Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
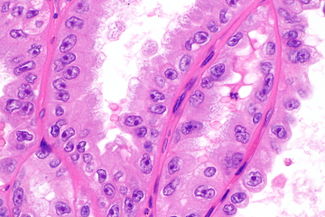
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome (abbreviated HLRCC), also hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer, is an uncommon syndrome caused by fumarate hydratase (FH) gene mutations.[1][2]

Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma showing the classically described prominent nucleoli with perinucleolar clearing. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron)
Characteristics:
Formal criteria
The diagnosis of the HLRCC syndrome requires both #1 and #2:[3]
- A pathogenic FH mutation is present by molecular testing.
- One of the following (pathologic) findings:
- Multiple cutaneous leiomyoma where one was proven histologically.
- One cutaneous leiomyoma in the context of a family history of HRLCC.
- RCC with a morphology suggestive of HRLCC syndrome-associated RCC.
General
- Autosomal dominant inheritance[4] with variable penetration.[5]
- In one series of 21 families: 62% had renal cancer, 76% had cutaneous leiomyomas and 100% had uterine leiomyomas.[6]
Features - clinical:
- Leiomyomas - high penetrance.
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma.
- Often aggressive and significant cause of mortality.[8]
Note:
- The RCC in the past was typically diagnosed as papillary renal cell carcinoma.[9]
See also
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 136850
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 150800
- ↑ Adam, MP.; Ardinger, HH.; Pagon, RA.; Wallace, SE.; Bean, LJH.; Mefford, HC.; Stephens, K.; Amemiya, A. et al. Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer. PMID 20301430.
- ↑ Merino, MJ.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Pinto, P.; Linehan, WM. (Oct 2007). "The morphologic spectrum of kidney tumors in hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC) syndrome.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (10): 1578-85. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31804375b8. PMID 17895761.
- ↑ Reyes, C.; Karamurzin, Y.; Frizzell, N.; Garg, K.; Nonaka, D.; Chen, YB.; Soslow, RA. (Jul 2014). "Uterine smooth muscle tumors with features suggesting fumarate hydratase aberration: detailed morphologic analysis and correlation with S-(2-succino)-cysteine immunohistochemistry.". Mod Pathol 27 (7): 1020-7. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2013.215. PMID 24309325.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Wei, MH.; Toure, O.; Glenn, GM.; Pithukpakorn, M.; Neckers, L.; Stolle, C.; Choyke, P.; Grubb, R. et al. (Jan 2006). "Novel mutations in FH and expansion of the spectrum of phenotypes expressed in families with hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer.". J Med Genet 43 (1): 18-27. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.033506. PMID 15937070.
- ↑ Toon, CW.; Hasovits, C.; Paik, J.; Field, M.; Chou, A.; Hugh, TJ.; Pavlakis, N.; Gill, AJ. (Jul 2014). "Skin rash, a kidney mass and a family mystery dating back to World War II.". Med J Aust 201 (1): 58-60. PMID 24999901.
- ↑ Chen, YB.; Brannon, AR.; Toubaji, A.; Dudas, ME.; Won, HH.; Al-Ahmadie, HA.; Fine, SW.; Gopalan, A. et al. (May 2014). "Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cancer: recognition of the syndrome by pathologic features and the utility of detecting aberrant succination by immunohistochemistry.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (5): 627-37. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000163. PMID 24441663.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 290. ISBN 978-0781765275.