Difference between revisions of "PEComa"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+EM) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
*[[Clear cell sarcoma]]. | *[[Clear cell sarcoma]]. | ||
Images | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
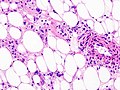
Image:Renal_angiomyolipoma_%282%29.jpg | Renal AML (WC/KGH) | |||
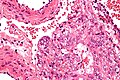
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | LAM - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
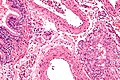
Image:Lymphangioleiomyomatosis_-_high_mag.jpg | LAM - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Revision as of 00:08, 16 May 2013
PEComa is a family of tumours derived from perivascular epithelioid cells (PECs).
General
- Associated with abnormalities in TSC1 and TSC2 - the genes involved in tuberous sclerosis.[1]
The PEComa family
- Angiomyolipoma.
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis.
- Clear-cell myomelanocytic tumour of ligamentum teres/falciform ligament.
- Abdominopelvic sarcoma of perivascular epitheloid cells.[2]
- Clear-cell sugar tumour (CCST).
- Primary extrapulmonary sugar tumour.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Epithelioid morphology.
- Clear or granular cytoplasm.
- Central oval (or round) nucleus.
- Indistinct/small nucleolus.
DDx:
Images
IHC
EM
- Premelanosomes.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Martignoni G, Pea M, Reghellin D, Zamboni G, Bonetti F (February 2008). "PEComas: the past, the present and the future". Virchows Arch. 452 (2): 119–32. doi:10.1007/s00428-007-0509-1. PMC 2234444. PMID 18080139. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2234444/.
- ↑ Bonetti, F.; Martignoni, G.; Colato, C.; Manfrin, E.; Gambacorta, M.; Faleri, M.; Bacchi, C.; Sin, VC. et al. (Jun 2001). "Abdominopelvic sarcoma of perivascular epithelioid cells. Report of four cases in young women, one with tuberous sclerosis.". Mod Pathol 14 (6): 563-8. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880351. PMID 11406657.
- ↑ Park, SH.; Ro, JY.; Kim, HS.; Lee, ES. (Nov 2003). "Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the uterus: immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and molecular study.". Pathol Int 53 (11): 800-5. PMID 14629307.