Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, abbreviated EHE, is rare malignant vascular tumour.
| Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
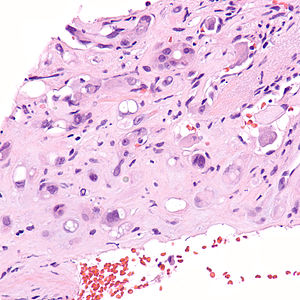 Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large epithelioid perivascular cells with abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and cytoplasmic vacuolation ("blister cells") - may form lumen and have RBC within, vesicular nucleus +/-prominent nucleolus; tuft-like projections into capillaries; cells may be in well-circumscribed paucicellular nodules or poorly formed cellular aggregates |
| LM DDx | epithelioid angiosarcoma, hemangioma |
| IHC | CD31 +ve, CD34 +ve, factor VIII +ve |
| Site | soft tissue - see vascular tumours |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
It should not be confused with epithelioid hemangioma.
General
- Malignant.[1]
- Adults - wide age range.
- Associated with oral contraceptives, vinyl chloride.[2]
- Rare - no standardized treatment.[3]
Prognosis - liver:
- ~55% five-year survival.[4]
- Better than other liver tumours.
Gross
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Large epithelioid perivascular cells with:
- Abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasmic vacuolation (some cells) - AKA "blister cells" - key feature.
- May form lumen and have RBC within.
- Vesicular nucleus with prominent nucleolus in some cells.
- Tuft-like projections into capillaries.
- Tumour cells may be in well-circumscribed paucicellular nodules or more cellular poorly formed aggregates.
DDx:[6]
- Angiosarcoma, epithelioid.
- Hemangioma.
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
- Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[2]
- CD31 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 603. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Gupta, R.; Mathur, SR.; Gupta, SD.; Durgapal, P.; Iyer, VK.; Das, CJ.; Shalimar, SK.; Acharya, . (2010). "Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A diagnostic pitfall in aspiration cytology.". Cytojournal 6: 25. doi:10.4103/1742-6413.58951. PMID 20165548.
- ↑ Chevreau, C.; Le Cesne, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Italiano, A.; Cioffi, A.; Isambert, N.; Robin, YM.; Fournier, C. et al. (Jul 2013). "Sorafenib in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a phase 2 study by the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO).". Cancer 119 (14): 2639-44. doi:10.1002/cncr.28109. PMID 23589078.
- ↑ Läuffer, JM.; Zimmermann, A.; Krähenbühl, L.; Triller, J.; Baer, HU. (Dec 1996). "Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver. A rare hepatic tumor.". Cancer 78 (11): 2318-27. PMID 8941001.
- ↑ Cardinal, J.; de Vera, ME.; Marsh, JW.; Steel, JL.; Geller, DA.; Fontes, P.; Nalesnik, M.; Gamblin, TC. (Nov 2009). "Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-institution experience with 25 cases.". Arch Surg 144 (11): 1035-9. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2009.121. PMID 19917940.
- ↑ Cardinal, J.; de Vera, ME.; Marsh, JW.; Steel, JL.; Geller, DA.; Fontes, P.; Nalesnik, M.; Gamblin, TC. (Nov 2009). "Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-institution experience with 25 cases.". Arch Surg 144 (11): 1035-9. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2009.121. PMID 19917940.