Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma, abbreviated FDCS, is a very rare malignant tumour.
| Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
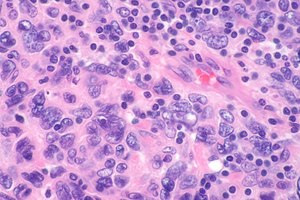 Micrograph showing a follicular dendritic cell sarcoma. The (benign) interspersed lymphocytes are a characteristic finding. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | follicular dendritic cell tumour, follicular dendritic cell neoplasm |
|
| |
| LM | oval or spindle-shaped cellular & nuclear morphology, variable architecture (sheets, fascicles, whorles, storiform pattern), nuclei with small nucleoli and clear or dispersed chromatin, multinucleated cells, interspersed small lymphocytes, +/-necrosis, +/-marked nuclear atypia, +/-abundant mitoses. |
| LM DDx | histiocytic sarcoma, thymoma, other spindle cell lesions |
| IHC | CD21 +ve, CD35 +ve, Ki-M4p +ve, Ki-FDRC1p +ve, vimentin +ve |
| Associated Dx | Castleman disease, hyaline-vascular type |
| Prevalence | very rare |
| Treatment | excision |
It is also known as follicular dendritic cell tumour (abbreviated FDCT),[1] and follicular dendritic cell neoplasm.[2]
General
- Very rare.
- Behave like a low-grade sarcoma.[3]
- Reported association with Castleman disease (hyaline-vascular type).[3]
WHO 2001 classification of dendritic cell neoplasms:[4]
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
- Langerhans cell sarcoma.
- Interdigitating dendritic cell sarcoma/tumour.
- Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma/tumour.
- Dendritic cell sarcoma, not specified otherwise.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Oval or spindle-shaped cellular & nuclear morphology.
- Variable architecture (sheets, fascicles, whorles, storiform pattern).
- Nuclei:
- Small nucleoli.
- Clear or dispersed chromatin.
- Multinucleated cells.
- Interspersed small lymphocytes - distinctive feature.
- +/-Necrosis.
- +/-Marked nuclear atypia.
- +/-Abundant mitoses.
DDx:
Images
IHC
Features:[3]
- CD21 +ve.
- CD35 +ve.
- Ki-M4p +ve
- Ki-FDRC1p +ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
- S-100 +ve/-ve.
- Muscle-specific actin +ve/-ve.
- EMA +ve/-ve.
Additional stains:[7]
- CD23 +ve.
- D2-40 +ve.
Note:
- The interspersed lymphocytes at B cells.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Leipsic, JA.; McAdams, HP.; Sporn, TA. (Jun 2007). "Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma of the mediastinum.". AJR Am J Roentgenol 188 (6): W554-6. doi:10.2214/AJR.04.1530. PMID 17515347.
- ↑ Denning, KL.; Olson, PR.; Maley, RH.; Flati, VR.; Myers, JL.; Silverman, JF. (Apr 2009). "Primary pulmonary follicular dendritic cell neoplasm: a case report and review of the literature.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 133 (4): 643-7. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-133.4.643. PMID 19391666.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Perez-Ordoñez, B.; Rosai, J. (May 1998). "Follicular dendritic cell tumor: review of the entity.". Semin Diagn Pathol 15 (2): 144-54. PMID 9606805.
- ↑ Kairouz, S.; Hashash, J.; Kabbara, W.; McHayleh, W.; Tabbara, IA. (Oct 2007). "Dendritic cell neoplasms: an overview.". Am J Hematol 82 (10): 924-8. doi:10.1002/ajh.20857. PMID 17636477.
- ↑ Alexiev, BA.; Sailey, CJ.; McClure, SA.; Ord, RA.; Zhao, XF.; Papadimitriou, JC. (2007). "Primary histiocytic sarcoma arising in the head and neck with predominant spindle cell component.". Diagn Pathol 2: 7. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-2-7. PMID 17324277. http://www.diagnosticpathology.org/content/2/1/7.
- ↑ URL: http://www.npplweb.com/wjsmro/fulltext/2/1. Accessed on: September 13, 2014.
- ↑ Yin, WH.; Yu, GY.; Ma, Y.; Rao, HL.; Lin, SX.; Shao, CK.; Liang, Q.; Guo, N. et al. (Aug 2010). "[Follicular dendritic cell sarcoma: a clinicopathologic analysis of ten cases].". Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 39 (8): 522-7. PMID 21055030.
- ↑ Lorenzi, L.; Lonardi, S.; Petrilli, G.; Tanda, F.; Bella, M.; Laurino, L.; Rossi, G.; Facchetti, F. (Feb 2012). "Folliculocentric B-cell-rich follicular dendritic cells sarcoma: a hitherto unreported morphological variant mimicking lymphoproliferative disorders.". Hum Pathol 43 (2): 209-15. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2011.02.029. PMID 21835430.