Difference between revisions of "Chiari malformation"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (histology in chiari (mostly type II)) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
*Chiari type I - tonsils herniated<ref>URL: [http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Disease.aspx?diseaseID=9230 http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Disease.aspx?diseaseID=9230]. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.</ref> (radiologic definition: 4-6 mm below the plane of the foramen magnum). | *Chiari type I - tonsils herniated<ref>URL: [http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Disease.aspx?diseaseID=9230 http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Disease.aspx?diseaseID=9230]. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.</ref> (radiologic definition: 4-6 mm below the plane of the foramen magnum). | ||
**Associated with: sudden death,<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhang | first1 = J. | last2 = Shao | first2 = Y. | last3 = Qin | first3 = Z. | last4 = Liu | first4 = N. | last5 = Zou | first5 = D. | last6 = Huang | first6 = P. | last7 = Chen | first7 = Y. | title = Sudden Unexpected Death due to Chiari Type I Malformation in a Road Accident Case. | journal = J Forensic Sci | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/1556-4029.12051 | PMID = 23278920 }}</ref> sleep apnea, cerebellar ataxia. | **Associated with: sudden death,<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zhang | first1 = J. | last2 = Shao | first2 = Y. | last3 = Qin | first3 = Z. | last4 = Liu | first4 = N. | last5 = Zou | first5 = D. | last6 = Huang | first6 = P. | last7 = Chen | first7 = Y. | title = Sudden Unexpected Death due to Chiari Type I Malformation in a Road Accident Case. | journal = J Forensic Sci | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Dec | year = 2012 | doi = 10.1111/1556-4029.12051 | PMID = 23278920 }}</ref> sleep apnea, cerebellar ataxia. | ||
*Chiari type II - often assoc. with hydrocephaly at birth. | *Chiari type II - often assoc. with hydrocephaly at birth. Often associated with [[myelomeningocele]]. | ||
*Chiari type III - cerebellum + brain stem herniate through foramen magnum +/- encephalocele.<ref>URL: [http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm]. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.</ref> | *Chiari type III - cerebellum + brain stem herniate through foramen magnum +/- encephalocele.<ref>URL: [http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm]. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.</ref> | ||
*Chiari type IV - cerebellar hypoplasia or no cerebellum. | *Chiari type IV - cerebellar hypoplasia or no cerebellum. | ||
==Histology== | |||
Surgery depends on clinical symptoms due to CSF obstructions. Specimens may include: <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Piatt | first1 = JH. | last2 = D'Agostino | first2 = A. | title = The Chiari II malformation: lesions discovered within the fourth ventricle. | journal = Pediatr Neurosurg | volume = 30 | issue = 2 | pages = 79-85 | month = Feb | year = 1999 | doi = 28767 | PMID = 10325563 }}</ref> | |||
* Vertebral bone (decompression) | |||
* Hermiated cerebellar tonsils. | |||
* Reactive / dysplastic [[choroid plexus]]. | |||
* Glial nodules. | |||
* Arachnoidal cysts. | |||
* [[Subependymoma]]s. | |||
In cases with [[myelomeningocele]] at autopsy, the posterior fossa should be examined. | |||
==Images== | |||
<gallery> | |||
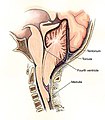
File:Chiari2.jpg|Schematic display of Chiari type II malformation. | |||
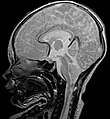
File:Chiari-Malformation_MRT_T2_sag.jpg | Radiology of Chiari type II. | |||
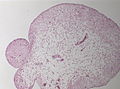
File:Hypertrophic_plexus_chiari_II_low_mag.jpg | Hypertrophic plexus choroideus in Chiari type II (low mag). | |||
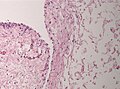
File:Hypertrophic_plexus_chiari_II_intermed_mag.jpg | Fibrous tissue within a hypertrophic plexus choroideus in Chiari type II (intermed mag). | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:12, 16 September 2015
Chiari malformation is a developmental abnormality of the brain.
General
- Usually a radiologic diagnosis.
- May be seen in a fetal autopsy.
Clinical:[1]
- Headaches, occipital.
- Dizziness.
- Nocturnal respiratory abnormalities.
Classification
Numbered from least severe to most severe:
- Chiari type I - tonsils herniated[2] (radiologic definition: 4-6 mm below the plane of the foramen magnum).
- Associated with: sudden death,[3] sleep apnea, cerebellar ataxia.
- Chiari type II - often assoc. with hydrocephaly at birth. Often associated with myelomeningocele.
- Chiari type III - cerebellum + brain stem herniate through foramen magnum +/- encephalocele.[4]
- Chiari type IV - cerebellar hypoplasia or no cerebellum.
Histology
Surgery depends on clinical symptoms due to CSF obstructions. Specimens may include: [5]
- Vertebral bone (decompression)
- Hermiated cerebellar tonsils.
- Reactive / dysplastic choroid plexus.
- Glial nodules.
- Arachnoidal cysts.
- Subependymomas.
In cases with myelomeningocele at autopsy, the posterior fossa should be examined.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Ferré Masó, A.; Poca, MA.; de la Calzada, MD.; Solana, E.; Romero Tomás, O.; Sahuquillo, J. (Mar 2011). "Sleep disturbance: a forgotten syndrome in patients with Chiari I malformation.". Neurologia. doi:10.1016/j.nrl.2011.01.008. PMID 21420201.
- ↑ URL: http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Disease.aspx?diseaseID=9230. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.
- ↑ Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, N.; Zou, D.; Huang, P.; Chen, Y. (Dec 2012). "Sudden Unexpected Death due to Chiari Type I Malformation in a Road Accident Case.". J Forensic Sci. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.12051. PMID 23278920.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm. Accessed on: 6 May 2011.
- ↑ Piatt, JH.; D'Agostino, A. (Feb 1999). "The Chiari II malformation: lesions discovered within the fourth ventricle.". Pediatr Neurosurg 30 (2): 79-85. doi:28767. PMID 10325563.