Difference between revisions of "Eosinophilic cholecystitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+infobox) |
|||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Acute cholecystitis]]. | *[[Acute cholecystitis]]. | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
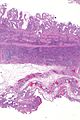
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis -- extremely low mag.jpg | EC - extremely low mag. | |||
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis -- very low mag.jpg | EC - very low mag. | |||
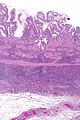
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis -- low mag.jpg | EC - low mag. | |||
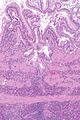
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis -- intermed mag.jpg | EC - intermed. mag. | |||
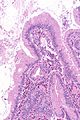
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis -- high mag.jpg | EC - high mag. | |||
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis - alt -- very low mag.jpg | EC - very low mag. | |||
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis - alt -- low mag.jpg | EC - low mag. | |||
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis - alt -- intermed mag.jpg | EC - intermed. mag. | |||
Image: Eosinophilic cholecystitis - alt -- high mag.jpg | EC - high mag. | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Revision as of 03:44, 7 July 2016
| Eosinophilic cholecystitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
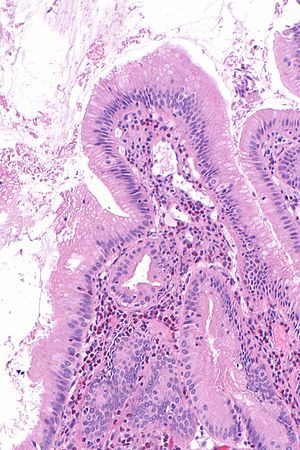 Eosinophilic cholecystitis. H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
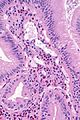
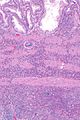
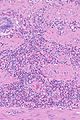
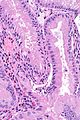
| LM | gallbladder wall with inflammatory infiltrate that is >90% eosinophils |
| Subtypes | (subtype of acute cholecystitis) |
| LM DDx | acute cholecystitis with eosinophils |
| Site | gallbladder |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | eosinophilic cholangitis, gypereosinophilic syndromes, parasitic infestations |
| Signs | see acute cholecystitis |
| Prevalence | rare - case reports |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | acute cholecystitis |
| Treatment | cholecystectomy |
Eosinophilic cholecystitis is a rare type of cholecystitis.
General
- Rare - case reports.
- Clinical presentation like acute cholecystitis.[1][2]
- Eosinophilic cholangitis.
- Hypereosinophilic syndromes (HES).
- Parasitic infestations.
Microscopic
Features:
DDx:
Images
Sign out
Gallbladder, Cholecystectomy: - Eosinophilic cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, see comment. Comment: Eosinophilic cholecystitis may be idiopathic or associated with other conditions characterized by eosinophilia, including but not limited to parasitic infections and hypereosinophilic syndromes. Clinical correlation is required.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Shakov, R.; Simoni, G.; Villacin, A.; Baddoura, W. (2007). "Eosinophilic cholecystitis, with a review of the literature.". Ann Clin Lab Sci 37 (2): 182-5. PMID 17522376.
- ↑ del-Moral-Martínez, M.; Barrientos-Delgado, A.; Crespo-Lora, V.; Cervilla-Sáez-de-Tejada, ME.; Salmerón-Escobar, J. (Jan 2015). "Eosinophilic cholecystitis: an infrequent cause of acute cholecystitis.". Rev Esp Enferm Dig 107 (1): 45-7. PMID 25603333.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Choudhury, M.; Pujani, M.; Katiyar, Y.; Jyotsna, PL.; Rautela, A. (2014). "Idiopathic eosinophilic cholecystitis with cholelithiasis: a report of two cases.". Turk Patoloji Derg 30 (2): 142-4. doi:10.5146/tjpath.2014.01235. PMID 24638193.