Difference between revisions of "Lobular capillary hemangioma"
(→Micro) |
|||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
===Micro=== | ===Micro=== | ||
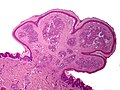
The sections shows a pendunculated vascular lesion with small capillaries arranged in a lobular fashion. The endothelial cells of the lesion show no atypia. The overlying acanthotic epidermis has hyperkeratosis and hypergranulosis, and is focally ulcerated and impetiginized. There is no significant keratocyte atypia. No melanocytic nests are seen. The dermis has a mild perivascular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. The lesion is excised in the plane of section. | The sections shows a pendunculated vascular lesion with small capillaries arranged in a lobular fashion. The endothelial cells of the lesion show no atypia. The overlying acanthotic epidermis has hyperkeratosis and hypergranulosis, and is focally ulcerated and impetiginized. There is no significant keratocyte atypia. No melanocytic nests are seen. The dermis has a mild perivascular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. The lesion is excised in the plane of section. | ||
====Alternate - tongue==== | |||
The sections shows a pendunculated vascular lesion with small capillaries arranged in a lobular fashion. The endothelial cells of the lesion show no significant atypia. The overlying epithelium is largely eroded. There is no significant keratocyte atypia. The lesion is excised in the plane of section. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 6 December 2015
| Lobular capillary hemangioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
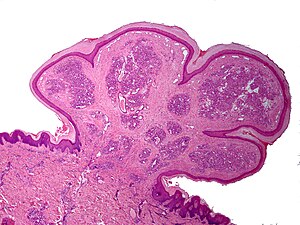 Lobular capillary hemangioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | pyogenic granuloma |
|
| |
| LM | polypoid or peduculated lesion, vascular - with plump endothelium, usu. thinned epithelium or ulcerated, lobular arrangement of vascular (seen at low power) |
| LM DDx | capillary hemangioma, myopericytoma (?), bacillary angiomatosis |
| Site | head and neck - lips, tongue, gingiva |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-rapid growth, young adults, children and pregnant women |
| Prognosis | benign |
Lobular capillary hemangioma, also known as pyogenic granuloma,[1] a benign head and neck lesion that can mimic malignancy.
On occasion it is referred to as pregnancy tumour.
General
- Seen in children, young adults, pregnant women.
Clinical:
- May grow quickly - clinically suspicious for a malignancy.
Note:
- Pyogenic granuloma is a misnomer:
- Not pyogenic, i.e. infectious.
- Not granulomatous.
- The WMSP advocates the name lobular capillary hemangioma.[2]
Gross
Features:[3]
- Erythematous.
- Hemorrhagic.
Usually location:[2]
- Lips.
- Tongue.
- Gingiva.
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Polypoid or peduculated.
- Vascular, i.e. many blood vessels, with plump endothelium.
- Usu. thinned epithelium[5] or ulcerated.[2]
- Lobular arrangement of vascular (seen at low power).[6]
DDx:
Why it is not...
- Glomus tumour - cookie cutter arrangement of cells.
Image
www:
IHC
Features - positive for vascular markers:[2]
- CD34 +ve.
- CD31 +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
- SMA +ve -- marks pericytes.[citation needed]
A panel:
- CD31, SMA, HMB-45.
Sign out
TONGUE, LEFT LATERAL, BIOPSY: - LOBULAR CAPILLARY HEMANGIOMA (PYOGENIC GRANULOMA).
LESION, POSTERIOR TO LEFT EAR, EXCISION: - LOBULAR CAPILLARY HEMANGIOMA (PYOGENIC GRANULOMA). COMMENT: The lesion stains as follows: POSITIVE: SMA, CD31. NEGATIVE: S-100, HMB-45.
Micro
The sections shows a pendunculated vascular lesion with small capillaries arranged in a lobular fashion. The endothelial cells of the lesion show no atypia. The overlying acanthotic epidermis has hyperkeratosis and hypergranulosis, and is focally ulcerated and impetiginized. There is no significant keratocyte atypia. No melanocytic nests are seen. The dermis has a mild perivascular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. The lesion is excised in the plane of section.
Alternate - tongue
The sections shows a pendunculated vascular lesion with small capillaries arranged in a lobular fashion. The endothelial cells of the lesion show no significant atypia. The overlying epithelium is largely eroded. There is no significant keratocyte atypia. The lesion is excised in the plane of section.
See also
References
- ↑ Baglin, AC. (Aug 2011). "[Vascular tumors and pseudotumors. Pyogenic granuloma (lobular capillary hemangioma)].". Ann Pathol 31 (4): 266-70. doi:10.1016/j.annpat.2011.05.014. PMID 21839350.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 12. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 776. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 775. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://basicpathology-histopathology.blogspot.com/2009/10/head-and-neck-oral-cavity-reactive_3282.html. Accessed on: 2 February 2011.
- ↑ S. Sade. 8 September 2011.
- ↑ Levy, I.; Rolain, JM.; Lepidi, H.; Raoult, D.; Feinmesser, M.; Lapidoth, M.; Ben-Amitai, D. (Dec 2005). "Is pyogenic granuloma associated with Bartonella infection?". J Am Acad Dermatol 53 (6): 1065-6. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.08.046. PMID 16310070.