Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia, also Masson's hemangioma,[1] is a benign vascular lesion.
| Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
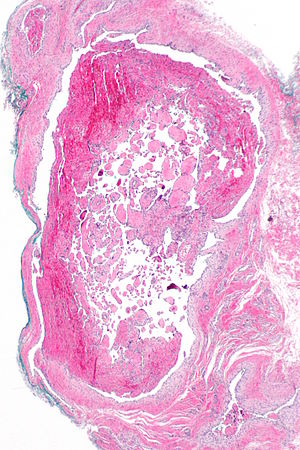 Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | Masson tumour, Masson hemangioma |
| LM DDx | Kaposi sarcoma, other hemangiomas |
| Site | blood vessel (artery) |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
It is also known as a Masson tumour.[2]
General
- Benign non-neoplastic lesion - a vessel that has thrombosed and recanalized.
- Histomorphologically may be confused with low-grade angiosarcoma or other soft tissue sarcomas.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Well-circumscribed - key (low power) feature.
- Abundant small vascular channels with benign endothelium.
- +/-Papillary formation with a fibrotic core covered by benign endothelium.[3]
Notes:
- Looks like Kaposi sarcoma at high power.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Korkolis DP, Papaevangelou M, Koulaxouzidis G, Zirganos N, Psichogiou H, Vassilopoulos PP (2005). "Intravascular papillary endothelial hyperplasia (Masson's hemangioma) presenting as a soft-tissue sarcoma". Anticancer Res. 25 (2B): 1409–12. PMID 15865098.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case544/dx.html. Accessed on: 25 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case544.html. Accessed on: 25 January 2012.