Difference between revisions of "Desmoid-type fibromatosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
*[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/29/7/2143/F28.expansion.html Desmoid tumour (radiographics.rsna.org)]. | *[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/29/7/2143/F28.expansion.html Desmoid tumour (radiographics.rsna.org)]. | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.qe2a-proxy.mun.ca/pmc/articles/PMC3700980/figure/f3-ol-05-06-1976/ Desmoid-type fibromatosis (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23833679>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ma | first1 = JH. | last2 = Ma | first2 = ZH. | last3 = Dong | first3 = XF. | last4 = Yin | first4 = H. | last5 = Zhao | first5 = YF. | title = Abdominal wall desmoid tumors: A case report. | journal = Oncol Lett | volume = 5 | issue = 6 | pages = 1976-1978 | month = Jun | year = 2013 | doi = 10.3892/ol.2013.1297 | PMID = 23833679 }}</ref> | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.qe2a-proxy.mun.ca/pmc/articles/PMC3700980/figure/f3-ol-05-06-1976/ Desmoid-type fibromatosis (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23833679>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ma | first1 = JH. | last2 = Ma | first2 = ZH. | last3 = Dong | first3 = XF. | last4 = Yin | first4 = H. | last5 = Zhao | first5 = YF. | title = Abdominal wall desmoid tumors: A case report. | journal = Oncol Lett | volume = 5 | issue = 6 | pages = 1976-1978 | month = Jun | year = 2013 | doi = 10.3892/ol.2013.1297 | PMID = 23833679 }}</ref> | ||
* | *[File:SoftTissue ChestWall DesmoidFirbomatosis MP CTR.jpg|thumb|Classic desmoid fibromatosis with delicate curving vessels and sweeping long fascicles.] | ||
* | *[File:SoftTissue DesmoidFibromatosis KelioidFx MP2 CTR.jpg|thumb|This example of desmoid fibromatosis shows a keloidal collagenous stroma and may evoke keloidal scar or even solitary fibrous tumor.] | ||
* | *[File:SoftTissue DesmoidFibromatosis GiantCell MP PA.jpg|thumb|Giant cells are an unusual but occasional component of desmoid fibromatosis. Sometimes the giant cells are histiocytic, sometimes they are entrapped rhabdomyocytes.] | ||
* | *[File:Pancreas DesmoidFibromatosis MP CTR.jpg|thumb|Intra-abdominal desmoids can overrun vital organs; in this case, the pancreas.] | ||
* | *[File:Peritoneum Desmoid Intraabdominal LP.JPG|thumb|Intraabdominal desmoids can extend through the bowel to the mucosa and provoke ulceration.] | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 2 October 2014
| Desmoid-type fibromatosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
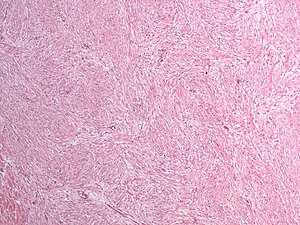 Desmoid-type fibromatosis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | "sweeping fascicles"/bundles, spindle cells with small slender nuclei, solid dark eosinophilic cytoplasm, +/-mitoses, long thin-walled vessels - parallel to one another |
| LM DDx | hypertrophic scar, gastrointestinal stromal tumour, retroperitoneal fibrosis, other fibromatoses, nodular fasciitis, schwannoma |
| IHC | beta-catenin +ve (nuclear), SMA +ve/-ve, CD117 -ve |
| Site | soft tissue |
|
| |
| Syndromes | familial adenomatous polyposis - esp. Gardner syndrome |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign but locally aggressive |
| Clin. DDx | trauma/hematoma |
Desmoid-type fibromatosis is a benign soft tissue lesion in the fibroblastic/myofibroblastic group of tumours.
It is also known as desmoid tumour and desmoid fibromatosis.
General
- Benign.
- One of many fibromatoses.
- Locally aggressive.[1]
- May be seen in the context of familial adenomatous polyposis.
Gross
Features:[2]
- Location:
- Abdominal wall, proximal extremities - classic for adolescents and women.
- Head and neck - classic for children.
- Circumscribed mass.
- May be quite large (>10 cm).
