↑ Bai J, Mazure R, Vazquez H, Niveloni S, Smecuol E, Pedreira S, Mauriño E (2004). "Whipple's disease". Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2 (10): 849?60. doi:10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00387-8. PMID 15476147.