Difference between revisions of "Sinus histiocytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Benign. | *Benign. | ||
*Non-specific finding. | *Non-specific finding. | ||
*Reported in association with hip replacements.<ref name=pmid8279630>{{Cite journal | last1 = Albores-Saavedra | first1 = J. | last2 = Vuitch | first2 = F. | last3 = Delgado | first3 = R. | last4 = Wiley | first4 = E. | last5 = Hagler | first5 = H. | title = Sinus histiocytosis of pelvic lymph nodes after hip replacement. A histiocytic proliferation induced by cobalt-chromium and titanium. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 18 | issue = 1 | pages = 83-90 | month = Jan | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 8279630 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Lymph node pathology]]. | *[[Lymph node pathology]]. | ||
*[[Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy]] | *[[Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy]]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 00:45, 1 December 2013
Sinus histiocytosis, abbreviated SH, is a common finding in lymph nodes.
It should not be confused with Rosai-Dorfman disease (also known as sinus histiocytosis and massive lymphadenopathy).
General
- Benign.
- Non-specific finding.
- Reported in association with hip replacements.[1]
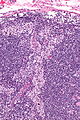
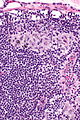
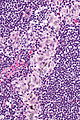
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Sinuses distended with histiocytes - key feature.
- Plasma cells increased.
DDx:
- Rosai-Dorfman disease - histiocyte nuclei large (~2-3x lymphocyte) and round with a prominent nucleoli.
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy - histiocytes have (melanin) pigment.
Images
Sign out
- The finding is often ignored; may be signed out as morphologically benign lymph nodes.
See also
References
- ↑ Albores-Saavedra, J.; Vuitch, F.; Delgado, R.; Wiley, E.; Hagler, H. (Jan 1994). "Sinus histiocytosis of pelvic lymph nodes after hip replacement. A histiocytic proliferation induced by cobalt-chromium and titanium.". Am J Surg Pathol 18 (1): 83-90. PMID 8279630.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 179. ISBN 978-0781775960.