Follicular thyroid carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Follicular thyroid carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
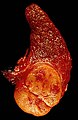
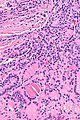
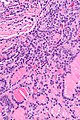
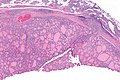
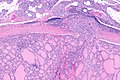
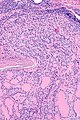
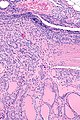
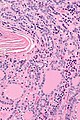
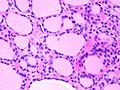
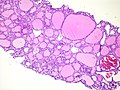
 Micrograph showing a follicular thyroid carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | bland thyroid cells invading through the (fibrous) capsule or lymphovascular invasion or distal metastases |
| LM DDx | follicular thyroid adenoma, papillary thyroid carcinoma follicular variant |
| Site | thyroid gland |
|
| |
| Signs | thyroid nodule/mass |
| Prevalence | uncommon, female predominant |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | surgical excision |
Follicular thyroid carcinoma, abbreviated FTC, is an uncommon malignancy of the thyroid gland. It is also known as follicular carcinoma.
General
- Usually spread by the hematologic route.
- PTC usually spreads via lymphatics.
Clinical
Medical school memory device 4 Fs:
- FNA NOT diagnosable.
- Far away mets (sometimes).
- Female predominant.
- Favourable prognosis.
Gross
- Encapuslated lesion +/-evidence of invasion through the capsule.
Images
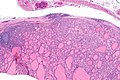
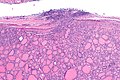
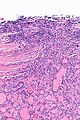
Microscopic
Features:
- Defined by either:
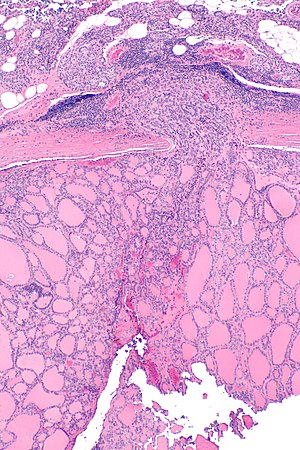
- Invasion through the capsule:
- Should be all the way through.[1]
- 1/2 does not count.
- Fibrous reaction does not count.
- "Above the contour" does not count.
- Should be all the way through.[1]
- Vascular invasion (all of the following):
- In a small vein (not a capillary), that is outside of the tumour mass.
- Tumour adherent to the side of the vessel.
- Tumour must be re-endothelialized.
- Invasion through the capsule:
Notes:
- Impossible to differentiate from follicular adenoma on FNA (no cytologic differences).
- Described as "over-diagnosed" ... misdiagnoses: PTC follicular variant, follicular adenoma, multinodular goitre with a thick capsule.
DDx:
Images
www
See also
References
- ↑ SR. 17 January 2011.