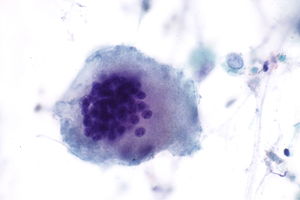
Giant cells
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Giant cells are "big" cells with multiple nuclei. They come in different flavours, which are suggestive of causality.
This article deals with the classic types of giant cells. A more general differential diagnosis of giant cells is in giant cell lesions.
Giant cell types
List:
- Touton giant cell.
- Osteoclast-like giant cell.
- Foreign body type giant cell.
Table
| Type | Histology | DDx | Other | Image |
| Touton giant cell | Nuclei form a ring around the cell periphery with eosinophilic cytoplasm centrally and foamy cytoplasm at the periphery. | Juvenile xanthogranuloma, xanthoma, Erdheim-Chester disease, fat necrosis, dermatofibroma | High lipid content lesions[1], Named after Karl Touton | |
| Epithelioid type | scattered nuclei[2] | drug reaction, neoplasm, foreign body, infection, idiopathic, autoimmune, allergic | granulomatous inflammation | |
| Langhans giant cell | peripheral eccentric nuclei[2] | tuberculosis, sarcoidosis. | not to be confused with Langerhans cells | |
| Osteoclast-like giant cells | round nuclei | osteoclasts, others | AKA osteoclast-type giant cells |
See also
- Basics.
- Giant cell lesions - includes a DDx of lesions with giant cells.
- Histiocytoses.
References
- ↑ URL: http://granuloma.homestead.com/giant_cells.html. Accessed on: 7 February 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Borley, Neil R.; Warren, Bryan F. (2007). Instant Pathology (1st ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 7. ISBN 978-1405132909.