Difference between revisions of "Keratocystic odontogenic tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infoboxes) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Keratocystic odontogenic tumour. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Keratocystic odontogenic tumour. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Micro = | | Micro = Stratified epithelium with "ribbon-like appearance" with palisaded basal cell layer, parakeratosis, artefactual separation of epithelium from the basement membrane | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[odontogenic cyst]] | | LMDDx = [[odontogenic cyst]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| Syndromes = [[nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome]] | | Syndromes = [[nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome]] | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = mass lesion | ||
| Symptoms = | | Symptoms = | ||
| Prevalence = | | Prevalence = uncommon | ||
| Bloodwork = | | Bloodwork = | ||
| Rads = | | Rads = | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 26 July 2013
| Keratocystic odontogenic tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
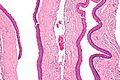
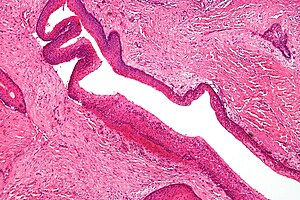 Keratocystic odontogenic tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | Stratified epithelium with "ribbon-like appearance" with palisaded basal cell layer, parakeratosis, artefactual separation of epithelium from the basement membrane |
| LM DDx | odontogenic cyst |
| Site | usually mandible |
|
| |
| Syndromes | nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome |
|
| |
| Signs | mass lesion |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Clin. DDx | ameloblastoma |
| Keratocystic odontogenic tumour | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Keratocystic odontogenic tumour, abbreviated KOT, is an uncommon odontogenic tumour.
It was previously known as odontogenic keratocyst, abbreviated OKC.[1]
General
- May be associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
Clinical
Features:[2]
- Most common presentation: swelling.
Gross
- Location: usually mandible.
- May mimic ameloblastoma radiologically.
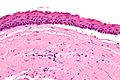
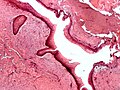
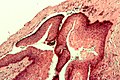
Microscopic
Features: [3]
- Stratified epithelium (resembling squamous epithelium) with:
- "Ribbon-like appearance" - important.
- Typically 8-10 cell layers thick - with relatively uniform thickness.
- Lacks rete ridges.
- Palisaded basal cell layer.
- "Ribbon-like appearance" - important.
- Parakeratosis (keratinized cells with nuclei) - key feature.
- Artefactual separation of epithelium from the basement membrane.
DDx:
- Odontogenic cyst.
- Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst[4] - usu. dentigerous cyst - has orthokeratosis instead of parakeratosis.
- Orthokeratosis = keratinized cells no nuclei; parakeratosis = keratinized cell with nuclei.
- Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst[4] - usu. dentigerous cyst - has orthokeratosis instead of parakeratosis.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ Madras, J.; Lapointe, H. (Mar 2008). "Keratocystic odontogenic tumour: reclassification of the odontogenic keratocyst from cyst to tumour.". J Can Dent Assoc 74 (2): 165-165h. PMID 18353202.
- ↑ Habibi, A.; Saghravanian, N.; Habibi, M.; Mellati, E.; Habibi, M. (Sep 2007). "Keratocystic odontogenic tumor: a 10-year retrospective study of 83 cases in an Iranian population.". J Oral Sci 49 (3): 229-35. PMID 17928730.
- ↑ Thompson LDR. Head and neck pathology - (Foundations in diagnostic pathology). Goldblum JR, Ed.. Churchill Livingstone. 2006. ISBN 0-443-06960-3.
- ↑ Macdonald-Jankowski, DS. (Dec 2010). "Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst: a systematic review.". Dentomaxillofac Radiol 39 (8): 455-67. doi:10.1259/dmfr/19728573.
- ↑ URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0968605305000992#fig5. Accessed on: 11 March 2013.