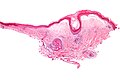
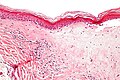
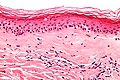
Lichen sclerosus
| Lichen sclerosus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
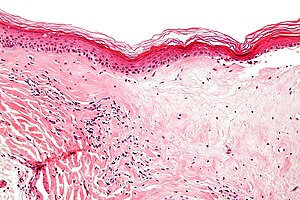 Lichen sclerosus. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | fibrosis of dermis with loss of adnexal structures - key feature, loss of the rete ridges, (severe) hyperkeratosis, inflammation - often with eosinophils |
| LM DDx | morphea profunda, differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, lichen planus, cutaneous amyloidosis |
| Site | vulva, penis |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia, vulvar squamous cell carcinoma |
| Symptoms | pruritis |
| Prognosis | chronic, benign |
| Lichen sclerosus | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 9993 |
Lichen sclerosus is a relatively common chronic condition classically associated with the vulva. On the vulva is also known as chronic atrophic vulvitis.
On the penis it is referred to as balanitis xerotica obliterans, abbreviated BXO.[1]
General
- Associated with differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia - important.
- Approximately 50% of vulvar cancer associated with lichen sclerosus.
Clinical:
- Pruritis -> leads to scratching.
- Chronic condition.
- Usu. post-menopausal women.
- May lead to labial fusion.
Treatment:
- Steroids - high dose initially, then a maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Notes:
- Mixed vulvar dystrophy = lichen sclerosus + squamous cell hyperplasia.[2]
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Loss of rete ridges.
- Severe hyperkeratosis.
- Hyperkeratosis = stratum corneum thickened.
- Fibrosis of dermis with loss of adnexal structures - key feature.
- May appear pale - directly deep to the epidermis.[4]
- Inflammation - often with eosinophils.
- May be prominent - in the inflammatory phase of the disease.[5]
DDx:
- Morphea profunda - deep fibrosis.
- Differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia - commonly co-exists with lichen sclerosus.
- Lichen planus (LP) - esp. for the inflammatory phase of lichen sclerosus.
- LP has wedge shaped hypergranulosis, lacks basilar exocytosis, no epidermal atrophy.[5]
- Cutaneous amyloidosis - classically has "cracked" appearance.
- Malignant melanoma with regression - esp. for the inflammatory phase of lichen sclerosus.
Images
www:
Sign out
VULVA, BIOPSY: - LICHEN SCLEROSUS.
FORESKIN, CIRCUMCISION: - BALANITIS XEROTICA OBLITERANS.
Micro
Inflammtory phase of lichen sclerosus
The sections show skin with a lymphoplasmacytic predominant interface dermatitis with hyperkeratosis. Spongiosis is present. Scattered inflammatory cell are found with the basal aspect of the epidermis; however, they do not form clusters. No mitotic activity is appreciated.
Focal hypergranulosis and focal parakeratosis is present. Numerous Civatte bodies are identified.
The focal hypergranulosis is not wedge-shaped. There are no pointed rete ridges. There is no basal squamatization.
Sclerotic phase of lichen sclerosus
The sections show skin with loss of the rete ridges, hyperkeratosis and marked fibrosis of the superficial dermis. Few, scattered lymphocytes are seen in the dermis.
A granular layer is present. There is no basal nuclear atypia. There is no acanthosis.
Sclerotic phase of lichen sclerosus with active inflammation
The sections show skin with loss of the rete ridges, a thin epidermis, hyperkeratosis and marked fibrosis of the superficial dermis. Numerous lymphocytes are seen scattered between the collagen fibres in the deeper aspect of the dermis.
A granular layer is present. There is no basal nuclear atypia.
See also
References
- ↑ Finkbeiner AE (January 2003). "Balanitis xerotica obliterans: a form of lichen sclerosus". South. Med. J. 96 (1): 7–8. PMID 12602704.
- ↑ Kini, U. (Jun 1997). "Squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva in association with mixed vulvar dystrophy. A brief report with review of literature.". Indian J Cancer 34 (2): 92-5. PMID 9491669.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/vulva.html#lichensclerosis. Accessed on: 19 April 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=2&Case=538. Accessed on: 25 August 2011.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Fung, MA.; LeBoit, PE. (Apr 1998). "Light microscopic criteria for the diagnosis of early vulvar lichen sclerosus: a comparison with lichen planus.". Am J Surg Pathol 22 (4): 473-8. PMID 9537476.