Chronic cholecystitis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Chronic cholecystitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
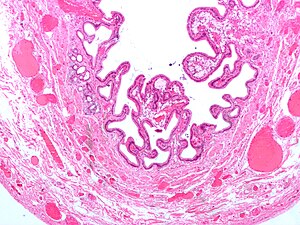 Gallbladder cholesterolosis - often seen together with chronic cholecystitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | entrapped epithelial crypts, fibrosis/muscular hypertrophy of gallbladder wall, +/-foamy macrophages |
| LM DDx | acute cholecystitis, gallbladder adenocarcinoma, gallbladder adenomyoma, intestinal metaplasia of the gallbladder |
| Gross | +/-strawberry-like appearance, yellow stones, fibrotic wall |
| Site | gallbladder |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | obesity |
| Clinical history | biliary colic, usu. fertile fat females forty years or less |
| Symptoms | constant right upper quadrant pain after a meal (biliary colic) |
| Prevalence | very common |
| Prognosis | good, benign |
Chronic cholecystitis, abbreviated CC, is a very common pathology of the gallbladder and increasing in prevalence with the expanding waist lines.
General
Epidemiology
- Female, fat, fertile, family history, forty (though now getting younger... as people get fatter).
Etiology
- Cholelithiasis.
- Thick bile (acalculous cholecystitis).
Clinical (classic)
- Constant right upper quadrant pain after a fatty meal.
- Positive Murphy's sign (physical exam, with ultrasound).
Gross
- +/-Cholelithiasis - strongly associated pathology.
- +/-Strawberry-like appearance - common (due to gallbladder cholesterolosis).
- Small ridges (microvillus architecture) + yellow.
- Normal gallbladder mucosa = smooth, green.
- Small ridges (microvillus architecture) + yellow.
- +/-Congestion/erythema.
- +/-Wall thickening - typically ~ 6-7 mm.[1]
Note:
- Wall thickening (due to congestion/edema) is the important gross finding in acute cholecystitis.
- Wall thickenss greater than 10 mm should raise the suspicion of malignancy.[1]
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Thickening of the gallbladder wall - due to fibrosis/muscular hypertrophy - key feature.
- Chronic inflammatory cells - usu. "minimal".
- Lymphocytes - most common.
- Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses - common.[3]
- Entrapped epithelial crypts -- pockets of epithelium in the wall of the gallbladder.
- +/-Foamy macrophages in the lamina propria (cholesterolosis of the gallbladder).
DDx:
- Gallbladder adenomyoma.
- Acute cholecystitis - more inflammation, lack Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses, +/-mucosal erosions.
- Cholecystectomy for gallstone pancreatitis - intraepithelial neutrophil clusters common, history essential.
- Intestinal metaplasia of the gallbladder - goblet cells present, may be focal.
- Gallbladder adenocarcinoma.
Sign out
GALLBLADDER, CHOLECYSTECTOMY: - CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS. - CHOLELITHIASIS.
Liver present
GALLBLADDER, CHOLECYSTECTOMY: - CHRONIC CHOLECYSTITIS. - CHOLELITHIASIS. - SMALL AMOUNT OF LIVER WITHOUT APPARENT PATHOLOGY.
Micro
The sections shows gallbladder wall with Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses and a moderate mixed inflammatory infiltrate predominantly consisting of lymphocytes. No nuclear atypia is seen.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kim, HJ.; Park, JH.; Park, DI.; Cho, YK.; Sohn, CI.; Jeon, WK.; Kim, BI.; Choi, SH. (Feb 2012). "Clinical usefulness of endoscopic ultrasonography in the differential diagnosis of gallbladder wall thickening.". Dig Dis Sci 57 (2): 508-15. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1870-0. PMID 21879282.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 439. ISBN 978-0443066573.
- ↑ URL: http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/983.html. Accessed on: 29 October 2011.