Difference between revisions of "Critical values"
(tweak) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Critical values''' is a concept which comes to anatomical pathology from clinical pathology.<ref name=pmid17491125>{{cite journal |author=Allen TC |title=Critical values in anatomic pathology? |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=131 |issue=5 |pages=684–7 |year=2007 |month=May |pmid=17491125 |doi= |url=http://arpa.allenpress.com/arpaonline/?request=get-document&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&issue=5&page=684}}</ref> | [[Image:ECG in hyperkalemia.png | thumb| right|200px| Hyperkalemia is a critical value as it is associated with [[cardiac arrhythmias]].]] | ||
'''Critical values''' is a concept which comes to anatomical [[pathology]] from clinical pathology.<ref name=pmid17491125>{{cite journal |author=Allen TC |title=Critical values in anatomic pathology? |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=131 |issue=5 |pages=684–7 |year=2007 |month=May |pmid=17491125 |doi= |url=http://arpa.allenpress.com/arpaonline/?request=get-document&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&issue=5&page=684}}</ref> | |||
In the context of surgical | In the context of surgical pathology, it is, perhaps more appropriately, called '''critical [[diagnosis]]'''. | ||
The general consensus is that these findings require a phone call and/or discussion with the clinician to ensure the situation is managed appropriately in a timely manner.<ref name=pmid16680772/> | The general consensus is that these findings (critical valves, critical diagnoses) require a phone call and/or discussion with the clinician to ensure the situation is managed appropriately in a timely manner.<ref name=pmid16680772/> | ||
==List== | ==List of critical diagnoses== | ||
===Cytology=== | |||
Critical diagnoses as per Pereira ''et al.'':<ref name=pmid16680772>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pereira | first1 = TC. | last2 = Clayton | first2 = AC. | last3 = Tazelaar | first3 = HD. | last4 = Liu | first4 = Y. | last5 = Leon | first5 = M. | last6 = Silverman | first6 = JF. | title = Critical values in cytology. | journal = Diagn Cytopathol | volume = 34 | issue = 6 | pages = 447-51 | month = Jun | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1002/dc.20443 | PMID = 16680772 }}</ref> | |||
*Unexpected malignancy - vast majority of cases. | |||
*Microorganisms in non-gynecologic specimens and FNA specimens. | |||
===Surgical pathology=== | |||
The following is primarily constructed from a list in Pereira ''et al.''<ref name=pmid15323136>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pereira | first1 = TC. | last2 = Liu | first2 = Y. | last3 = Silverman | first3 = JF. | title = Critical values in surgical pathology. | journal = Am J Clin Pathol | volume = 122 | issue = 2 | pages = 201-5 | month = Aug | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1309/7NRW-7G68-4VEP-WPMR | PMID = 15323136 }}</ref> | The following is primarily constructed from a list in Pereira ''et al.''<ref name=pmid15323136>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pereira | first1 = TC. | last2 = Liu | first2 = Y. | last3 = Silverman | first3 = JF. | title = Critical values in surgical pathology. | journal = Am J Clin Pathol | volume = 122 | issue = 2 | pages = 201-5 | month = Aug | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1309/7NRW-7G68-4VEP-WPMR | PMID = 15323136 }}</ref> | ||
===General=== | ====General==== | ||
*[[blood vessels|Large vessel]] in core biopsy specimen. | *[[blood vessels|Large vessel]] in core biopsy specimen. | ||
*Unexpected malignant diagnosis. | *Unexpected malignant diagnosis. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
**Malignancy causing superior vena cava syndrome. | **Malignancy causing superior vena cava syndrome. | ||
=== | ====Gynecologic==== | ||
*D&C on pregnant individual (or specimen labelled "[[products of conception]]") without [[chorionic villi]] or trophoblasts. | |||
* | |||
*[[Fat on endometrial biopsy]]. | *[[Fat on endometrial biopsy]]. | ||
*Fat on endocervical canal sampling. | *Fat on endocervical canal sampling. | ||
===Diagnostic of infection=== | ====Diagnostic of infection==== | ||
*Fungal. | *Fungal. | ||
*Microbacterial. | *Microbacterial. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 33: | ||
*Viral. | *Viral. | ||
===Suggestive of infection=== | ====Suggestive of infection==== | ||
*Necrotic [[granulomas]]. | *Necrotic [[granulomas]]. | ||
===Cardiac=== | ====Cardiac==== | ||
*Mesothelial cells in heart muscle biopsy. | *Mesothelial cells in heart muscle biopsy. | ||
