Difference between revisions of "Ependymoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Ependymoma''' is a [[neuropathology tumour]]. | ||
==General== | |||
*Called the forgotten glial tumour. | |||
Epidemiology:<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_1334>{{Ref PBoD8|1334}}</ref> | |||
*Usual site: | |||
**Adults: usu. spinal cord. | |||
**Children: usu. posterior fossa. | |||
*May be assoc. with [[neurofibromatosis]] 2. | |||
Comes in two main flavours: | |||
#Ependymoma (not otherwise specified). | |||
#Myxopapillary ependymoma. | |||
#*Classically at filum terminale. | |||
Other flavours:<ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1744030-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1744030-overview]. Accessed on: 17 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*Papillary ependymoma. | |||
*Clear cell ependymoma. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
===Classic ependymoma=== | |||
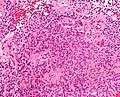
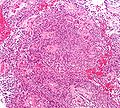
Features: | |||
*Cells have a "tadpole-like" morphology. | |||
**May also be described as ''ice cream cone-shaped''.<ref>[http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/WirSelfInst/tumor-2.html http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/WirSelfInst/tumor-2.html]</ref> | |||
*'''Rosettes''' = circular nuclear free zones/cells arranged in a pseudoglandular fashion; comes in two flavours in ependymoma: | |||
**''Perivascular pseudorosettes'' = (tumour) cells arranged around a blood vessel; nuclei of cells distant from the blood vessel, i.e. rim of cytoplasm (from tumour cells) surround blood vessel (nucleus-free zone); more common than ependymal rosette... but less specific. | |||
**''Ependymal rosette'' ([[AKA]] ''true ependymal rosette'') = rosette has an empty space at the centre - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Nuclear features monotonous, i.e. "boring".<ref>MUN. 6 Oct 2009.</ref> | |||
**There is little variation in size, shape and staining. | |||
DDx (classic ependymoma): | |||
*[[Subependymoma]]. | |||
*[[Glioblastoma]] (GBM). | |||
**Invasive border = GBM; circumscribed border of lesion = ependymoma. | |||
====Images==== | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/ckrishnan/3862487821/in/photostream Ependymoma (flickr.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.ajnr.org/cgi/content-nw/full/27/3/488/F10 Ependymoma - ependymal rosettes (ajnr.org)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case95/micro.html Anaplastic ependymoma - case 1 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case324.html Anaplastic ependymoma - case 2 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Ependymoma_intermed_mag.jpg | Ependymoma - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Ependymoma_low_intermed_mag.jpg | Ependymoma - low mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Myxopapillary ependymoma=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Perivascular pseudorosettes: | |||
**Myxoid material surround blood vessels. | |||
***[[Myxoid]] material surrounded by tumour cells. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Myxopapillary_ependymoma_-_high_mag.jpg Myxopapillary ependymoma - high mag. (WC)]. | |||
*[http://careers.bmj.com/article-images/cf0708.f2_default.gif Myxopapillary ependymoma (bmj.com)] - part of [http://careers.bmj.com/careers/advice/view-article.html?id=351 careers.bmj.com article on paediatric pathology]. | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Myxopapillary_ependymoma.jpg Myxopapillary ependymoma - cytology (WC)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case626.html Myxopapillary ependymoma - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
===Grading=== | |||
Easy: | |||
*Subependymoma = WHO grade I. | |||
*Myxopapillary ependymoma = WHO grade I. | |||
Not-so-easy: | |||
*Classic ependymoma = WHO grade II. | |||
*Anaplastic ependymoma = WHO grade III. | |||
Grade II vs. Grade III: | |||
*Cellular density. | |||
*Mitoses. | |||
*Necrosis. | |||
*Microvascular proliferation. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Many tumours fall between grade II and grade III. These are called "indeterminate" by many. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*Reticulin. | |||
*GFAP. | |||
*MIB1. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Neuropathology tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Neuropathology tumours]] | |||
Revision as of 06:27, 10 December 2014
Ependymoma is a neuropathology tumour.
General
- Called the forgotten glial tumour.
Epidemiology:[1]
- Usual site:
- Adults: usu. spinal cord.
- Children: usu. posterior fossa.
- May be assoc. with neurofibromatosis 2.
Comes in two main flavours:
- Ependymoma (not otherwise specified).
- Myxopapillary ependymoma.
- Classically at filum terminale.
Other flavours:[2]
- Papillary ependymoma.
- Clear cell ependymoma.
Microscopic
Classic ependymoma
Features:
- Cells have a "tadpole-like" morphology.
- May also be described as ice cream cone-shaped.[3]
- Rosettes = circular nuclear free zones/cells arranged in a pseudoglandular fashion; comes in two flavours in ependymoma:
- Perivascular pseudorosettes = (tumour) cells arranged around a blood vessel; nuclei of cells distant from the blood vessel, i.e. rim of cytoplasm (from tumour cells) surround blood vessel (nucleus-free zone); more common than ependymal rosette... but less specific.
- Ependymal rosette (AKA true ependymal rosette) = rosette has an empty space at the centre - key feature.
- Nuclear features monotonous, i.e. "boring".[4]
- There is little variation in size, shape and staining.
DDx (classic ependymoma):
- Subependymoma.
- Glioblastoma (GBM).
- Invasive border = GBM; circumscribed border of lesion = ependymoma.
Images
www:
- Ependymoma (flickr.com).
- Ependymoma - ependymal rosettes (ajnr.org).
- Anaplastic ependymoma - case 1 (upmc.edu).
- Anaplastic ependymoma - case 2 (upmc.edu).
Myxopapillary ependymoma
Features:
- Perivascular pseudorosettes:
- Myxoid material surround blood vessels.
- Myxoid material surrounded by tumour cells.
- Myxoid material surround blood vessels.
Images:
- Myxopapillary ependymoma - high mag. (WC).
- Myxopapillary ependymoma (bmj.com) - part of careers.bmj.com article on paediatric pathology.
- Myxopapillary ependymoma - cytology (WC).
- Myxopapillary ependymoma - several images (upmc.edu).
Grading
Easy:
- Subependymoma = WHO grade I.
- Myxopapillary ependymoma = WHO grade I.
Not-so-easy:
- Classic ependymoma = WHO grade II.
- Anaplastic ependymoma = WHO grade III.
Grade II vs. Grade III:
- Cellular density.
- Mitoses.
- Necrosis.
- Microvascular proliferation.
Notes:
- Many tumours fall between grade II and grade III. These are called "indeterminate" by many.
IHC
- Reticulin.
- GFAP.
- MIB1.
See also
References
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1334. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1744030-overview. Accessed on: 17 January 2012.
- ↑ http://www.pathology.vcu.edu/WirSelfInst/tumor-2.html
- ↑ MUN. 6 Oct 2009.