Difference between revisions of "Salivary gland mucocele"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Salivary gland mucocele''', also '''salivary mucocele''' and '''[[mucocele]]''', is a benign lesion of the head and neck. | '''Salivary gland mucocele''', also '''salivary mucocele''' and '''[[mucocele]]''', is a benign lesion of the head and neck. | ||
''Ranula'' redirects here. A ranula is a | ''Ranula'' redirects here. A ranula is a mucocele that occurs in the floor mouth.<ref name=pmid28194490>{{cite journal |authors=Kokong D, Iduh A, Chukwu I, Mugu J, Nuhu S, Augustine S |title=Ranula: Current Concept of Pathophysiologic Basis and Surgical Management Options |journal=World J Surg |volume=41 |issue=6 |pages=1476–1481 |date=June 2017 |pmid=28194490 |pmc=5422487 |doi=10.1007/s00268-017-3901-2 |url=}}</ref> | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:24, 23 June 2020
Salivary gland mucocele, also salivary mucocele and mucocele, is a benign lesion of the head and neck.
Ranula redirects here. A ranula is a mucocele that occurs in the floor mouth.[1]
General
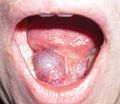
Gross
Features:
- Floor of mouth lesion.
Images
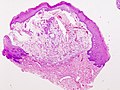
Microscopic
Features:[3]
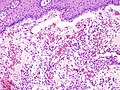
- Granulation tissue-like and pseudocyst-like.
- Granulation tissue-like:
- Fibroblasts.
- Small caliber blood vessels.
- Histocytes.
- Neutrophils.
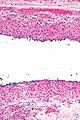
- Pseudocyst:
- No epithelial lining.
- Poorly circumscribed.
- Granulation tissue-like:
- Pale pink extracellular material (mucous) - key feature.
- +/-Granulomas.[4]
DDx:
- Granulation tissue.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma - muciphages may mimic signet ring cells.
Images
www:
Sign out
LESION, LEFT LOWER LIP, EXCISION: - BENIGN MUCOCELE.
Micro
The sections show a stratified squamous epithelium with a thin layer of parakeratosis, minor salivary glands, and a well-circumscribed cystic lesion.
The cystic lesion has a mildly fibrotic appearing wall, is lined by histiocytes intermixed with rare lymphocytes, and contains mucous and macrophages. No significant nuclear atypia is identified. Mitotic activity is not readily apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ Kokong D, Iduh A, Chukwu I, Mugu J, Nuhu S, Augustine S (June 2017). "Ranula: Current Concept of Pathophysiologic Basis and Surgical Management Options". World J Surg 41 (6): 1476–1481. doi:10.1007/s00268-017-3901-2. PMC 5422487. PMID 28194490. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5422487/.
- ↑ Sousa Melo SL, Lanzel E, Pagedar NA, Alhazmi D, Dahmoush L, Policeni BA, Campos MS (May 2018). "Mucoepidermoid carcinoma mimicking a mucocele (ranula) in the floor of the mouth". Dentomaxillofac Radiol 47 (4): 20170331. doi:10.1259/dmfr.20170331. PMC 5991757. PMID 29231036. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5991757/.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1076717-workup. Accessed on: 6 March 2012.
- ↑ Seifert, G.; Donath, K.; von Gumberz, C. (Jun 1981). "[Mucoceles of the minor salivary glands. Extravasation mucoceles (mucus granulomas) and retention mucoceles (mucus retention cysts) (author's transl)].". HNO 29 (6): 179-91. PMID 7251405.