Littoral cell angioma
| Littoral cell angioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
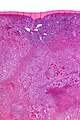
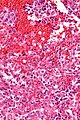
 Littoral cell angioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | anastoming, small vascular channels, cystic spaces - may have papillary projections |
| LM DDx | hemangioendothelioma, angiosarcoma, hemangiopericytoma, splenic hamartoma |
| IHC | lining cells: CD68 +ve, CD31 +ve, CD34 -ve, CD8 -ve |
| Site | spleen |
|
| |
| Clinical history | weight loss |
| Signs | pyrexia (fever), splenomegaly |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Radiology | solitary hypodense lesion |
| Prognosis | benign |
Littoral cell angioma, abbreviated LCA, is an uncommon benign vascular lesion of the spleen.
Angioma, in general, is dealt with in vascular malformations.
General
Features:[1]
- Rare.
- Benign.
- Pyrexia (fever), splenomegaly, weight loss, solitary hypodense lesion on imaging.
Note:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Anastoming, small vascular channels.
- Cystic spaces.
- May have papillary projections.[2]
DDx:[1]
- Vascular lesions:
Images
www:
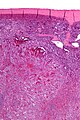
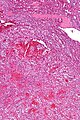
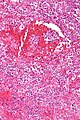
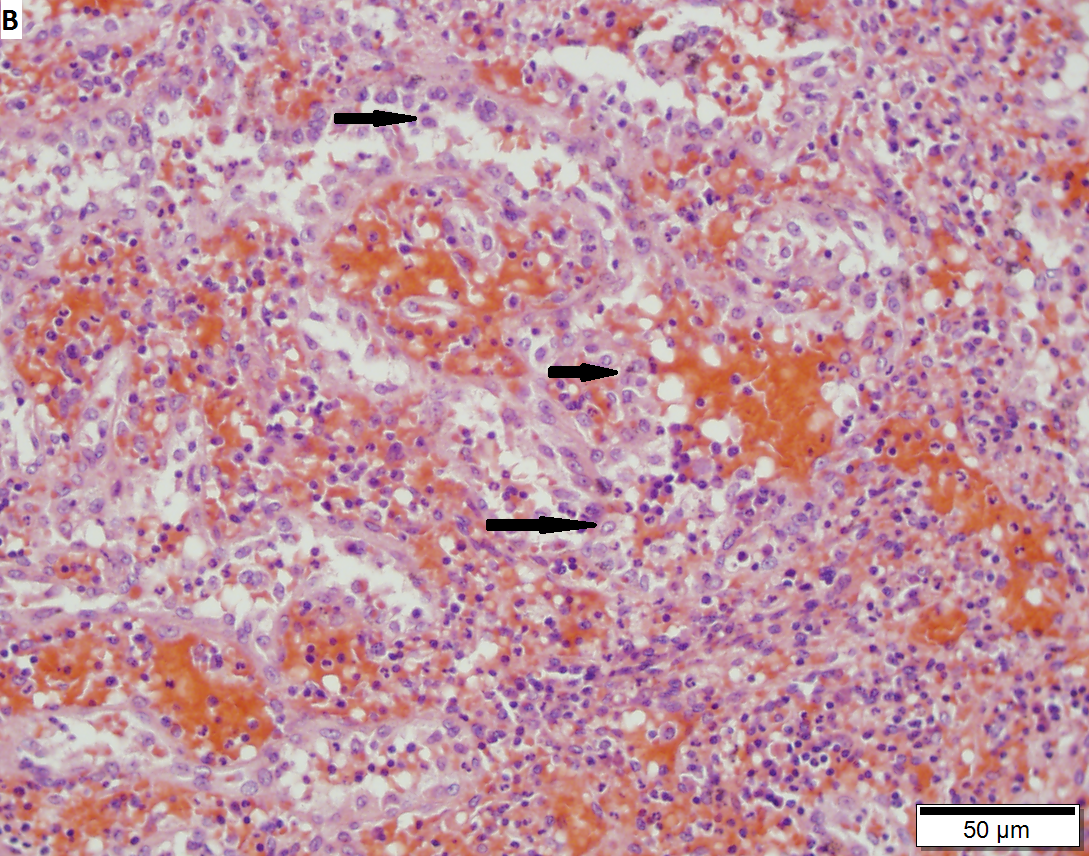
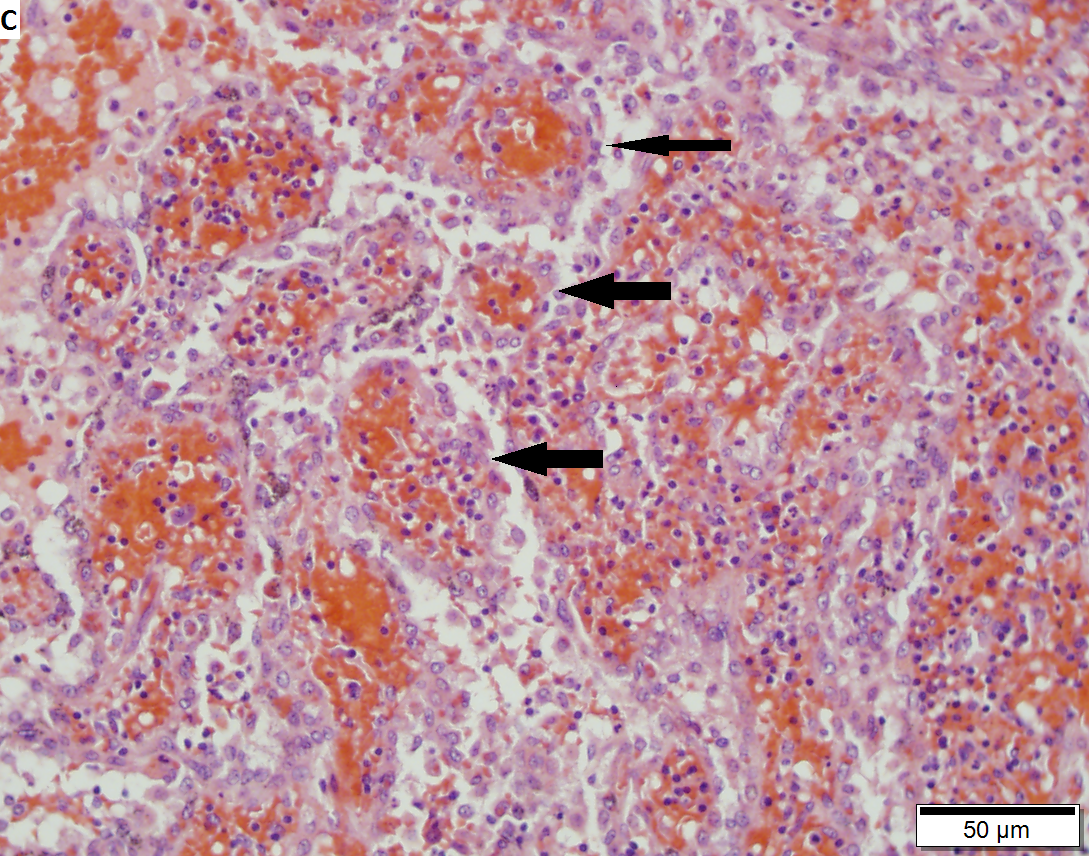
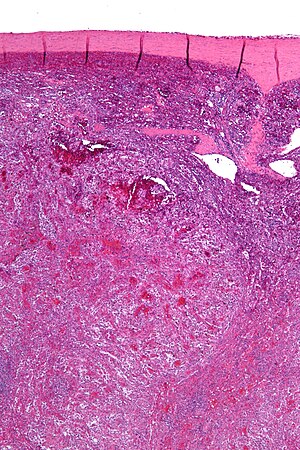
