Difference between revisions of "Meckel diverticulum"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
*[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/24/2/565.long Pancreatic glands in a MD (radiographics.rsna.org)]. | *[http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/24/2/565.long Pancreatic glands and gastric mucosa in a MD (radiographics.rsna.org)]. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 21:37, 8 April 2018
| Meckel diverticulum | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
|
| |
| LM | small bowel mucosa, +/-gastric mucosa (foveolar epithelium, oxyntic mucosa), +/-pancreatic epithelium |
| Gross | small bowel outpouching on antemesenteric aspect ~5 cm long, ~60 cm from the ileocecal valve |
| Site | small intestine |
|
| |
| Symptoms | abdominal pain |
| Prevalence | uncommon ~2% of population |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | acute appendicitis, other causes of abdominal pain |
| Treatment | surgical removal |
Meckel diverticulum (also Meckel's diverticulum), is congenital structure of the distal small bowel that occasionally gets inflamed and may present with acute appendicitis-like symptoms.
General
- Most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract.[1]
- Remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct - a connection of the yolk sac and midgut.
The rule of 2s:
- 2 feet from the terminal ileum
- 2% of the population
- 2% symptomatic.
- 2 inches long.
- 2 year old.
- 2 types of epithelium - gastric and pancreatic.
Main clinical DDx of a symptomatic Meckel diverticulum:
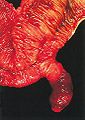
Gross
- Antimesenteric attachement, i.e. a Meckel's diverticulum hangs off the side opposite of the mesentery.
Image
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Small bowel mucosa.
- +/-Gastric mucosa:
- Foveolar epithelium: champagne flute-like columnar epithelium.
- Oxyntic mucosa: parietal cells (pink) and chief cells (purple).
- +/-Pancreatic epithelium:
- Pancreatic acini.