Difference between revisions of "Extramammary Paget disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
* | *Two types | ||
* | **Primary Paget disease - a malignancy of the cutaneous apocrine glands | ||
***Arises in apocrine rich areas - usually the vulva but also the groin, inguinal area, perineum, penis<ref name=pmid19126202>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ekwueme | first1 = KC. | last2 = Zakhour | first2 = HD. | last3 = Parr | first3 = NJ. | title = Extramammary Paget's disease of the penis: a case report and review of the literature. | journal = J Med Case Reports | volume = 3 | issue = | pages = 4 | month = | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1186/1752-1947-3-4 | PMID = 19126202 }}</ref> or [[scrotum]].<ref name=pmid24349803>{{Cite journal | last1 = Guerra | first1 = R. | last2 = Misra | first2 = S. | title = Management of Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. | journal = Case Rep Dermatol Med | volume = 2013 | issue = | pages = 436390 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1155/2013/436390 | PMID = 24349803 }}</ref> and rarely axilla or eye. | |||
***Usually entirely intraepidermal but may be associated with an underlying apocrine gland carcinoma (in contrast to mammary Paget disease which is usually associated with underlying mammary carcinoma). | |||
**Secondary Paget disease - intraepidermal spread from a distant tumor | |||
***Usually of urothelial or colorectal origin. | |||
***Arises in the perineal areas near these organs | |||
Clinical: | Clinical: | ||
*Pruritis. | *Pruritis. | ||
*R/O VIN | |||
*R/O vulvitis | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
Revision as of 10:39, 11 March 2015
| Extramammary Paget disease | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
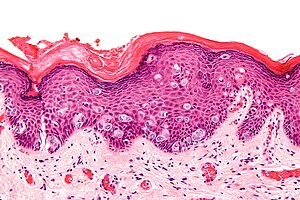 Extramammary Paget's disease. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
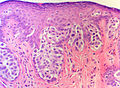
| LM | large epithelioid cells - nested or single - in the epidermis, clear/pale cytoplasm (occasionally eosinophilic), large nucleoli |
| LM DDx | benign Toker cell hyperplasia, malignant melanoma, Bowen's disease, apocrine carcinoma of the skin |
| IHC | CK7 +ve, CEA +ve, S-100 -ve, CK5/6 -ve, HER2 +ve |
| Gross | erythema, +/-weeping, +/-crusted |
| Site | vulva, penis, scrotum, others |
|
| |
| Symptoms | pruritis (itchy) |
| Prognosis | typically benign - usually not associated with an underlying malignancy (unlike Paget's disease of the breast) |
| Clin. DDx | contact dermatitis, lichen sclerosus |
Extramammary Paget disease, abbreviated EMPD, is a skin disease. As the name suggests, there is also a Paget disease of the breast.
There is also a Paget disease of the bone - just to make things confusing. This is dealt with in the bone article and has nothing (from a pathologic perspective) to do with the Paget disease discussed in this article
General
- Two types
- Primary Paget disease - a malignancy of the cutaneous apocrine glands
- Arises in apocrine rich areas - usually the vulva but also the groin, inguinal area, perineum, penis[1] or scrotum.[2] and rarely axilla or eye.
- Usually entirely intraepidermal but may be associated with an underlying apocrine gland carcinoma (in contrast to mammary Paget disease which is usually associated with underlying mammary carcinoma).
- Secondary Paget disease - intraepidermal spread from a distant tumor
- Usually of urothelial or colorectal origin.
- Arises in the perineal areas near these organs
- Primary Paget disease - a malignancy of the cutaneous apocrine glands
Clinical:
- Pruritis.
- R/O VIN
- R/O vulvitis
Gross
Features:[2]
- Plaque with an irregular border.
- Erythematous or white.
Clinical DDx:
Images
Microscopic
Features:
- Epitheliod morphology (round/ovoid).
- Cells nested or single.
- Clear/pale cytoplasm key feature - may also be eosinophilic.
- Large nucleoli.
Images
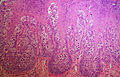
- Anus Pagets Disease PA.JPG
Anus Pagets Disease - (SKB)
DDx
- Benign Toker cell hyperplasia.
- Malignant melanoma.
- Bowen disease.
- Apocrine carcinoma of the skin.[4]
- Vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
Stains
- Mucicarmine stain +ve.
IHC
Panel:
- CEA +ve (-ve in Bowen's disease, -ve in Toker cells).
- CK7 +ve.
- Toker cells CK7 +ve.[5]
- S100 -ve, HMB-45 -ve (both typically +ve in melanoma).
Additional:
- HER2/neu - usually +ve.
- CK5/6 -ve.[6]
- Usu. +ve in squamous cell carcinoma.
- CAM 5.2 +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ Ekwueme, KC.; Zakhour, HD.; Parr, NJ. (2009). "Extramammary Paget's disease of the penis: a case report and review of the literature.". J Med Case Reports 3: 4. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-3-4. PMID 19126202.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Guerra, R.; Misra, S. (2013). "Management of Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.". Case Rep Dermatol Med 2013: 436390. doi:10.1155/2013/436390. PMID 24349803.
- ↑ Bansal, D.; Bowman, CA. (Feb 2004). "Extramammary Paget's disease masquerading as lichen sclerosus.". Int J STD AIDS 15 (2): 141-2. doi:10.1258/095646204322764361. PMID 15006079.
- ↑ URL: http://derm101.com/searchResults.aspx?searchStr=apocrine+carcinoma&rootTerm=apocrine+carcinoma&searchType=2&rootID=12687. Accessed on: 9 September 2011.
- ↑ Nofech-Mozes, S.; Hanna, W.. "Toker cells revisited.". Breast J 15 (4): 394-8. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4741.2009.00743.x. PMID 19601945.
- ↑ RS. May 2010.