Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Papillary renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated PRCC, PaRCC and papillary RCC, is the second most common type of renal cell carcinoma.
| Papillary renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
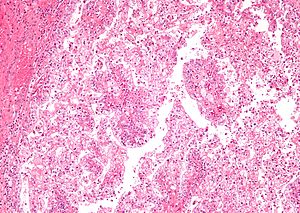 Papillary renal cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cuboidal or low columnar cells (simple or pseudostratified) on papillae, interstitial foam cells in the vascular cores |
| Subtypes | type 1, type 2, eosinophilic variant |
| LM DDx | clear cell renal cell carcinoma, clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma, metanephric adenoma (esp. solid PRCC type 1), collecting duct carcinoma (esp. PRCC type 2), renal papillary adenoma |
| Gross | may be multifocal, must be >0.5 cm (otherwise renal papillary adenoma) |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | acquired renal cystic disease (end-stage renal disease) |
| Prevalence | relatively common |
| Clin. DDx | other kidney tumours |
General
- Often subclassified[1] into type 1 and type 2 -- see microscopic.
- Type 1 and Type 2 are different on a cytogenetic and molecular basis.[2]
Epidemiology
- Associated with acquired renal cystic disease.[3]
- May be familial.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Cuboidal or low columnar cell in papillae.
- Interstitial foam cells in vascular cores - key feature.[5]
- Most sensitive and specific feature of PRCC.[6]
- Highly vascular.
Size criterion:
- Papillary lesions must be >0.5 cm to be called carcinoma; smaller lesions (<=0.5 cm) are called papillary adenomas.[7]
Mnemonic HIP: highly vascular, interstitial foam cells, papillae.
DDx:
- Clear cell RCC.
- Papillary: +histiocytes, +intracellular hemosiderin, CK7+.
- Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Metanephric adenoma - esp. solid PRCC type 1.
- Collecting duct carcinoma - esp. PRCC type 2.
- Renal papillary adenoma.
Images
Histological subtyping
Generally accepted subtypes:[1][8]
- Type 1 - single layer of cells on basement membrane - most important.
- Usually low grade nuclear features, i.e. low Fuhrman grade.
- Other characteristics:
- Clear cytoplasm.
- Foamy macrophages - common.
- Cells smaller.
- Type 2 - pseudostratification of cells - most important.
- Usually high grade nuclear features, i.e. high Fuhrman grade.
- Other characteristics:
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Foamy macrophages - uncommon.
- Cells larger.
Another subtype:
- Oncocytic - oncocytic cytoplasm.
- Extremely rare ~ largest series is 12 cases.[9]
IHC
Features:[1]
- AMACR +ve.[10]
- HMWCK (34betaE12) +ve.
- Panker (AE1/AE3) +ve.
- CK7 +ve ~90% of type 1, 20% of type 2.
More reading:
Type 1 versus Type 2:[11]
- CK7:
- Type 1 ~ 100%.
- Type 2 ~ 19%.
- CK19:
- Type 1 ~ 100%.
- Type 2 ~ 53%.
Metanephric adenoma vs. PaRCC type 1:[12]
- AMACR +ve.
- WT-1 -ve.
- CD57 -ve.
Molecular
Features:[13]
- Sporadic: trisomies 7, 16, 17.
- Familial: trisomy 7.
- Chromosome 7 = location of MET gene.
Note:
- Not used for diagnosis.[14]
Sign out
KIDNEY, RIGHT, NEPHRECTOMY: - PAPILLARY RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, ONCOCYTIC -- SEE COMMENT; - FUHRMANN GRADE 2; - SURGICAL MARGINS NEGATIVE; - PLEASE SEE TUMOUR SUMMARY. COMMENT: The oncocytic variant of papillary renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is uncommon and not widely recognized as a subtype of papillary RCC. The prognostic significance of the oncocytic cytoplasm is uncertain.[1] The histomorphology in this case is compatible with a type 1 papillary RCC. 1. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2006 Jun;10(3):133-9.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 289. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Klatte, T.; Pantuck, AJ.; Said, JW.; Seligson, DB.; Rao, NP.; LaRochelle, JC.; Shuch, B.; Zisman, A. et al. (Feb 2009). "Cytogenetic and molecular tumor profiling for type 1 and type 2 papillary renal cell carcinoma.". Clin Cancer Res 15 (4): 1162-9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1229. PMID 19228721.
- ↑ Fogo, Agnes B.; Kashgarian, Michael (2005). Diagnostic Atlas of Renal Pathology: A Companion to Brenner and Rector's The Kidney 7E (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 438. ISBN 978-1416028710.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1017-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ ALS Feb 9, 2009.
- ↑ Granter SR, Perez-Atayde AR, Renshaw AA (October 1998). <303::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-7 "Cytologic analysis of papillary renal cell carcinoma". Cancer 84 (5): 303?8. PMID 9801205. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19981025)84:5<303::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-7.
- ↑ Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 288. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Delahunt, B.; Eble, JN. (Jun 1997). "Papillary renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 105 tumors.". Mod Pathol 10 (6): 537-44. PMID 9195569.
- ↑ Srigley, JR.; Delahunt, B. (Jun 2009). "Uncommon and recently described renal carcinomas.". Mod Pathol 22 Suppl 2: S2-S23. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.70. PMID 19494850.
- ↑ ALS Feb 9, 2009.
- ↑ Ono, Y.; Ito, T.; Tsujino, S.; Aizawa, S.; Suzuki, M. (Jun 1997). "[A study of papillary renal cell carcinoma. Clinicopathological, immunohistochemical features and its typing].". Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 88 (6): 587-95. PMID 9234615.
- ↑ Watanabe, S.; Naganuma, H.; Shimizu, M.; Ota, S.; Murata, S.; Nihei, N.; Matsushima, J.; Mikami, S. et al. (2013). "Adult nephroblastoma with predominant epithelial component: a differential diagnostic candidate of papillary renal cell carcinoma and metanephric adenoma-report of three cases.". Case Rep Pathol 2013: 675875. doi:10.1155/2013/675875. PMID 24083046.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1016. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 292. ISBN 978-0781765275.