Difference between revisions of "Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
m (DNT --> DNET) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour''', abbreviated ''' | '''Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour''', abbreviated '''DNET''',<ref name=pmid25311417>{{Cite journal | last1 = Alexander | first1 = H. | last2 = Tannenburg | first2 = A. | last3 = Walker | first3 = DG. | last4 = Coyne | first4 = T. | title = Progressive dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour. | journal = J Clin Neurosci | volume = 22 | issue = 1 | pages = 221-4 | month = Jan | year = 2015 | doi = 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.07.022 | PMID = 25311417 }}</ref> is a rare [[neuropathology tumour]] that is associated with [[epilepsy]]. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
Revision as of 22:14, 16 February 2015
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour, abbreviated DNET,[1] is a rare neuropathology tumour that is associated with epilepsy.
General
Gross/radiology
- Temporal lobe.
- Variable architecture:[3] cystic, solitary nodular, multinodular.
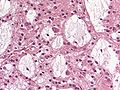
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Cells similar to oligodendrocytes:
- Large central nuclei with indentations.
- Multiple small nucleoli (common).
- Clear cytoplasm.
DDx:
- Oligodendroglioma.
- These have rounder, smaller nuclei with occasional nucleoli.[3]
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ Alexander, H.; Tannenburg, A.; Walker, DG.; Coyne, T. (Jan 2015). "Progressive dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour.". J Clin Neurosci 22 (1): 221-4. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2014.07.022. PMID 25311417.
- ↑ Cataltepe, O.; Turanli, G.; Yalnizoglu, D.; Topçu, M.; Akalan, N. (Apr 2005). "Surgical management of temporal lobe tumor-related epilepsy in children.". J Neurosurg 102 (3 Suppl): 280-7. doi:10.3171/ped.2005.102.3.0280. PMID 15881751.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 O'Brien, DF.; Farrell, M.; Delanty, N.; Traunecker, H.; Perrin, R.; Smyth, MD.; Park, TS. (Dec 2007). "The Children's Cancer and Leukaemia Group guidelines for the diagnosis and management of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours.". Br J Neurosurg 21 (6): 539-49. doi:10.1080/02688690701594817. PMID 18071981.