Acute duodenitis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Acute duodenitis, abbreviated AD, is an acute inflammatory process of the duodenum. It is relatively uncommon.
| Acute duodenitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
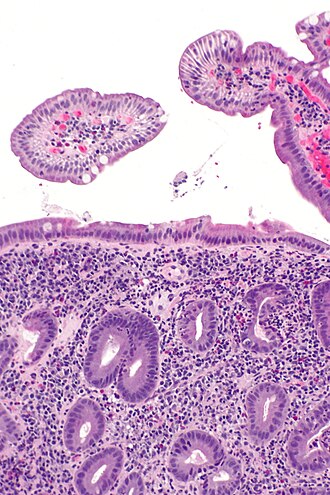 Acute duodenitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | neutrophils - "found without searching", eosinophils - "found without searching", plasma cells (increased), intraepithelial lymphocytes |
| Site | duodenum |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | Helicobacter gastritis |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Endoscopy | erythema |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
General
DDx:
- Infection.
- Medications (NSAIDs).
- Crohn's disease (usually focal/patchy).
- Portal hypertension (portal hypertensive duodenopathy).[2]
- Celiac sprue.
Microscopic
Features:
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes.
- Neutrophils - "found without searching" - key feature.
- Eosinophils - "found without searching" - key feature.
- Plasma cells (increased).
Notes:
- One needs stomach concurrent biopsies to r/o Helicobactor.
- Erosions make celiac sprue much less likely.
- Presence of chronic inflammation useful for NSAIDs vs. Helicobacter organisms:
Images
Sign out
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - ACUTE DUODENITIS.
Acute on chronic duodenitis
DUODENUM, BIOPSY: - ACUTE ON CHRONIC DUODENITIS.
Micro
The sections show small bowel mucosa with intraepithelial neutrophils. The epithelium shows nuclear hyperchromasia, pseudostratification and nuclear enlargement; however, it matures toward the surface (reactive changes of the epithelium).
Brunner's glands are found focally in the lamina propria. Gastric foveolar-type epithelium is identified. Lamina propria plasma cells are abundant.
See also
References
- ↑ Madsen, JE.; Vetvik, K.; Aase, S. (Nov 1991). "Helicobacter-associated duodenitis and gastric metaplasia in duodenal ulcer patients.". APMIS 99 (11): 997-1000. PMID 1683540.
- ↑ Shudo, R.; Yazaki, Y.; Sakurai, S.; Uenishi, H.; Yamada, H.; Sugawara, K. (Apr 2002). "Duodenal erosions, a common and distinctive feature of portal hypertensive duodenopathy.". Am J Gastroenterol 97 (4): 867-73. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05602.x. PMID 12003421.
- ↑ Taha AS, Dahill S, Nakshabendi I, Lee FD, Sturrock RD, Russell RI (September 1993). "Duodenal histology, ulceration, and Helicobacter pylori in the presence or absence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs". Gut 34 (9): 1162–6. PMC 1375446. PMID 8406146. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1375446/.
- ↑ Hashash JG, Atweh LA, Saliba T, et al. (November 2007). "Acute NSAID-related transmural duodenitis and extensive duodenal ulceration". Clin Ther 29 (11): 2448–52. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.012. PMID 18158085.