Difference between revisions of "Craniopharyngioma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Images: remove for the moment) |
(rearrange) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
*Develop from remains of Rathke's pouch or squamous epithelial cell rests.<ref name=pmid17425791>{{Cite journal | last1 = Garnett | first1 = MR. | last2 = Puget | first2 = S. | last3 = Grill | first3 = J. | last4 = Sainte-Rose | first4 = C. | title = Craniopharyngioma. | journal = Orphanet J Rare Dis | volume = 2 | issue = | pages = 18 | month = | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1186/1750-1172-2-18 | PMID = 17425791 }}</ref> | *Develop from remains of Rathke's pouch or squamous epithelial cell rests.<ref name=pmid17425791>{{Cite journal | last1 = Garnett | first1 = MR. | last2 = Puget | first2 = S. | last3 = Grill | first3 = J. | last4 = Sainte-Rose | first4 = C. | title = Craniopharyngioma. | journal = Orphanet J Rare Dis | volume = 2 | issue = | pages = 18 | month = | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1186/1750-1172-2-18 | PMID = 17425791 }}</ref> | ||
Subtypes:<ref name=pmid17425791/> | |||
*Adamantinomatous type. | *Adamantinomatous type. | ||
*Squamous papillary type. | *Squamous papillary type. | ||
**Adults individuals.<ref name=pmid6696166>{{Cite journal | last1 = Giangaspero | first1 = F. | last2 = Burger | first2 = PC. | last3 = Osborne | first3 = DR. | last4 = Stein | first4 = RB. | title = Suprasellar papillary squamous epithelioma ("papillary craniopharyngioma"). | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 8 | issue = 1 | pages = 57-64 | month = Jan | year = 1984 | doi = | PMID = 6696166 }}</ref> | |||
===Adamantinomatous=== | |||
*Adults and children. | |||
*Typically contain mutations in CTNNB1 (the gene that encoding β-catenin).<ref name=pmid25355426>{{Cite journal | last1 = Preda | first1 = V. | last2 = Larkin | first2 = SJ. | last3 = Karavitaki | first3 = N. | last4 = Ansorge | first4 = O. | last5 = Grossman | first5 = AB. | title = The Wnt Signalling Cascade and the Adherens Junction Complex in Craniopharyngioma Tumorigenesis. | journal = Endocr Pathol | volume = | issue = | pages = | month = Oct | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1007/s12022-014-9341-8 | PMID = 25355426 }}</ref> | |||
**Usually intranuclear β-catenin [[immunostain|immunohistochemical]] positivity. | |||
===Papillary=== | |||
*Adults individuals.<ref name=pmid6696166>{{Cite journal | last1 = Giangaspero | first1 = F. | last2 = Burger | first2 = PC. | last3 = Osborne | first3 = DR. | last4 = Stein | first4 = RB. | title = Suprasellar papillary squamous epithelioma ("papillary craniopharyngioma"). | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 8 | issue = 1 | pages = 57-64 | month = Jan | year = 1984 | doi = | PMID = 6696166 }}</ref> | |||
*Usually solid. | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 36: | ||
*"Wet" keratin - nests of whorled keratin. | *"Wet" keratin - nests of whorled keratin. | ||
*Calcifications (non-psammomatous). | *Calcifications (non-psammomatous). | ||
====Images==== | ====Images==== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:51, 16 November 2014
Craniopharyngioma is a benign neuropathology tumour.
It is subdivided into papillary craniopharyngioma and adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma.
General
- Develop from remains of Rathke's pouch or squamous epithelial cell rests.[1]
Subtypes:[1]
- Adamantinomatous type.
- Squamous papillary type.
Adamantinomatous
- Adults and children.
- Typically contain mutations in CTNNB1 (the gene that encoding β-catenin).[2]
- Usually intranuclear β-catenin immunohistochemical positivity.
Papillary
- Adults individuals.[3]
- Usually solid.
Gross
- Cystic mass filled with motor oil-like fluid.[4]
- May not be seen in the papillary variant of craniopharyngioma.
Radiology:[1]
- Calcified - adamantinomatous type only.
- Solid & cystic.
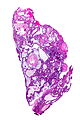
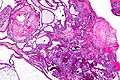
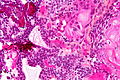
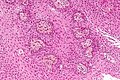
Microscopic
Adamantinomatous
Features (adamantinomatous):[5]
- Well-circumscribed (or pseudoinvasive border).
- Multicystic.
- Small-to-medium sized cells with moderate amount of basophilic cytoplasm.
- Bland nuclei (with occ. small nucleoli).
- "Wet" keratin - nests of whorled keratin.
- Calcifications (non-psammomatous).
Images
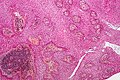
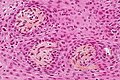
Papillary
Features (papillary):[6]
- Non-keratinized squamous epithelium (without nuclear atypia).
- Fibrovascular cores (required for papillary).
Notes:
- +/-Cilia (rare).
- +/-Goblet cell-like formations (rare).
Image
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Garnett, MR.; Puget, S.; Grill, J.; Sainte-Rose, C. (2007). "Craniopharyngioma.". Orphanet J Rare Dis 2: 18. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-18. PMID 17425791.
- ↑ Preda, V.; Larkin, SJ.; Karavitaki, N.; Ansorge, O.; Grossman, AB. (Oct 2014). "The Wnt Signalling Cascade and the Adherens Junction Complex in Craniopharyngioma Tumorigenesis.". Endocr Pathol. doi:10.1007/s12022-014-9341-8. PMID 25355426.
- ↑ Giangaspero, F.; Burger, PC.; Osborne, DR.; Stein, RB. (Jan 1984). "Suprasellar papillary squamous epithelioma ("papillary craniopharyngioma").". Am J Surg Pathol 8 (1): 57-64. PMID 6696166.
- ↑ Fernandez-Miranda, JC.; Gardner, PA.; Snyderman, CH.; Devaney, KO.; Strojan, P.; Suárez, C.; Genden, EM.; Rinaldo, A. et al. (Jul 2012). "Craniopharyngioma: a pathologic, clinical, and surgical review.". Head Neck 34 (7): 1036-44. doi:10.1002/hed.21771. PMID 21584897.
- ↑ Tadrous, Paul.J. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: A Surgical Pathology Vade Mecum (1st ed.). Wiley. pp. 184. ISBN 978-0470519035.
- ↑ Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 406. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ URL: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/jpeg4/ENDO115.jpg. Accessed on: 6 December 2010.