Difference between revisions of "Asbestosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect +cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | Asbestosis is [[diffuse lung disease]] due to asbestos exposure. | ||
==General== | |||
Definition: | |||
*Interstitial lung disease due to asbestos exposure.<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_375>{{Ref PCPBoD8|375}}</ref> | |||
**Important to diagnose... asbestosis = compensation. | |||
Conditions associated with asbestos exposure (mnemonic ''PALM''):<ref name=Ref_PCPBoD8_375>{{Ref PCPBoD8|375}}</ref> | |||
*[[Pleural plaques]]. | |||
*Asbestosis. | |||
*[[Lung carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Malignant mesothelioma]]. | |||
Possible association with asbestos exposure: | |||
*[[Gestational trophoblastic disease]].<ref name=pmid19900938>{{Cite journal | last1 = Reid | first1 = A. | last2 = Heyworth | first2 = J. | last3 = de Klerk | first3 = N. | last4 = Musk | first4 = AW. | title = Asbestos exposure and gestational trophoblastic disease: a hypothesis. | journal = Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev | volume = 18 | issue = 11 | pages = 2895-8 | month = Nov | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0731 | PMID = 19900938 }}</ref> | |||
Diagnosis: | |||
*Rests on morphology with special techniques (e.g. polarization)<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Galateau-Salle | first1 = F. | title = [Anatomopathological tools for screening and medical surveillance of people exposed to asbestos]. | journal = Rev Mal Respir | volume = 16 | issue = 6 Pt 2 | pages = 1244-56 | month = Dec | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10897845 }}</ref> and includes tunneling [[electron microscopy]] (TEM),<ref name=pmid21479897>{{Cite journal | last1 = Neumann | first1 = V. | last2 = Löseke | first2 = S. | last3 = Tannapfel | first3 = A. | title = Mesothelioma and analysis of tissue fiber content. | journal = Recent Results Cancer Res | volume = 189 | issue = | pages = 79-95 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1007/978-3-642-10862-4_6 | PMID = 21479897 }}</ref> as done at special centres. | |||
**Tissue is typically digested prior to fibre counting.<ref name=pmid20196674>{{Cite journal | last1 = Roggli | first1 = VL. | last2 = Gibbs | first2 = AR. | last3 = Attanoos | first3 = R. | last4 = Churg | first4 = A. | last5 = Popper | first5 = H. | last6 = Cagle | first6 = P. | last7 = Corrin | first7 = B. | last8 = Franks | first8 = TJ. | last9 = Galateau-Salle | first9 = F. | title = Pathology of asbestosis- An update of the diagnostic criteria: Report of the asbestosis committee of the college of american pathologists and pulmonary pathology society. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 134 | issue = 3 | pages = 462-80 | month = Mar | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1043/1543-2165-134.3.462 | PMID = 20196674 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid20196674/> | |||
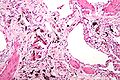
#Interstitial fibrosis - similar to [[usual interstitial pneumonia]] (UIP). | |||
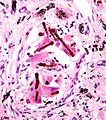
#''Ferruginous bodies'' - '''key feature'''. | |||
#*Segmented twirling baton with long slender fibre within. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Ferruginous_body.jpg | Ferruginous bodies. (WC) | |||
Image:Asbestosis_high_mag.jpg | Asbestosis. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pleural plaques]]. | |||
*[[Malignant mesothelioma]]. | |||
*[[Diffuse lung diseases]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Diffuse lung diseases]] | |||
Revision as of 04:19, 31 March 2014
Asbestosis is diffuse lung disease due to asbestos exposure.
General
Definition:
- Interstitial lung disease due to asbestos exposure.[1]
- Important to diagnose... asbestosis = compensation.
Conditions associated with asbestos exposure (mnemonic PALM):[1]
- Pleural plaques.
- Asbestosis.
- Lung carcinoma.
- Malignant mesothelioma.
Possible association with asbestos exposure:
Diagnosis:
- Rests on morphology with special techniques (e.g. polarization)[3] and includes tunneling electron microscopy (TEM),[4] as done at special centres.
- Tissue is typically digested prior to fibre counting.[5]
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Interstitial fibrosis - similar to usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP).
- Ferruginous bodies - key feature.
- Segmented twirling baton with long slender fibre within.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 375. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Reid, A.; Heyworth, J.; de Klerk, N.; Musk, AW. (Nov 2009). "Asbestos exposure and gestational trophoblastic disease: a hypothesis.". Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18 (11): 2895-8. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0731. PMID 19900938.
- ↑ Galateau-Salle, F. (Dec 1999). "[Anatomopathological tools for screening and medical surveillance of people exposed to asbestos].". Rev Mal Respir 16 (6 Pt 2): 1244-56. PMID 10897845.
- ↑ Neumann, V.; Löseke, S.; Tannapfel, A. (2011). "Mesothelioma and analysis of tissue fiber content.". Recent Results Cancer Res 189: 79-95. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-10862-4_6. PMID 21479897.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Roggli, VL.; Gibbs, AR.; Attanoos, R.; Churg, A.; Popper, H.; Cagle, P.; Corrin, B.; Franks, TJ. et al. (Mar 2010). "Pathology of asbestosis- An update of the diagnostic criteria: Report of the asbestosis committee of the college of american pathologists and pulmonary pathology society.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 134 (3): 462-80. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-134.3.462. PMID 20196674.