===Transplant related=== | ====Transplant related==== | ||
*Transplant rejection. | *Transplant rejection. | ||
===Medical diseases=== | ====Medical diseases==== | ||
*Vasculitis. | *[[Vasculitis]]. | ||
====Renal==== | |||
*[[Glomerular crescents|Crescents]] in kidney biopsy. | |||
==List of diagnoses that should be reviewed== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''review diagnoses''. | |||
Review diagnoses are diagnoses that have significant treatment implications, and often mandate the opinion of a second pathologist and/or a sub-specialist. There is no general consensus around which diagnoses require review. | |||
=== | Examples of diagnoses that are high impact and are frequently reviewed: | ||
* | *[[Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus|High grade columnar esophageal dysplasia]].<ref name=pmid9189080>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wright | first1 = TA. | title = High-grade dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus. | journal = Br J Surg | volume = 84 | issue = 6 | pages = 760-6 | month = Jun | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9189080 }}</ref> | ||
*[[urothelial carcinoma|Muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder]].<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Coblentz | first1 = TR. | last2 = Mills | first2 = SE. | last3 = Theodorescu | first3 = D. | title = Impact of second opinion pathology in the definitive management of patients with bladder carcinoma. | journal = Cancer | volume = 91 | issue = 7 | pages = 1284-90 | month = Apr | year = 2001 | doi = | PMID = 11283928 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Basics]]. | *[[Basics]]. | ||
*[[Quality]]. | *[[Quality]]. | ||
*[[Diagnosis]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:09, 4 November 2015
Critical values is a concept which comes to anatomical pathology from clinical pathology.[1]
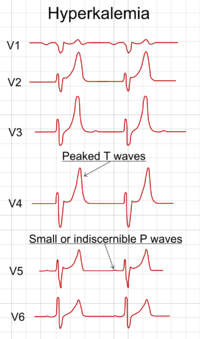
In the context of surgical pathology, it is, perhaps more appropriately, called critical diagnosis.
The general consensus is that these findings (critical valves, critical diagnoses) require a phone call and/or discussion with the clinician to ensure the situation is managed appropriately in a timely manner.[2]
List of critical diagnoses
Cytology
Critical diagnoses as per Pereira et al.:[2]
- Unexpected malignancy - vast majority of cases.
- Microorganisms in non-gynecologic specimens and FNA specimens.
Surgical pathology
The following is primarily constructed from a list in Pereira et al.[3]
General
- Large vessel in core biopsy specimen.
- Unexpected malignant diagnosis.
- Malignant diagnosis in the context of a medical emergency:
- Neoplasm causing paralysis.
- Malignancy causing superior vena cava syndrome.
Gynecologic
- D&C on pregnant individual (or specimen labelled "products of conception") without chorionic villi or trophoblasts.
- Fat on endometrial biopsy.
- Fat on endocervical canal sampling.
Diagnostic of infection
- Fungal.
- Microbacterial.
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
Suggestive of infection
- Necrotic granulomas.
Cardiac
- Mesothelial cells in heart muscle biopsy.
- Transplant rejection.
Medical diseases
Renal
- Crescents in kidney biopsy.
List of diagnoses that should be reviewed
- AKA review diagnoses.
Review diagnoses are diagnoses that have significant treatment implications, and often mandate the opinion of a second pathologist and/or a sub-specialist. There is no general consensus around which diagnoses require review.
Examples of diagnoses that are high impact and are frequently reviewed:
See also
References
- ↑ Allen TC (May 2007). "Critical values in anatomic pathology?". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 131 (5): 684–7. PMID 17491125. http://arpa.allenpress.com/arpaonline/?request=get-document&issn=0003-9985&volume=131&issue=5&page=684.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Pereira, TC.; Clayton, AC.; Tazelaar, HD.; Liu, Y.; Leon, M.; Silverman, JF. (Jun 2006). "Critical values in cytology.". Diagn Cytopathol 34 (6): 447-51. doi:10.1002/dc.20443. PMID 16680772.
- ↑ Pereira, TC.; Liu, Y.; Silverman, JF. (Aug 2004). "Critical values in surgical pathology.". Am J Clin Pathol 122 (2): 201-5. doi:10.1309/7NRW-7G68-4VEP-WPMR. PMID 15323136.
- ↑ Wright, TA. (Jun 1997). "High-grade dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus.". Br J Surg 84 (6): 760-6. PMID 9189080.
- ↑ Coblentz, TR.; Mills, SE.; Theodorescu, D. (Apr 2001). "Impact of second opinion pathology in the definitive management of patients with bladder carcinoma.". Cancer 91 (7): 1284-90. PMID 11283928.