Difference between revisions of "Glycogen storage diseases"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Cori disease: +image) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (+pictures) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Glycogen storage diseases''' a group of diseases characterized by the accumulation of glycogen. | '''Glycogen storage diseases''' a group of diseases characterized by the accumulation of glycogen. | ||
=Clinical picture= | |||
*Exercise intolerance | |||
*Usually due to specific muscle enzyme defects | |||
DDx: | |||
* Mitochondriopathies | |||
* Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT2) deficiency | |||
=General microscopic= | =General microscopic= | ||
Features:<ref>URL: [http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm]. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.</ref> | Features:<ref>URL: [http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm]. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.</ref> | ||
*+/-Vacuolated muscle fibres. | *+/-Vacuolated muscle fibres. | ||
*acid phosphatase+ve in vaculoes. | |||
*PAS+ve. | |||
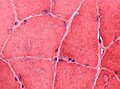
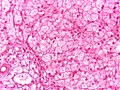
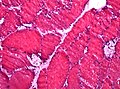
Images: | Images: | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:HE_glycogen_storage_disease_highmag.jpg | Abnormal glycogen is not easy to spot in this muscle biopsy HE stain (WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:PAS_glycogen_storage_disease_intermed_mag.jpg | Intramuscular glycogen is usually PAS+++ve (WC/jensflorian) | |||
Trichrom_glycogen_storage_disease_intermed_mag..jpg | Lack of staining in intramuscular deposits, Trichrom Gömöri (WC/jensflorian) | |||
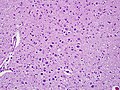
File:Polyglucosan body disease.jpg | Lafora-like polyglucosan bodies in the CNS, low magnification (WC/jensflorian) | |||
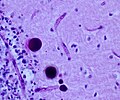
File:Adult polyglucosan body disease histopathology.jpg | Lafora-like polyglucosan bodies in the CNS, higher magnification(WC/marvin101) | |||
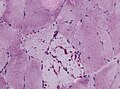
File:Glycogen storage disorder - Liver.jpg | Large vacuoles in the liver, HE stain (WC/Netha Hussain) | |||
</gallery> | |||
*[http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmalt.htm Glycogen storage disease (wustl.edu)]. | *[http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmalt.htm Glycogen storage disease (wustl.edu)]. | ||
*[http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/hepatobiliary/gsd1.html Glycogen storage disease (brown.edu)]. | *[http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/hepatobiliary/gsd1.html Glycogen storage disease (brown.edu)]. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 40: | ||
*Big heart. | *Big heart. | ||
**Often early death from cardiac failure. | **Often early death from cardiac failure. | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Pompe_vacuoles.jpg | Large vacuoles in Pompe disease (H&E, WC/jensflorian) | |||
File:Phenotypical-variation-within-22-families-with-Pompe-disease-1750-1172-8-182-S1.ogv | Clinical phenotype in Pompe disease (WC/Wens et. al.) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Cori disease== | ==Cori disease== | ||
Revision as of 11:53, 17 April 2015
Glycogen storage diseases a group of diseases characterized by the accumulation of glycogen.
Clinical picture
- Exercise intolerance
- Usually due to specific muscle enzyme defects
DDx:
- Mitochondriopathies
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (CPT2) deficiency
General microscopic
Features:[1]
- +/-Vacuolated muscle fibres.
- acid phosphatase+ve in vaculoes.
- PAS+ve.
Images:
Electron microscopy
- Electron dense deposits.
Specific diseases
Pompe disease
General
Deficiency of alpha-1,4-glucosidase; it degrades glycogen to glucose in lysosomes.
Clinical:
- Floppy baby.
- Big heart.
- Often early death from cardiac failure.
Cori disease
General
- Hepatomegaly.
Microscopic
Features:
- Hypertrophic hepatocytes with pale cytoplasm.
- Classically: PAS +ve, PAS-D -ve.
- Portal fibrosis.
Image:
Stains
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://neuromuscular.wustl.edu/pathol/acidmchi.htm. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/606800. Accessed on: 11 January 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/232400. Accessed on: 25 January 2011.