Difference between revisions of "Thymoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Thymoma''' is a common tumour of the [[thymus]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Strong association with autoimmune disease, esp. myasthenia gravis. | |||
===Classification=== | |||
The ''WHO'' published a widely used system - WHO classification:<ref>{{Ref Sternberg4|1264}}</ref> | |||
====Type A==== | |||
*AKA ''Spindle cell'' or ''medullary''. | |||
*Arise from ''medullary epithelial cells''. | |||
*Good prognosis. | |||
IHC: | |||
*Usu. keratin+. | |||
====Type AB==== | |||
*Like Type A... but with foci of lymphocytes. | |||
====Type B1==== | |||
*Near normal, expanded cortex. | |||
Lesion consists of: | |||
*>2/3 lymphocytes, <1/3 cortical epithelial cells. | |||
====Type B2==== | |||
*Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells. | |||
**Epithelioid cells with distinct nucleoli. | |||
**May be perivascular. | |||
*Large population of lymphocytes. | |||
Lesion consists of: | |||
*<2/3 but >1/3 lymphocytes, >1/3 but <2/3 cortical epithelial cells. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Most common '''B''' type. | |||
====Type B3==== | |||
*Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells. | |||
**Polygonal/round shape. | |||
**Form sheets (of cells) - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Lymphocytes - less than in Type B2. | |||
*AKA ''well-differentiated thymic carcinoma''. | |||
Lesion consists of: | |||
*<1/3 lymphocytes, >2/3 cortical epithelial cells. | |||
Note: | |||
*Neoplastic cells derived from the thymus with cytologic features of malignancy are [[thymic carcinoma]]s. | |||
Images: | |||
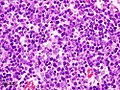
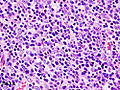
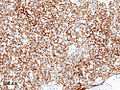
<gallery> | |||
Image:Thymoma_type_B1_(1).JPG | Thymoma Type B1. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Thymoma_B1_(2).JPG | Thymoma Type B1. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Thymoma_B1_(3)_CK_CAM5-2.JPG | Thymoma Type B1 - CAM5.2. (WC/KGH) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Gross== | |||
*Light brown/tan. | |||
*Encapsulated. | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/253251/enlarge Thymoma (sciencephoto.com)]. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Lymphocytes. | |||
*Epithelial cells. | |||
**Spindle cells - Type A. | |||
**Epithelioid cells - Type B. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Lymphoma]]. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Thymoma_B1_%282%29.JPG Thymoma (WC)]. | |||
===Staging=== | |||
There is a system by Masaoka and colleagues<ref name=pmid7296496 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Masaoka | first1 = A. | last2 = Monden | first2 = Y. | last3 = Nakahara | first3 = K. | last4 = Tanioka | first4 = T. | title = Follow-up study of thymomas with special reference to their clinical stages. | journal = Cancer | volume = 48 | issue = 11 | pages = 2485-92 | month = Dec | year = 1981 | doi = | PMID = 7296496 }}</ref> that was subsequently modified, and is known as the ''modified Masaoka staging system''.<ref name=pmid8044305>{{Cite journal | last1 = Koga | first1 = K. | last2 = Matsuno | first2 = Y. | last3 = Noguchi | first3 = M. | last4 = Mukai | first4 = K. | last5 = Asamura | first5 = H. | last6 = Goya | first6 = T. | last7 = Shimosato | first7 = Y. | title = A review of 79 thymomas: modification of staging system and reappraisal of conventional division into invasive and non-invasive thymoma. | journal = Pathol Int | volume = 44 | issue = 5 | pages = 359-67 | month = May | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 8044305 }}</ref> | |||
====Based on CAP protocol==== | |||
Staging as per Butnor ''et al.'':<ref>Butnor KJ et al. Thymus. Version 3.1.0.0. 2011. URL: [http://www.cap.org/cancerprotocols www.cap.org/cancerprotocols]. Accessed on: 31 August 2015.</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Stage | |||
!Characteristics | |||
|- | |||
|I | |||
|encapsulated lesion, tumour does not penetrate capsule | |||
|- | |||
|IIa | |||
|microscopic penetration of the capsule | |||
|- | |||
|IIb | |||
|macroscopic penetration of the capsule | |||
|- | |||
|III | |||
|macroscopic invasion of adjacent organs | |||
|- | |||
|IVa | |||
|pleural or pericardial spread | |||
|- | |||
|IVb | |||
|lymphatic or hematogenous spread | |||
|} | |||
====Modified Masaoka as per Masaoka ''et al.'' (1999)==== | |||
