Difference between revisions of "Usual interstitial pneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect +cat.) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Usual interstitial pneumonia''', abbreviated '''UIP''', is common [[diffuse lung disease]]. Overall, it is uncommon. | |||
==General== | |||
*It is sometimes used incorrectly as a synonym for ''idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis''. It is a histomorphologic pattern and has a DDx (see below). | |||
*UIP cannot be diagnosed via bronchoscopic or transbronchial biopsy,<ref name=Ref_PPP186>{{Ref PPP|186}}</ref> as it is peripheral. | |||
===Epidemiology=== | |||
*Disease of the old - rare in under 50 years old.<ref>AC UBC S.102.</ref> | |||
*Dismal prognosis - mean survival after diagnosis ~ 2.8 years.<ref name=pmid9445300>{{Cite journal | last1 = Bjoraker | first1 = JA. | last2 = Ryu | first2 = JH. | last3 = Edwin | first3 = MK. | last4 = Myers | first4 = JL. | last5 = Tazelaar | first5 = HD. | last6 = Schroeder | first6 = DR. | last7 = Offord | first7 = KP. | title = Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. | journal = Am J Respir Crit Care Med | volume = 157 | issue = 1 | pages = 199-203 | month = Jan | year = 1998 | doi = | PMID = 9445300 }}</ref> | |||
==Radiology== | |||
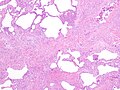
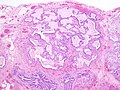
*Honeycombing - ''multiple'' defects that obliterate the normal lung architecture - multiple spherical voids in the lung parenchyma; radiologically these are seen as lucencies.<ref>[http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/h/honeycombing.aspx http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/h/honeycombing.aspx]</ref> | |||
**Usually subplural, i.e. peripheral lung. | |||
**Classically lower lobe predominant. | |||
*Traction [[bronchiectasis]]. | |||
Note: | |||
*Cysts - have thin walls (think of emphysema, [[lymphangioleiomyomatosis]] et cetera). | |||
**Cysts may be isolated/not close to a neighbour. | |||
**Medcyclopaedia defines it as: thin-walled, well-demarcated and >1 cm.<ref>[http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/l/lung_cyst.aspx http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/l/lung_cyst.aspx]</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PPP186-9>{{Ref PPP|186-9}}</ref> | |||
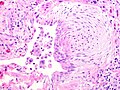
*Fibroblast foci: | |||
**"Crescent-shaped bulge" of fibroblasts -- a rounded projection of spindle cells into the airspace. | |||
**Location: in the areas of transisition between active inflammation and old inflammation.<ref>[http://www.epler.com/IPFWhat%27sIPFDiseaseInformation2.htm http://www.epler.com/IPFWhat%27sIPFDiseaseInformation2.htm]</ref> | |||
**Note: Technically, ''fibroblast foci'' are composed of myofibroblasts.<ref name=Ref_PPP189>{{Ref PPP|189}}</ref> | |||
*Interstitial inflammation. | |||
*Microscopic honeycombing. | |||
**Typically peripheral - cysts lined by ciliated epithelium. | |||
*Spatial heterogeneity - patchy lesional distribution (areas of abnormal and normal lung may appear beside one another). | |||
*Temporal heterogeneity - lesions of differing age side-by-side.<ref name=Ref_WMSP92>{{Ref WMSP|92}}</ref> | |||
Notes: | |||
*Disease worse distant from large airways: lower lung field predominance, typically worse at periphery of lobule and lung.<ref>A. Churg. UBC S.103.</ref> | |||
*Heterogeneity of inflammation: airspace macrophages & inflammation minimal in honeycombed foci. | |||
DDx of UIP:<ref name=leslie>{{cite book |author=Wick, Mark R.; Leslie, Kevin |title=Practical pulmonary pathology: a diagnostic approach |publisher=Churchill Livingstone |location=Edinburgh |year=2005 |pages= |isbn=0-443-06631-0 |oclc= 156861539|doi= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
*Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP not otherwise specified). | |||
*Asbestosis = UIP pattern + ferruginous bodies with asbestos fibers. | |||
*Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis ([[AKA]] extrinsic allergic alveolitis) - classically centrilobular predominant +/- granulomas. | |||
*Collagen vascular disease - includes [[systemic lupus erythematosus]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]], [[scleroderma]].<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_374>{{Ref PCPBoD8|374}}</ref> | |||
*Chronic drug toxicity.<ref name=pmid10992015>{{cite journal |author=Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Sporn TA, Goodman PC |title=Pulmonary drug toxicity: radiologic and pathologic manifestations |journal=Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc |volume=20 |issue=5 |pages=1245-59 |year=2000 |pmid=10992015 |doi=}}</ref> | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:UIPlungbiopsy.jpg|UIP - fibrosis - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Honeycomb change.jpg|UIP - honeycomb change in UIP - low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Fibroblast focus.jpg|UIP - fibroblast focus - high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Diffuse lung diseases]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diffuse lung diseases]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 19:44, 18 April 2014
Usual interstitial pneumonia, abbreviated UIP, is common diffuse lung disease. Overall, it is uncommon.
