Difference between revisions of "Nasopharyngeal carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(split out) |
(→Images: fix) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Lymphoepithelioma_met_to_LN_6.jpg | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - intermed. mag. (WC) | Image:Lymphoepithelioma_met_to_LN_6.jpg | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - intermed. mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lymphoepithelioma_met_to_LN_4.jpg Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - low mag. (WP)]. | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lymphoepithelioma_met_to_LN_2.jpg Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - high mag. (WP)]. | |||
===Histologic subclassification=== | ===Histologic subclassification=== | ||
World Health Classification (2005) for NPC:<ref name=Ref_WMSP39>{{Ref WMSP|39}}</ref> | World Health Classification (2005) for NPC:<ref name=Ref_WMSP39>{{Ref WMSP|39}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 23 February 2014
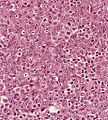
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma, abbreviated NPC, is malignant epithelial tumour of the head and neck closely related to squamous cell carcinoma.
General
- "Nasopharyngeal carcinoma" is the name of an entity - it is not a descriptive term.
- Strong association with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Note:
- A morphologically identical tumour elsewhere is called lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma.
Gross
- Nasopharynx - as the name would suggest.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Prominent lymphoid component - key feature.
- Features of squamous cell carcinoma:
- Cohesive cells with:
- Abundant dense eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Central nuclei +/- small/indistinct nucleoli.
- Cohesive cells with:
Images
www:
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - low mag. (WP).
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma - in a LN - high mag. (WP).
Histologic subclassification
World Health Classification (2005) for NPC:[2]
| Type | Histology | Description | EBV | Prevalence | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | keratinizing SCC | graded poorly-well-diff. | -ve | ? | bad |
| 2a | nonkeratinizing carcinoma, differentiated | well def. cell borders & tumour nest borders, mimics appearance of UCC | +ve | ? | good |
| 2b | nonkeratinizing carcinoma, undifferentiated | sheets/syncytial, vescicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli, pink cytoplasm | ? | most common | ? |
| 3 | basaloid SCC | mimics BCC - see basaloid SCC | ? | least common | ? |
How to remember KNUB:
- Keratinizing, Non-keratinizing diff., non-keratinizing Undiff., Basaloid SCC.
IHC
- EBER +ve.
- p16 -ve.[3]
Notes:
See also
References
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 145. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 39. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Gulley ML, Nicholls JM, Schneider BG, Amin MB, Ro JY, Geradts J (April 1998). "Nasopharyngeal carcinomas frequently lack the p16/MTS1 tumor suppressor protein but consistently express the retinoblastoma gene product". Am. J. Pathol. 152 (4): 865–9. PMC 1858242. PMID 9546345. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1858242/.
- ↑ Singhi, AD.; Califano, J.; Westra, WH. (Feb 2012). "High-risk human papillomavirus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.". Head Neck 34 (2): 213-8. doi:10.1002/hed.21714. PMID 21484924.