Littorral cell angioma of spleen. A. Multiple irregular cysts and proliferated erythrocyte filled vessels. B. Plump lesional cells form the lining and are seen to lie within vascular lumens (arrows). C. Small papillae (arrows) appear to form. D. High power view shows them to be vascular lining cells, sometimes even columnar; they are enlarged endothelial cells positive for CD31, CD163, and CD68. Note the presence also of macrophages, some with hemosiderin pigment.
IHC
Normal littoral cells express CD8+, macrophage/histiocytic markers and vascular markers. In comparison, littoral cell angioma is:[1]
- CD68 +ve (and other histiocytic markers)
- CD31 +ve (and other vascular markers, e.g. Factor VIII, but not CD34)
- CD34 -ve (normally in red pulp).[1]
- CD8 -ve (normally in red pulp).[1]
- CD21 +ve (at least focally)
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Tan, YM.; Chuah, KL.; Wong, WK. (Jul 2004). "Littoral cell angioma of the spleen.". Ann Acad Med Singapore 33 (4): 524-6. PMID 15329769. http://www.annals.edu.sg/pdf200408/V33N4p524.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dascalescu, CM.; Wendum, D.; Gorin, NC. (Sep 2001). "Littoral-cell angioma as a cause of splenomegaly.". N Engl J Med 345 (10): 772-3. doi:10.1056/NEJM200109063451016. PMID 11547761. http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM200109063451016.
- ↑ URL: http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/littoral. Accessed on: 24 July 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/littoral. Accessed on: 24 July 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=2&Case=382. Accessed on: 11 April 2014.