Difference between revisions of "KRAS mutation"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
In the context of colorectal carcinoma:<ref name=pmid20956938>{{cite journal |author=Dunn EF, Iida M, Myers RA, ''et al.'' |title=Dasatinib sensitizes KRAS mutant colorectal tumors to cetuximab |journal=Oncogene |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2010 |month=October |pmid=20956938 |doi=10.1038/onc.2010.430 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid19001320>{{cite journal |author=Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, ''et al.'' |title=Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=26 |issue=35 |pages=5705–12 |year=2008 |month=December |pmid=19001320 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0786 |url=}}</ref> | In the context of colorectal carcinoma:<ref name=pmid20956938>{{cite journal |author=Dunn EF, Iida M, Myers RA, ''et al.'' |title=Dasatinib sensitizes KRAS mutant colorectal tumors to cetuximab |journal=Oncogene |volume= |issue= |pages= |year=2010 |month=October |pmid=20956938 |doi=10.1038/onc.2010.430 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid19001320>{{cite journal |author=Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, ''et al.'' |title=Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer |journal=J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=26 |issue=35 |pages=5705–12 |year=2008 |month=December |pmid=19001320 |doi=10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0786 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Patient must have ''wild type'' KRAS to get drugs; KRAS mutation predicts resistance to [[cetuximab]] (Erbitux) and [[panitumumab]] (Vectibix). | *Patient must have ''wild type'' KRAS to get drugs; KRAS mutation predicts resistance to [[cetuximab]] (Erbitux) and [[panitumumab]] (Vectibix). | ||
==Gross== | |||
In colorectal cancer: | |||
*Typically right sided lesions.<ref name=pmid24925349/> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Typically [[mucinous carcinoma]] in lung.<ref name=pmid25029118>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kadota | first1 = K. | last2 = Yeh | first2 = YC. | last3 = D'Angelo | first3 = SP. | last4 = Moreira | first4 = AL. | last5 = Kuk | first5 = D. | last6 = Sima | first6 = CS. | last7 = Riely | first7 = GJ. | last8 = Arcila | first8 = ME. | last9 = Kris | first9 = MG. | title = Associations between mutations and histologic patterns of mucin in lung adenocarcinoma: invasive mucinous pattern and extracellular mucin are associated with KRAS mutation. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 1118-27 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000246 | PMID = 25029118 }}</ref> | *Typically [[mucinous carcinoma]] in lung.<ref name=pmid25029118>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kadota | first1 = K. | last2 = Yeh | first2 = YC. | last3 = D'Angelo | first3 = SP. | last4 = Moreira | first4 = AL. | last5 = Kuk | first5 = D. | last6 = Sima | first6 = CS. | last7 = Riely | first7 = GJ. | last8 = Arcila | first8 = ME. | last9 = Kris | first9 = MG. | title = Associations between mutations and histologic patterns of mucin in lung adenocarcinoma: invasive mucinous pattern and extracellular mucin are associated with KRAS mutation. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 38 | issue = 8 | pages = 1118-27 | month = Aug | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000246 | PMID = 25029118 }}</ref> | ||
* | *In [[colorectal carcinoma]]: | ||
**No correlation in one study.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gao | first1 = J. | last2 = Zhang | first2 = J. | last3 = Lu | first3 = T. | last4 = Li | first4 = XY. | last5 = Jia | first5 = N. | last6 = Liang | first6 = ZY. | title = [Correlation between KRAS mutations and clinicopathologic features in colorectal carcinomas]. | journal = Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi | volume = 41 | issue = 9 | pages = 595-8 | month = Sep | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 23157826 }}</ref> | |||
**Not high-grade.<ref name=pmid24925349>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gonsalves | first1 = WI. | last2 = Mahoney | first2 = MR. | last3 = Sargent | first3 = DJ. | last4 = Nelson | first4 = GD. | last5 = Alberts | first5 = SR. | last6 = Sinicrope | first6 = FA. | last7 = Goldberg | first7 = RM. | last8 = Limburg | first8 = PJ. | last9 = Thibodeau | first9 = SN. | title = Patient and tumor characteristics and BRAF and KRAS mutations in colon cancer, NCCTG/Alliance N0147. | journal = J Natl Cancer Inst | volume = 106 | issue = 7 | pages = | month = Jul | year = 2014 | doi = 10.1093/jnci/dju106 | PMID = 24925349 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 15:46, 6 September 2014

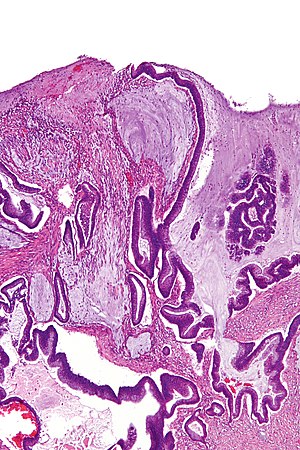
Micrograph showing mucinous carcinoma, a histology associated with KRAS mutations.
KRAS mutation is a re-occuring theme in molecular pathology. KRAS is an oncogene.[1]
General
Seen in:
Not seen in the context of:
- ALK rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer.[3]
Implication
In the context of colorectal carcinoma:[4][5]
- Patient must have wild type KRAS to get drugs; KRAS mutation predicts resistance to cetuximab (Erbitux) and panitumumab (Vectibix).
Gross
In colorectal cancer:
- Typically right sided lesions.[6]
Microscopic
Features:
- Typically mucinous carcinoma in lung.[7]
- In colorectal carcinoma:
See also
References
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 190070
- ↑ Monzon, FA.; Ogino, S.; Hammond, ME.; Halling, KC.; Bloom, KJ.; Nikiforova, MN. (Oct 2009). "The role of KRAS mutation testing in the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 133 (10): 1600-6. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-133.10.1600. PMID 19792050.
- ↑ Gainor, JF.; Varghese, AM.; Ou, SH.; Kabraji, S.; Awad, MM.; Katayama, R.; Pawlak, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M. et al. (Aug 2013). "ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: an analysis of 1,683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer.". Clin Cancer Res 19 (15): 4273-81. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0318. PMID 23729361.
- ↑ Dunn EF, Iida M, Myers RA, et al. (October 2010). "Dasatinib sensitizes KRAS mutant colorectal tumors to cetuximab". Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.430. PMID 20956938.
- ↑ Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, et al. (December 2008). "Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer". J. Clin. Oncol. 26 (35): 5705–12. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0786. PMID 19001320.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Gonsalves, WI.; Mahoney, MR.; Sargent, DJ.; Nelson, GD.; Alberts, SR.; Sinicrope, FA.; Goldberg, RM.; Limburg, PJ. et al. (Jul 2014). "Patient and tumor characteristics and BRAF and KRAS mutations in colon cancer, NCCTG/Alliance N0147.". J Natl Cancer Inst 106 (7). doi:10.1093/jnci/dju106. PMID 24925349.
- ↑ Kadota, K.; Yeh, YC.; D'Angelo, SP.; Moreira, AL.; Kuk, D.; Sima, CS.; Riely, GJ.; Arcila, ME. et al. (Aug 2014). "Associations between mutations and histologic patterns of mucin in lung adenocarcinoma: invasive mucinous pattern and extracellular mucin are associated with KRAS mutation.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (8): 1118-27. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000246. PMID 25029118.
- ↑ Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, T.; Li, XY.; Jia, N.; Liang, ZY. (Sep 2012). "[Correlation between KRAS mutations and clinicopathologic features in colorectal carcinomas].". Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 41 (9): 595-8. PMID 23157826.