T-stage - based on Masaoka ''et al.'' (1999):<ref name=pmid10047676>{{Cite journal | last1 = Masaoka | first1 = A. | last2 = Yamakawa | first2 = Y. | last3 = Fujii | first3 = Y. | title = Well-differentiated thymic carcinoma: is it thymic carcinoma or not? | journal = J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | volume = 117 | issue = 3 | pages = 628-30 | month = Mar | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10047676 }}</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Stage | |||
!Features | |||
|- | |||
| T1 | |||
| macroscopically and microscopically encapulated | |||
|- | |||
| T2 | |||
| macroscopic invasion or adhesion to surrounding tissue (fat or pleura) ''or'' microscopic invasion into the capsule | |||
|- | |||
| T3 | |||
| Spread to adjacent organs, e.g. pericardium, lung, great vessels. | |||
|- | |||
| T4 | |||
| pericardial or pleural spread | |||
|} | |||
N-stage - based on Masaoka ''et al.'' (1999):<ref name=pmid10047676>{{Cite journal | last1 = Masaoka | first1 = A. | last2 = Yamakawa | first2 = Y. | last3 = Fujii | first3 = Y. | title = Well-differentiated thymic carcinoma: is it thymic carcinoma or not? | journal = J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | volume = 117 | issue = 3 | pages = 628-30 | month = Mar | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10047676 }}</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Stage | |||
!Features | |||
|- | |||
| N0 | |||
| no lymph node spread | |||
|- | |||
| N1 | |||
| spread to anterior mediastinal lymph nodes | |||
|- | |||
| N2 | |||
| spread to intrathoracic lymph nodes other than the mediastinal lymph nodes | |||
|- | |||
| N3 | |||
| spread to supraclavicular lymph nodes | |||
|} | |||
M-stage - based on Masaoka ''et al.'' (1999):<ref name=pmid10047676>{{Cite journal | last1 = Masaoka | first1 = A. | last2 = Yamakawa | first2 = Y. | last3 = Fujii | first3 = Y. | title = Well-differentiated thymic carcinoma: is it thymic carcinoma or not? | journal = J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg | volume = 117 | issue = 3 | pages = 628-30 | month = Mar | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10047676 }}</ref> | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
!Stage | |||
!Features | |||
|- | |||
| M0 | |||
| no hematogeneous spread and extrathoracic lymph nodes with the exception of the supraclavicular nodes | |||
|- | |||
| M1 | |||
| hematogeneous spread and/or extrathoracic lymph nodes | |||
|} | |||
==IHC== | |||
*[[p63]] +ve.<ref name=pmid24923897>{{cite journal |author=Adam P, Hakroush S, Hofmann I, Reidenbach S, Marx A, Ströbel P |title=Thymoma with loss of keratin expression (and giant cells): a potential diagnostic pitfall |journal=Virchows Arch. |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2014 |month=June |pmid=24923897 |doi=10.1007/s00428-014-1606-6 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*TdT +ve. | |||
*Ki-67 variable.<ref name=pmid24585679>{{Cite journal | last1 = Viti | first1 = A. | last2 = Bertolaccini | first2 = L. | last3 = Cavallo | first3 = A. | last4 = Fortunato | first4 = M. | last5 = Bianchi | first5 = A. | last6 = Terzi | first6 = A. | title = 18-Fluorine fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the pretreatment evaluation of thymic epithelial neoplasms: a metabolic biopsy confirmed by Ki-67 expression. | journal = Eur J Cardiothorac Surg | volume = 46 | issue = 3 | pages = 369-74; discussion 374 | month = Sep | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1093/ejcts/ezu030 | PMID = 24585679 }}</ref> | |||
**~5-70% for A, AB & B1. | |||
**~80-100% for B2 & B3. | |||
A panel: | |||
*TdT, CD1a, CD3, CD5, CD20, Ki-67, CD117, p63, CK5/6. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
A. Lymph Node, Station 6, Lymphadenectomy: | |||
- One benign lymph node (0/1). | |||
B. Submitted as "Anterior Mediastinal Tumour (Thymus)", Excision: | |||
- Thymoma, WHO type B2. | |||
- Modified Masaoka stage IIa. | |||
- Three benign lymph nodes (0/3). | |||
- Rim of benign thymus. | |||
- Please see synoptic report. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Thymus]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Haematopathology]] | |||
Revision as of 22:29, 20 December 2015
Thymoma is a common tumour of the thymus.
General
- Strong association with autoimmune disease, esp. myasthenia gravis.
Classification
The WHO published a widely used system - WHO classification:[1]
Type A
- AKA Spindle cell or medullary.
- Arise from medullary epithelial cells.
- Good prognosis.
IHC:
- Usu. keratin+.
Type AB
- Like Type A... but with foci of lymphocytes.
Type B1
- Near normal, expanded cortex.
Lesion consists of:
- >2/3 lymphocytes, <1/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Type B2
- Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells.
- Epithelioid cells with distinct nucleoli.