General
- It is sometimes used incorrectly as a synonym for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It is a histomorphologic pattern and has a DDx (see below).
- UIP cannot be diagnosed via bronchoscopic or transbronchial biopsy,[1] as it is peripheral.
Epidemiology
- Disease of the old - rare in under 50 years old.[2]
- Dismal prognosis - mean survival after diagnosis ~ 2.8 years.[3]
Radiology
- Honeycombing - multiple defects that obliterate the normal lung architecture - multiple spherical voids in the lung parenchyma; radiologically these are seen as lucencies.[4]
- Usually subplural, i.e. peripheral lung.
- Classically lower lobe predominant.
- Traction bronchiectasis.
Note:
- Cysts - have thin walls (think of emphysema, lymphangioleiomyomatosis et cetera).
- Cysts may be isolated/not close to a neighbour.
- Medcyclopaedia defines it as: thin-walled, well-demarcated and >1 cm.[5]
Microscopic
Features:[6]
- Fibroblast foci:
- Interstitial inflammation.
- Microscopic honeycombing.
- Typically peripheral - cysts lined by ciliated epithelium.
- Spatial heterogeneity - patchy lesional distribution (areas of abnormal and normal lung may appear beside one another).
- Temporal heterogeneity - lesions of differing age side-by-side.[9]
Notes:
- Disease worse distant from large airways: lower lung field predominance, typically worse at periphery of lobule and lung.[10]
- Heterogeneity of inflammation: airspace macrophages & inflammation minimal in honeycombed foci.
DDx of UIP:[11]
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP not otherwise specified).
- Asbestosis = UIP pattern + ferruginous bodies with asbestos fibers.
- Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (AKA extrinsic allergic alveolitis) - classically centrilobular predominant +/- granulomas.
- Collagen vascular disease - includes systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma.[12]
- Chronic drug toxicity.[13]
Images
See also
References
- ↑ Leslie, Kevin O.; Wick, Mark R. (2004). Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 186. ISBN 978-0443066313.
- ↑ AC UBC S.102.
- ↑ Bjoraker, JA.; Ryu, JH.; Edwin, MK.; Myers, JL.; Tazelaar, HD.; Schroeder, DR.; Offord, KP. (Jan 1998). "Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.". Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157 (1): 199-203. PMID 9445300.
- ↑ http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/h/honeycombing.aspx
- ↑ http://www.medcyclopaedia.com/library/topics/volume_v_1/l/lung_cyst.aspx
- ↑ Leslie, Kevin O.; Wick, Mark R. (2004). Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 186-9. ISBN 978-0443066313.
- ↑ http://www.epler.com/IPFWhat%27sIPFDiseaseInformation2.htm
- ↑ Leslie, Kevin O.; Wick, Mark R. (2004). Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 189. ISBN 978-0443066313.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 92. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ A. Churg. UBC S.103.
- ↑ Wick, Mark R.; Leslie, Kevin (2005). Practical pulmonary pathology: a diagnostic approach. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-06631-0. OCLC 156861539.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 374. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, McAdams HP, Sporn TA, Goodman PC (2000). "Pulmonary drug toxicity: radiologic and pathologic manifestations". Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 20 (5): 1245-59. PMID 10992015.