Pigmented spindle cell nevus
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Pigmented spindle cell nevus | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
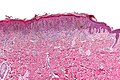
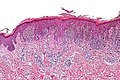
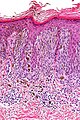
 Pigmented spindle cell nevus. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | malignant melanoma, Spitz nevus |
| Site | skin - usu. shoulder or pelvic girdle region |
|
| |
| Clinical history | classically women - teens and 20s |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good |
| Clin. DDx | other melanocytic lesions |
Pigmented spindle cell nevus, also pigmented spindle cell nevus of Reed, is an uncommon benign melanocytic lesion.
General
- Uncommon.
- Women in teens & 20s.
Gross
- Location: shoulder, pelvic girdle region.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Nests of heavily pigmented spindle cells at dermal-epidermal junction - key feature.
- Nevoid cells in epidermis & dermis - form "basket weave" pattern
- Well-circumscribed lesion.
Notes:
- No epithelioid nevus cells.
DDx:
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[2]
- Cyclin D1 ~12% of cells (range 1-40%) vs. ~42% of cells (range 1-95%).
- Ki-67 ~1% of cells (range 0-5%) vs. ~13% (range 1-40%).
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT POSTERIOR NECK, EXCISION: - PIGMENTED SPINDLE CELL NEVUS OF REED. -- COMPLETELY EXCISED (CLEARANCE ~ 1 MM).
Micro
The sections show spindled pigmented melanocytes in nests confined to the epidermis. The lesion is symmetrical in its architecture and pigment distribution. There is no pagetoid spread of melanocytes in the epidermis. No significant nuclear atypia is identified. No mitotic activity is appreciated. Melanophages are present in the superficial dermis. The lesion is completely excised in the plane of section.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 500. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Díaz, A.; Valera, A.; Carrera, C.; Hakim, S.; Aguilera, P.; García, A.; Palou, J.; Puig, S. et al. (Nov 2011). "Pigmented spindle cell nevus: clues for differentiating it from spindle cell malignant melanoma. A comprehensive survey including clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and FISH studies.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (11): 1733-42. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318229cf66. PMID 21997694.