- May be perivascular.
- Large population of lymphocytes.
Lesion consists of:
- <2/3 but >1/3 lymphocytes, >1/3 but <2/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Notes:
- Most common B type.
Type B3
- Neoplastic cells with some resemblance to cortical epithelial cells.
- Polygonal/round shape.
- Form sheets (of cells) - key feature.
- Lymphocytes - less than in Type B2.
- AKA well-differentiated thymic carcinoma.
Lesion consists of:
- <1/3 lymphocytes, >2/3 cortical epithelial cells.
Note:
- Neoplastic cells derived from the thymus with cytologic features of malignancy are thymic carcinomas.
Images:
Gross
- Light brown/tan.
- Encapsulated.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Lymphocytes.
- Epithelial cells.
- Spindle cells - Type A.
- Epithelioid cells - Type B.
DDx:
Images:
Staging
There is a system by Masaoka and colleagues[2] that was subsequently modified, and is known as the modified Masaoka staging system.[3]
Based on CAP protocol
Staging as per Butnor et al.:[4]
| Stage | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| I | encapsulated lesion, tumour does not penetrate capsule |
| IIa | microscopic penetration of the capsule |
| IIb | macroscopic penetration of the capsule |
| III | macroscopic invasion of adjacent organs |
| IVa | pleural or pericardial spread |
| IVb | lymphatic or hematogenous spread |
Modified Masaoka as per Masaoka et al. (1999)
T-stage - based on Masaoka et al. (1999):[5]
| Stage | Features |
|---|---|
| T1 | macroscopically and microscopically encapulated |
| T2 | macroscopic invasion or adhesion to surrounding tissue (fat or pleura) or microscopic invasion into the capsule |
| T3 | Spread to adjacent organs, e.g. pericardium, lung, great vessels. |
| T4 | pericardial or pleural spread |
N-stage - based on Masaoka et al. (1999):[5]
| Stage | Features |
|---|---|
| N0 | no lymph node spread |
| N1 | spread to anterior mediastinal lymph nodes |
| N2 | spread to intrathoracic lymph nodes other than the mediastinal lymph nodes |
| N3 | spread to supraclavicular lymph nodes |
M-stage - based on Masaoka et al. (1999):[5]
| Stage | Features |
|---|---|
| M0 | no hematogeneous spread and extrathoracic lymph nodes with the exception of the supraclavicular nodes |
| M1 | hematogeneous spread and/or extrathoracic lymph nodes |
IHC
A panel:
- TdT, CD1a, CD3, CD5, CD20, Ki-67, CD117, p63, CK5/6.
Sign out
A. Lymph Node, Station 6, Lymphadenectomy: - One benign lymph node (0/1). B. Submitted as "Anterior Mediastinal Tumour (Thymus)", Excision: - Thymoma, WHO type B2. - Modified Masaoka stage IIa. - Three benign lymph nodes (0/3). - Rim of benign thymus. - Please see synoptic report.
See also
References
- ↑ Mills, Stacey E; Carter, Darryl; Greenson, Joel K; Oberman, Harold A; Reuter, Victor E (2004). Sternberg's Diagnostic Surgical Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1264. ISBN 978-0781740517.
- ↑ Masaoka, A.; Monden, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Tanioka, T. (Dec 1981). "Follow-up study of thymomas with special reference to their clinical stages.". Cancer 48 (11): 2485-92. PMID 7296496.
- ↑ Koga, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Mukai, K.; Asamura, H.; Goya, T.; Shimosato, Y. (May 1994). "A review of 79 thymomas: modification of staging system and reappraisal of conventional division into invasive and non-invasive thymoma.". Pathol Int 44 (5): 359-67. PMID 8044305.
- ↑ Butnor KJ et al. Thymus. Version 3.1.0.0. 2011. URL: www.cap.org/cancerprotocols. Accessed on: 31 August 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Masaoka, A.; Yamakawa, Y.; Fujii, Y. (Mar 1999). "Well-differentiated thymic carcinoma: is it thymic carcinoma or not?". J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117 (3): 628-30. PMID 10047676.
- ↑ Adam P, Hakroush S, Hofmann I, Reidenbach S, Marx A, Ströbel P (June 2014). "Thymoma with loss of keratin expression (and giant cells): a potential diagnostic pitfall". Virchows Arch.. doi:10.1007/s00428-014-1606-6. PMID 24923897.
- ↑ Viti, A.; Bertolaccini, L.; Cavallo, A.; Fortunato, M.; Bianchi, A.; Terzi, A. (Sep 2014). "18-Fluorine fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the pretreatment evaluation of thymic epithelial neoplasms: a metabolic biopsy confirmed by Ki-67 expression.". Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 46 (3): 369-74; discussion 374. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezu030. PMID 24585679.