Microscopic
- "Sweeping fascicles"/bundles.
- Spindle cells with:
- Small slender nuclei.
- Solid dark eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- +/-Mitoses - may be abundant.
- Long thin-walled vessels - parallel to one another - important feature.
DDx:
- Hypertrophic scar-like lesion, see dermal scar.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumour[4] - reported in abdominal wall.[5]
- Retroperitoneal fibrosis - no beta-catenin staining.[4]
- Other fibromatoses.
- Nodular fasciitis - esp. with RBC extravasation.
- Schwannoma.
Images
www:
- Desmoid tumour (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
- Desmoid tumour (cheapmedicinechest.com).[6]
- Desmoid tumour (radiographics.rsna.org).
- Desmoid-type fibromatosis (nih.gov).[7]
- [File:SoftTissue ChestWall DesmoidFirbomatosis MP CTR.jpg|thumb|Classic desmoid fibromatosis with delicate curving vessels and sweeping long fascicles.]
- [File:SoftTissue DesmoidFibromatosis KelioidFx MP2 CTR.jpg|thumb|This example of desmoid fibromatosis shows a keloidal collagenous stroma and may evoke keloidal scar or even solitary fibrous tumor.]
- [File:SoftTissue DesmoidFibromatosis GiantCell MP PA.jpg|thumb|Giant cells are an unusual but occasional component of desmoid fibromatosis. Sometimes the giant cells are histiocytic, sometimes they are entrapped rhabdomyocytes.]
- [File:Pancreas DesmoidFibromatosis MP CTR.jpg|thumb|Intra-abdominal desmoids can overrun vital organs; in this case, the pancreas.]
- [File:Peritoneum Desmoid Intraabdominal LP.JPG|thumb|Intraabdominal desmoids can extend through the bowel to the mucosa and provoke ulceration.]
IHC
Features:[2]
- Beta-catenin +ve (nuclear[4]) - important.
- 100% sensitive... may not be completely specific (?).[8]
- SMA +ve ~50% of lesions.
Others:
- CD117 -ve.
Sign out
LESION, ABDOMINAL WALL, BIOPSY: - DESMOID-TYPE FIBROMATOSIS. COMMENT: The tumour stains strongly with beta-catenin and weakly with SMA. It is negative for CD117.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.dtrf.org/dtrf_aboutdesmoids.htm. Accessed on: 15 April 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 609. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ URL: http://www.surgicalpathologyatlas.com/glfusion/mediagallery/media.php?f=0&sort=0&s=20090717111548196. Accessed on: 4 October 2011.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Huss, S.; Nehles, J.; Binot, E.; Wardelmann, E.; Mittler, J.; Kleine, MA.; Künstlinger, H.; Hartmann, W. et al. (Jan 2013). "β-catenin (CTNNB1) mutations and clinicopathological features of mesenteric desmoid-type fibromatosis.". Histopathology 62 (2): 294-304. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04355.x. PMID 23020601.
- ↑ Thalheimer, A.; Meyer, D.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Timmermann, W.; Thiede, A. (Jul 2004). "[Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the abdominal wall. An unusual localization of a rare tumor].". Chirurg 75 (7): 708-12. doi:10.1007/s00104-003-0696-5. PMID 15257404.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cheapmedicinechest.com/abdominal-pain-and-colonic-obstruction-from-an-intra-abdominal-desmoid-tumor.html. Accessed on: 4 October 2011.
- ↑ Ma, JH.; Ma, ZH.; Dong, XF.; Yin, H.; Zhao, YF. (Jun 2013). "Abdominal wall desmoid tumors: A case report.". Oncol Lett 5 (6): 1976-1978. doi:10.3892/ol.2013.1297. PMID 23833679.
- ↑ Amary, MF.; Pauwels, P.; Meulemans, E.; Roemen, GM.; Islam, L.; Idowu, B.; Bousdras, K.; Diss, TC. et al. (Sep 2007). "Detection of beta-catenin mutations in paraffin-embedded sporadic desmoid-type fibromatosis by mutation-specific restriction enzyme digestion (MSRED): an ancillary diagnostic tool.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (9): 1299-309. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31802f581a. PMID 17721184.
