Spitz nevus
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Spitz nevus, also known as epithelioid and spindle cell nevus, is an uncommon melanocytic lesion that can be difficult to differentiate from malignant melanoma.
| Spitz nevus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
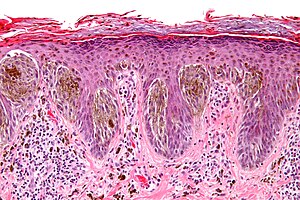 Spitz nevus. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | nests of cells (spindle, epithelioid or spindle/epithelioid) - in both dermis and epidermis - nests are vertically arranged ("hanging bananas"), +/-hyperkeratosis, +/-hypergranulosis, +/-acanthosis (thick stratum spinosum), Kamino bodies - dense eosinophilic bodies (rare in melanoma) |
| LM DDx | malignant melanoma, pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed |
| Stains | HMB-45 -ve deep aspect, Ki-67 usu. low |
| Site | skin - typically face or extremity |
|
| |
| Clinical history | children and adolescents |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | melanoma, other melanocytic lesions |
General
- May be very difficult to differentiate from melanoma.
Epidemiology:
- Children & adolescents.
Treatment:
- Complete excision.[1]
Gross
- Usually face or extremity.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Architecture:
- Nests of cells (spindle, epithelioid or spindle/epithelioid) - in both dermis and epidermis.
- Nests are vertically arranged, i.e. the long axis of the nests are perpendicular to the skin surface.
- Nest arrangement/orientation described as "cluster of bananas".
- Nests are vertically arranged, i.e. the long axis of the nests are perpendicular to the skin surface.
- Nests of cells (spindle, epithelioid or spindle/epithelioid) - in both dermis and epidermis.
- +/-Hyperkeratosis (more keratin, i.e. thick stratum corneum).
- +/-Hypergranulosis (thick stratum granulosum).
- +/-Acanthosis (thick stratum spinosum).
- Kamino bodies (also written Camino bodies) - dense eosinophilic bodies.[4]
- Apoptotic cells.
- Kamino bodies are rare in melanoma.
Notes:
- Never in the setting of solar elastosis.[5]
- If there is solar elastosis -- it's melanoma.
DDx:
- Malignant melanoma - so-called Spitzoid melanoma.
- Pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed.
Images
www:
IHC
- HMB-45 -ve at deep aspect.
- Ki-67 low.
See also
References
- ↑ Gelbard, SN.; Tripp, JM.; Marghoob, AA.; Kopf, AW.; Koenig, KL.; Kim, JY.; Bart, RS. (Aug 2002). "Management of Spitz nevi: a survey of dermatologists in the United States.". J Am Acad Dermatol 47 (2): 224-30. PMID 12140468.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 449. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 499. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Kirkwood, John M.; Jukic, Drazen; Averbook, Bruce J.; Sender, Leonard S. (October 2009). "Melanoma in Pediatric, Adolescent, and Young Adult Patients". Semin Oncol. 36 (5): 419-31. PMC 2797485. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2797485/.
- ↑ Jakubovic, H. 16 July 2010.