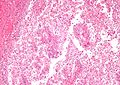
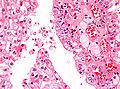
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Papillary renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated PRCC, PaRCC and papillary RCC, is the second most common type of renal cell carcinoma.
General
- Often subclassified[1] into type 1 and type 2 -- see microscopic.
- Type 1 and Type 2 are different on a cytogenetic and molecular basis.[2]
Epidemiology
- Associated with acquired renal cystic disease.[3]
- May be familial.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Cuboidal or low columnar cell in papillae.
- Interstitial foam cells in vascular cores - key feature.[5]
- Most sensitive and specific feature of PRCC.[6]
- Highly vascular.
Size criterion:
- Papillary lesions must be >0.5 cm to be called carcinoma; smaller lesions (<=0.5 cm) are called papillary adenomas.[7]
Mnemonic HIP: highly vascular, interstitial foam cells, papillae.
DDx:
- Clear cell RCC.
- Papillary: +histiocytes, +intracellular hemosiderin, CK7+.
- Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Metanephric adenoma - esp. solid PRCC type 1.
- Collecting duct carcinoma - esp. PRCC type 2.
- Renal papillary adenoma.
Images
Histological subtyping
Subtypes:[1]
- Type 1 - single layer of cells on basement membrane.
- usually low grade nuclear features, i.e. low Fuhrman grade.
- Type 2 - pseudostratification of cells.
- Usually high grade nuclear features, i.e. high Fuhrman grade.
Others:
- Oncocytic - oncocytic cytoplasm.
- Extremely rare ~ largest series is 12 cases.[8]
IHC
Features:[1]
- AMACR +ve.[9]
- HMWCK (34betaE12) +ve.
- Panker (AE1/AE3) +ve.
- CK7 +ve ~90% of type 1, 20% of type 2.
More reading:
Molecular
Features:[10]
- Sporadic: trisomies 7, 16, 17.
- Familial: trisomy 7.
- Chromosome 7 = location of MET gene.
Note:
- Not used for diagnosis.[11]
Sign out
KIDNEY, RIGHT, NEPHRECTOMY: - PAPILLARY RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, ONCOCYTIC -- SEE COMMENT; - FUHRMANN GRADE 2; - SURGICAL MARGINS NEGATIVE; - PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY. COMMENT: The oncocytic variant of papillary renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is uncommon and not widely recognized as a subtype of papillary RCC. The prognostic significance of the oncocytic cytoplasm is uncertain.[1] The histomorphology in this case is compatible with a type 1 papillary RCC. 1. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2006 Jun;10(3):133-9.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 289. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Klatte, T.; Pantuck, AJ.; Said, JW.; Seligson, DB.; Rao, NP.; LaRochelle, JC.; Shuch, B.; Zisman, A. et al. (Feb 2009). "Cytogenetic and molecular tumor profiling for type 1 and type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma.". Clin Cancer Res 15 (4): 1162-9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1229. PMID 19228721.
- ↑ Fogo, Agnes B.; Kashgarian, Michael (2005). Diagnostic Atlas of Renal Pathology: A Companion to Brenner and Rector's The Kidney 7E (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 438. ISBN 978-1416028710.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1017-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ ALS Feb 9, 2009.
- ↑ Granter SR, Perez-Atayde AR, Renshaw AA (October 1998). <303::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-7 "Cytologic analysis of papillary renal cell carcinoma". Cancer 84 (5): 303?8. PMID 9801205. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19981025)84:5<303::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-7.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 288. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B. (Jun 2009). "Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 22 Suppl 2: S2-S23. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.70. PMID 19494850.
- ↑ ALS Feb 9, 2009.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1016. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 292. ISBN 978-0781765275.