Difference between revisions of "Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
#Vasculitic disorders: | #Vasculitic disorders: | ||
#*ANCA mediated vasculitides: | #*ANCA mediated vasculitides: | ||
#**[[Wegener granulomatosis | #**[[Granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Wegener granulomatosis). | ||
#**[[Churg-Strauss syndrome | #**[[Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Churg-Strauss syndrome). | ||
#*[[Henoch–Schönlein purpura]].<ref name=pmid9713395>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kraft | first1 = DM. | last2 = Mckee | first2 = D. | last3 = Scott | first3 = C. | title = Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a review. | journal = Am Fam Physician | volume = 58 | issue = 2 | pages = 405-8, 411 | month = Aug | year = 1998 | doi = | PMID = 9713395 }}</ref> | #*[[Henoch–Schönlein purpura]].<ref name=pmid9713395>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kraft | first1 = DM. | last2 = Mckee | first2 = D. | last3 = Scott | first3 = C. | title = Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a review. | journal = Am Fam Physician | volume = 58 | issue = 2 | pages = 405-8, 411 | month = Aug | year = 1998 | doi = | PMID = 9713395 }}</ref> | ||
#*Urticarial vasculitis. | #*Urticarial vasculitis. | ||
Revision as of 21:42, 28 November 2016
| Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
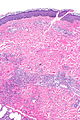
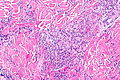
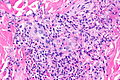
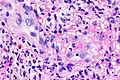
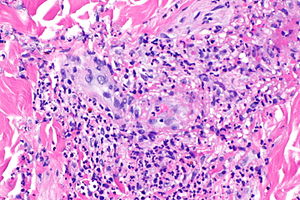 Leukocytoclastic vasculitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | leukocytoclastic vasculitis |
|
| |
| LM | small vessels intramural inflammatory cells (neutrophils), vessel damage (fibrin deposition) |
| LM DDx | dermatitides with perivascular inflammation |
| Stains | PAS -ve |
| Site | blood vessels - see vasculitides |
|
| |
| Signs | palpable purpura |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Clin. DDx | see etiology section |
| Treatment | remove underlying cause; colchicine and/or dapsone; immunosuppression |
Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis, also leukocytoclastic vasculitis (abbreviated LCV), is an inflammatory process of the small blood vessel.
General
- Most common cutaneous vasculitis.[1]
Clinical:
- Palpable purpura, usu. lower extremity.
Treatment - dependent on cause - may include:[2]
- Remove underlying cause if it can be determined.
- Colchicine and/or dapsone.
- Immunosuppression.
Etiology
Has a very broad DDx:[1]
- Infectious:
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
- Fungal.
- Vasculitic disorders:
- ANCA mediated vasculitides:
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis).
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome).
- Henoch–Schönlein purpura.[3]
- Urticarial vasculitis.
- ANCA mediated vasculitides:
- Other:
- Connective tissue disease, e.g. mixed connective tissue disease, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cryoglobulinemia - may be due to multiple myeloma, hepatitis C; have intravascular thrombi.
- Paraneoplastic.
- Drugs.
Gross
- Palpable purpura - raised lesions that can appreciated with touch, red/purple in colour.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Small upper dermis vessels with:
- Neutrophils.
- Fragmentation of neutrophils (leukocytoclasia).
- Vessel damage: fibrin deposition (bright pink acellular stuff).
- Neutrophils.
DDx:
Image
Case
www
Stains
- PAS - look for fungus.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Brinster, NK. (Nov 2008). "Dermatopathology for the surgical pathologist: a pattern-based approach to the diagnosis of inflammatory skin disorders (part II).". Adv Anat Pathol 15 (6): 350-69. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e31818b1ac6. PMID 18948765.
- ↑ Goeser, MR.; Laniosz, V.; Wetter, DA. (Aug 2014). "A practical approach to the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis.". Am J Clin Dermatol 15 (4): 299-306. doi:10.1007/s40257-014-0076-6. PMID 24756249.
- ↑ Kraft, DM.; Mckee, D.; Scott, C. (Aug 1998). "Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a review.". Am Fam Physician 58 (2): 405-8, 411. PMID 9713395.