Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, abbreviated SNUC, is a rare epithelial malignancy of the head and neck.
| Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
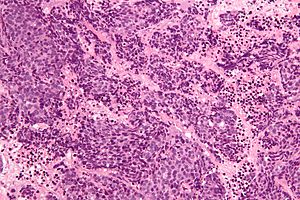 SNUC. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | tumour with variable architecture (nested, trabecular or lobular), small-to-moderate cytoplasm, +/-distinct nucleoli, cell size variable (small to large); glandular and squamous differentiation are absent by definition |
| LM DDx | poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, small cell carcinoma, SMARCB1-deficient sinonasal carcinoma, others |
| IHC | pankeratin +ve, EMA +ve, CK7 +ve, CK5/6 -ve, NSE +ve/-ve, chromogranin A -ve, synaptophysin -ve, p63 +ve/-ve |
| Site | head and neck |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other head and neck tumours |
General
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Architecture: nested, trabecular or lobular.
- Distinct cellular borders.
- Small-to-moderate cytoplasm.
- +/-Distinct nucleoli.
- Tumour cell size variable (small to large).
Note:
- Glandular and squamous differentiation are absent by definition.[4]
DDx:
- Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
- Small cell carcinoma.
- SMARCB1-deficient sinonasal carcinoma.[5]
- Other tumours, especially small round blue cell tumours and lymphoma.
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[3]
Others:
- NSE +ve/-ve.
- Chromogranin A -ve.
- Synaptophysin -ve.
- p63 +ve/-ve.[6]
- SMARCB1 (INI1) +ve (nuclear staining present).
- Nuclear staining lost in SMARCB1-deficient sinonasal carcinoma.
See also
References
- ↑ Pitman, KT.; Costantino, PD.; Lassen, LF. (1995). "Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: current trends in treatment.". Skull Base Surg 5 (4): 269-72. PMC 1656535. PMID 17170968. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1656535/.
- ↑ Al-Mamgani, A.; van Rooij, P.; Mehilal, R.; Tans, L.; Levendag, PC. (Apr 2012). "Combined-modality treatment improved outcome in sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: single-institutional experience of 21 patients and review of the literature.". Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. doi:10.1007/s00405-012-2008-5. PMID 22476411.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 38. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mills, SE. (Mar 2002). "Neuroectodermal neoplasms of the head and neck with emphasis on neuroendocrine carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 15 (3): 264-78. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880522. PMID 11904342.
- ↑ Bishop, JA.; Antonescu, CR.; Westra, WH. (Sep 2014). "SMARCB1 (INI-1)-deficient carcinomas of the sinonasal tract.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (9): 1282-9. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000285. PMID 25007146.
- ↑ Wadsworth, B.; Bumpous, JM.; Martin, AW.; Nowacki, MR.; Jenson, AB.; Farghaly, H. (Dec 2011). "Expression of p16 in sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma (SNUC) without associated human papillomavirus (HPV).". Head Neck Pathol 5 (4): 349-54. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0285-8. PMC 3210220. PMID 21805120. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3210220/.