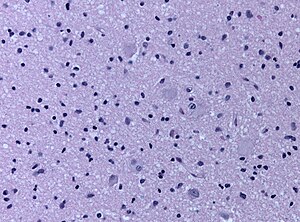
Cortical tuber
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cortical tubers are malformative lesions in the CNS observed in tuberous sclerosis complex (abbreviated TSC), an autosomal dominant syndrome.
General
- Cortical tubers are malformative, epilepsy-associated.[1]
- Seen in 80-90% of the TSC cases.
- Gyrus is usu. thickened, raised, and occasionally dimpled.
- Giant cells, dysmorphic neurons, gliosis, calcifications.
- Prominent cell loss in all cortical layers.[2]
- Normal cortical lamination is lost in the lesion.
- TSC2 has larger and more numerous tubers.[3]
IHC
- Ballon cells are Vim+ve, MAP2+ve, Nestin+ve, GFAP+/-ve, NeuN+/-ve.
Imaging
Examples on Radiopedia [[1]]
DDx
- Focal cortical dysplasia ILAE type IIB (Tubers are usu. multifocal).
See also
References
- ↑ Cotter, JA. (Apr 2019). "An update on the central nervous system manifestations of tuberous sclerosis complex.". Acta Neuropathol. doi:10.1007/s00401-019-02003-1. PMID 30976976.
- ↑ Mühlebner, A.; Iyer, AM.; van Scheppingen, J.; Anink, JJ.; Jansen, FE.; Veersema, TJ.; Braun, KP.; Spliet, WG. et al. (2016). "Specific pattern of maturation and differentiation in the formation of cortical tubers in tuberous sclerosis omplex (TSC): evidence from layer-specific marker expression.". J Neurodev Disord 8: 9. doi:10.1186/s11689-016-9142-0. PMID 27042238.
- ↑ Overwater, IE.; Swenker, R.; van der Ende, EL.; Hanemaayer, KB.; Hoogeveen-Westerveld, M.; van Eeghen, AM.; Lequin, MH.; van den Ouweland, AM. et al. (12 2016). "Genotype and brain pathology phenotype in children with tuberous sclerosis complex.". Eur J Hum Genet 24 (12): 1688-1695. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2016.85. PMID 27406250.