Salivary duct carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Salivary duct carcinoma, abbreviated SDC, is a rare salivary gland tumour that typically has an aggressive course.
| Salivary duct carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
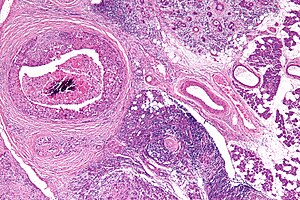 Salivary duct carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | varied arch. (sheets, nests, cords, cribriform, micropapillary), neoplastic cells line-up around cystic spaces "Roman bridges", nuclear atypia, apocrine snouts, decapitation secretions |
| LM DDx | carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma with SDC component, ductal carcinoma of the breast |
| IHC | LMWK, EMA, CK7, CK19 +ve, AR +ve, BRST2 (GCDFP-15) +ve, HER2 -ve/+ve, p63 -ve |
| Site | salivary gland - usu. parotid gland |
|
| |
| Clinical history | typically male, usu. >50 years old |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other salivary gland tumours |
General
- Malignant counterpart of salivary duct adenoma.
- Male:female ~= 4:1.
- Dismal prognosis.[1]
- Typically >50 years old.
- Mostly in the parotid.
Microscopic
Features - resembles ductal breast carcinoma:[1]
- Architecture: sheets, nests, cords, cribriform, micropapillary.
- Neoplastic cells line-up around cystic spaces "Roman bridges".
- Nuclear atypia (variation in size, shape, staining).
- Apocrine snouts - pseudopod-like/lollipop-like undulations of the cell membrane.
- Decapitation secretions - apocrine snouts (membrane bound blobs of cytoplasm) that have separated from its mother cell.
Notes:
- Similar to ductal breast carcinoma - key to remember.
DDx:
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma with SDC component.
Images
www:
Subtypes
- Conventional.
- Mucinous - worse prognosis; opposite of what would one expect from the outcomes in breast cancer.
- Micropapillary - assoc. with a poor prognosis.
- Sarcomatoid/spindle cell.
IHC
- LMWK, EMA, CK7, CK19 +ve.
- p63 -ve.
- Androgen receptor +ve (~90% of cases).[2]
- BRST2 (GCDFP-15) +ve.
- HER2 +ve ~21%; use of trastuzumab (Herceptin) not systematically studied.
Curiosity:
- PSA +ve/-ve.
- PSAP +ve/-ve.
- ER-beta +ve.[3]
- ER-alpha -ve (the common ER stain).
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Rajesh, NG.; Prayaga, AK.; Sundaram, C.. "Salivary duct carcinoma: correlation of morphologic features by fine needle aspiration cytology and histopathology.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 54 (1): 37-41. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.77321. PMID 21393874. http://www.ijpmonline.org/text.asp?2011/54/1/37/77321.
- ↑ Fan, CY.; Wang, J.; Barnes, EL. (Apr 2000). "Expression of androgen receptor and prostatic specific markers in salivary duct carcinoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 13 cases and review of the literature.". Am J Surg Pathol 24 (4): 579-86. PMID 10757407.
- ↑ URL: http://www.cap.org/apps/docs/committees/cancer/cancer_protocols/2011/MajorSalGlands_11protocol.pdf. Accessed on: 3 April 2012.