Difference between revisions of "Lichen simplex chronicus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(fix redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
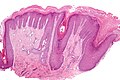
| Image = Lichen_simplex_chronicus_-_low_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Lichen simplex chronicus. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Micro = irregular psoriasiform change (acanthosis), hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, +/-spongiosis | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[prurigo nodularis]], oral lichen simplex chronicus | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[skin]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = scratching, irritation | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Lichen simplex chronicus''', abbreviated '''LSC''', a relatively common diagnosis in [[dermatopathology]]. | |||
It is also known as ''squamous cell hyperplasia''.<ref name=Ref_PBoD1011>{{Ref PBoD8|1011}}</ref> | |||
==General== | |||
*May be considered a variant of ''spongiotic dermatitis''.<ref name=Ref_DCHH296>{{Ref DCHH|296}}</ref>; more specifically, some think it is an ''atopic dermatitis'' (which fits in the large ''[[spongiotic dermatitis]]'' category).<ref name=Ref_Derm26>{{Ref Derm|26}}</ref> | |||
*It is lumped with the [[psoriasiform dermatitides]]. | |||
Etiology:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-overview]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref> | |||
*Pruritus (itchness) -> mechanical trauma -> lichenification (thickened/leathery<ref>URL: [http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10131 http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10131]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref>. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD1065-6>{{Ref PBoD|1065-6}}</ref> | |||
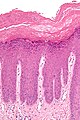
*Acanthosis (epithelial thickening) - irregular. | |||
*Hyperkeratosis. | |||
Other features:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-diagnosis http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-diagnosis]. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.</ref> | |||
*[[Spongiosis]] (epidermal intercellular edema -- cells appear to have a clear halo around 'em). | |||
*[[Parakeratosis]] = retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Prurigo nodularis]] - focal process (nodule or papule). | |||
*Benign alveolar ridge keratosis ([[AKA]] oral lichen simplex chronicus<ref name=pmid18158926>{{Cite journal | last1 = Natarajan | first1 = E. | last2 = Woo | first2 = SB. | title = Benign alveolar ridge keratosis (oral lichen simplex chronicus): A distinct clinicopathologic entity. | journal = J Am Acad Dermatol | volume = 58 | issue = 1 | pages = 151-7 | month = Jan | year = 2008 | doi = 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.07.011 | PMID = 18158926 }}</ref>) - see [[oral pathology]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Lichen_simplex_chronicus_-_low_mag.jpg | LSC - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Lichen_simplex_chronicus_-_high_mag.jpg | LSC - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
SKIN, PUNCH BIOPSY: | |||
- LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Oral=== | |||
<pre> | |||
RETROMOLAR PAD, RIGHT, PUNCH BIOPSY: | |||
- ORAL LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Micro=== | |||
The sections show a squamous mucosa with irregular psoriasiform change, parakeratosis, and focal hypergranulosis. There is no inflammation at the interface. Epidermal intercellular bridges are easily seen. There is no significant nuclear atypia. Mitoses are not evident. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Non-malignant skin disease]]. | |||
*[[Dermatopathology]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Dermatopathology]] | |||
Revision as of 20:54, 12 July 2013
| Lichen simplex chronicus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Lichen simplex chronicus. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | irregular psoriasiform change (acanthosis), hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, +/-spongiosis |
| LM DDx | prurigo nodularis, oral lichen simplex chronicus |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Clinical history | scratching, irritation |
Lichen simplex chronicus, abbreviated LSC, a relatively common diagnosis in dermatopathology.
It is also known as squamous cell hyperplasia.[1]
General
- May be considered a variant of spongiotic dermatitis.[2]; more specifically, some think it is an atopic dermatitis (which fits in the large spongiotic dermatitis category).[3]
- It is lumped with the psoriasiform dermatitides.
Etiology:[4]
- Pruritus (itchness) -> mechanical trauma -> lichenification (thickened/leathery[5].
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Acanthosis (epithelial thickening) - irregular.
- Hyperkeratosis.
Other features:[7]
- Spongiosis (epidermal intercellular edema -- cells appear to have a clear halo around 'em).
- Parakeratosis = retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum.
DDx:
- Prurigo nodularis - focal process (nodule or papule).
- Benign alveolar ridge keratosis (AKA oral lichen simplex chronicus[8]) - see oral pathology.
Images
Sign out
SKIN, PUNCH BIOPSY: - LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Oral
RETROMOLAR PAD, RIGHT, PUNCH BIOPSY: - ORAL LICHEN SIMPLEX CHRONICUS. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show a squamous mucosa with irregular psoriasiform change, parakeratosis, and focal hypergranulosis. There is no inflammation at the interface. Epidermal intercellular bridges are easily seen. There is no significant nuclear atypia. Mitoses are not evident.
See also
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1011. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 296. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 26. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-overview. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=10131. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1065-6. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1123423-diagnosis. Accessed on: 20 August 2010.
- ↑ Natarajan, E.; Woo, SB. (Jan 2008). "Benign alveolar ridge keratosis (oral lichen simplex chronicus): A distinct clinicopathologic entity.". J Am Acad Dermatol 58 (1): 151-7. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.07.011. PMID 18158926.