Rectal prolapse
| Rectal prolapse | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
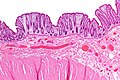
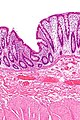
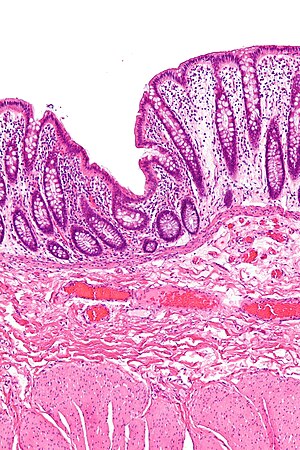 Fibromuscular hyperplasia as seen in rectal prolapse. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | fibromuscular hyperplasia: lamina propria fibrosis and lamina propria muscle, thick muscularis propria, submucosal fibrosis, +/-ischemic mucosal changes |
| Site | rectum |
|
| |
| Clinical history | women - multiparous & postmenopausal |
| Signs | "rectal mass" |
| Prevalence | not common |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | rectal carcinoma (rarely) |
| Treatment | surgery |
Rectal prolapse is a benign pathology of the rectum, typically seen in women that are multiparous and postmenopausal.
General
Epidemiology:
- ~90% women, postmenopausal and multiparous.[2]
Treatment:
- Surgical:
- Delorme procedure = mucosa stripped.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- "Fibromuscular hyperplasia" - key feature:
- Fibrosis (submucosa, lamina propria).
- Muscularis mucosae is "too superficial" (muscle in the lamina propria).
- Surface ulceration + inflammation (neutrophils).
- May show frank ischemic changes - see ischemic colitis.
- +/-Serration of epithelium at the surface.
Notes:
- Important negative: no nuclear atypia.
- May be seen if ischemic changes are present.
Images
Sign out
RECTAL MUCOSA, DELORME PROCEDURE: - SUPERFICIAL RECTAL WALL WITH FIBROMUSCULAR HYPERPLASIA AND EDEMA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The sections show rectal mucosa, submucosa and a small amount of muscularis propria. The mucosa shows fibromuscular hyperplasia with thickening of the muscularis mucosae and mild lamina propria fibrosis. The submucosa is edematous. The small amount of muscularis propria is unremarkable. The epithelium matures normally to the surface. No significant nuclear atypia is identified.
Ischemic changes present
RECTAL MUCOSA, DELORME PROCEDURE: - SUPERFICIAL RECTAL WALL WITH REACTIVE CHANGES, ISCHEMIC CHANGES AND FIBROMUSCULAR HYPERPLASIA, SEE COMMENT. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: The changes are compatible with prolapse (fibromuscular hyperplasia) and suggestive of concurrent ischemia (see microscopic). The mucosal reactive changes are marked. No definite dysplasia is identified; however, it is difficult to completely exclude. Follow-up is recommended.
Micro
The sections show superficial rectal wall with ischemic changes (focal cryptitis, marked reactive epithelial changes, erosions, capillary congestion, goblet cell paucitity, epithelium with attenuated cytoplasm) and changes compatible with prolapse (fibromuscular hyperplasia).
See also
References
- ↑ Brosens LA, Montgomery EA, Bhagavan BS, Offerhaus GJ, Giardiello FM (November 2009). "Mucosal prolapse syndrome presenting as rectal polyposis". J. Clin. Pathol. 62 (11): 1034–6. doi:10.1136/jcp.2009.067801. PMC 2853932. PMID 19861563. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2853932/.
- ↑ Lee, S.; Kye, BH.; Kim, HJ.; Cho, HM.; Kim, JG. (Feb 2012). "Delorme's Procedure for Complete Rectal Prolapse: Does It Still Have It's Own Role?". J Korean Soc Coloproctol 28 (1): 13-8. doi:10.3393/jksc.2012.28.1.13. PMID 22413077.
- ↑ Schneider A, Fritze C, Bosseckert H, Machnik G (1988). "[Primary clinical, endoscopic and histologic findings in solitary rectal ulcer]" (in German). Dtsch Z Verdau Stoffwechselkr 48 (3-4): 183–9. PMID 3234303.